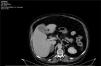
We present the case of a 64-year-old woman from Romania with a medical history of obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome, hepatic cirrhosis, COPD, and osteoarthritis. She smokes one pack of cigarettes per day. The patient is referred from the pulmonology department for an outpatient evaluation for an incidental finding of bilateral adrenal adenomas and progressive weight gain over the last five years. Cushing syndrome is detected during study of the adrenal adenomas and obesity. It is important to study recent-onset obesity in multimorbid patients as there could be other secondary causes in addition to the underlying diseases they present with. During the presentation of this clinical case, an essential, practical approach to the adrenal pathology is made.
Presentamos el caso de una paciente de 64 años, natural de Rumanía, con antecedentes médicos de: síndrome de apnea-hipopnea, cirrosis hepática, EPOC y artrosis. Fumadora activa de 1 paquete cigarrillos/día. La paciente es remitida desde la consulta de Neumología para estudio ambulatorio por presentar como hallazgo incidental adenomas suprarrenales bilaterales y aumento progresivo de peso en los últimos 5 años. En el estudio de adenomas suprarrenales y obesidad se objetiva la presencia de un síndrome de Cushing. Es importante estudiar la aparición de la obesidad reciente en una paciente pluripatológica dado que puede haber otras causas secundarias además de las patologías subyacentes que presenta. Durante la presentación del caso clínico se realiza un abordaje esencial y práctico de la patología adrenal.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<