The incidence and mortality of sepsis remain high in the intensive care units (ICU). WBC, CRP and PCT are frequently used as tools for sepsis detection; however, none of them is specific to sepsis. The aim of the current study was to evaluate whether monocyte distribution width (MDW) is useful for early sepsis detection in critically ill patients.
MethodsProspective cohort study was conducted in a critical care unit. MDW, CRP, PCT and WBC were evaluated for sepsis detection at the time of intensive care unit admission.
ResultsThere were 344 critically ill patients enrolled consecutively and categorized as no sepsis (200), sepsis (76) and septic shock (68). MDW in patients with sepsis diagnoses in ICU was notably higher than non-sepsis group [29.7 (24.7–35.7) vs 20.4 (18.6−22.7); P < .001] under the assumption of no mean difference between the groups. Compared to other parameters, MDW was the best to discriminate sepsis from all other conditions (area under curve [AUC], 0.877; 95% CI, 0.841 0.914), sensitivity 80.6, specificity 84.5 at a cut-off point of 24. MDW adjusted for age, sex and SOFA score was associated with mortality [OR 1.056 (95% CI: 1.004–1.09) P < .01].
ConclusionThe measurement of MDW is a tool that can help in the early diagnosis of sepsis in ICU settings and its value is a factor associated with the prognosis of septic patients.
La incidencia y mortalidad de la sepsis es elevada en las unidades de cuidados intensivos (UCI). Los leucocitos, la PCR y la PCT se utilizan frecuentemente como herramientas de diagnóstico de sepsis; sin embargo, ninguno de ellos es un marcador específico. El objetivo del presente estudio fue evaluar si la amplitud de distribución de monocitos (MDW) es útil para la detección temprana de sepsis en los pacientes críticamente enfermos.
Métodosestudio de cohortes prospectivo realizado en pacientes de UCI. Se evaluaron el MDW, la PCR, la PCT y los leucocitos para el diagnóstico de sepsis en el momento del ingreso en UCI.
Resultadosse incluyeron 344 pacientes críticamente enfermos, categorizados en tres grupos: no sepsis (200), sepsis (76) y shock séptico (68). El MDW en los pacientes con sepsis fue notablemente más alto que en el grupo sin sepsis [29,7 (24,7–35,7) vs 20,4 (18,6–22,7); P < ,001]. En comparación con otros parámetros, el MDW fue el mejor para discriminar la sepsis de todas las demás condiciones (área bajo la curva [AUC], 0,877; IC 95%, 0,841–0,914), con una sensibilidad del 80,6 y una especificidad del 84,5 para un punto de corte de 24. El MDW ajustado por edad, sexo y la escala SOFA se asoció con la mortalidad [OR 1,056 (IC 95%: 1,004–1,09); P < ,01].
ConclusiónEl MDW es una herramienta que puede ayudar en el diagnóstico temprano de sepsis en la UCI, cuyo valor es un factor asociado con el pronóstico de los pacientes sépticos.
Despite therapeutic advances in the management of patients with sepsis, their hospital and Intensive Care Unit (ICU) mortality is still high (36% and 27% each).1 Several factors are associated with this, one of the most important being the delay in diagnosis. Among the reasons for this is the difficulty in diagnosis, especially in patients with comorbidities (diabetes mellitus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, among others), the rapid progression of apparently healthy patients to septic conditions, and the absence of biomarkers with sensitivity and specificity high enough to discern patients with sepsis. On the other hand, erroneous diagnostic orientation leads to administration of antibiotics to all such patients and carries problems of antibiotic resistance, drug toxicity, and financial considerations.2
Critically ill patients are a special group of the population because most of them present a state of generalized inflammation not necessarily associated with an infection, which makes the detection of sepsis much more difficult. The monocyte distribution width (MDW) is a new marker that is based on the ability of monocytes to increase in size when the patient is undergoing a septic process and this variation can be easily monitored by measuring the spread of monocytes volume using the Coulter principle. Therefore, it can be used to discriminate between patients without infection, patients with sepsis or patients with septic shock.3 We hypothesized that volume increases in circulating monocytes quantified with MDW, alone or in combination with other parameters, would improve sepsis detection in the critical care units and that the MDW value is associated with mortality in patients with sepsis.
MethodsStudy design and populationThe present study was a prospective observational study of patients consecutively admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) of the Germans Trias i Pujol University Hospital (HUGTiP) during the period from February 2019 to January 2020. This is a polyvalent ICU in a tertiary hospital, specializing in high-complexity pathologies. The ICU has approximately 1.000 annual admissions, with a sepsis incidence of 30% at the time of admission.
All adult patients (over 18-years old) admitted to the ICU were consecutively included in the study. MDW and serum biomarkers (CRP and PCT) were analyzed every 72 h to assess their trends. All patients included had a properly performance of immune system. The exclusion criteria were: patients who stayed in ICU less than 24 h, under 18 years of age, incomplete informed consent, incomplete data or patients already included in the study. Patients with underlying conditions potentially associated with dysregulation of their immune system (AIDS, organ or bone marrow transplantation, malignancy, hematologic diseases) were excluded.
This study was carried out following the basic ethical principles contained in the Helsinski Declaration (Fortaleza, October 2013). It was reviewed and approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee (CEIC) of the Germans Trias i Pujol University Hospital (PI-18-249). All patients included in the study have an informed consent previously approved by the CEIC.
Clinical classification of patient in ICUStudy patients were categorized based upon the “Sepsis-3” consensus criteria (Singer et al.): non-sepsis, sepsis, and septic shock during the first 24 h of admission. According to The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3), sepsis was defined as a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection and septic shock with a clinical construct of sepsis with persisting hypotension requiring vasopressors to maintain MAP (Mean Arterial Pressure) ≥ 65 mm Hg and having a serum lactate level >2 mmol/L (18 mg/dL) despite adequate volume resuscitation.4
MDW determinationWhole blood specimen was collected in K3EDTA tubes (BD Vacutainer®) to determine CBC-DIFF and MDW on an UniCel DxH 900 analyzer (Beckman Coulter, Inc., Brea, CA) with version 1.1.0.96 software within 2 h of blood draw. The UniCel DxH 900 Coulter Cellular Analysis System uses VCSn technology (volume, conductivity and scatter), measuring about 8000 cells in their “near native state”. DxH 900 analyzer uses direct current impedance for determining volume (V) of the cells, radiofrequency for conductivity (C) and a laser beam scatter in five different angles to analyze Light scatter (Sn) dispersion. VCSn analysis provides the mean and standard deviation values of volume, conductivity, and 5-angle light scattering parameters, corresponding to a total of 14 cell population parameters for each WBC sub-population. MDW corresponds to the standard deviation of the volume component of the monocyte population derived from the differential dataplot from VCSn technology and reflects the variation in the size distribution of circulating monocytes. MDW parameter was assessed daily by different internal quality controls (QC) procedures. Coulter Latron CP-X; which evaluates VCSn technology through latex particles and Coulter 6C Plus Cell Control in three levels at different concentrations. In addition, Beckman Coulter’s Interlaboratory Quality Assurance Program (IQAP) was used to compare MDW QC results with other laboratories within peer groups during the study. MDW was analyzed according to the study protocol on days 0, 3, 6, 9, 12 and on the day of ICU discharged.
Biochemical biomarkers analysisCRP and PCT were analyzed in serum samples after centrifugation (at 1500×g for 10 min) within 4 h of blood draw. The CPR level was analyzed by immunoturbidimetry in the AU5800 (Beckman Coulter, Inc, Brea, CA, USA) and PCT concentration was measured by immunoassay using Liaison XL analyzer (Diasorin, Saluggia, Italy). CRP and PCT were analyzed with the same frequency as MDW. Both serum biomarkers were measured on days 0, 3, 6, 9, 12 and on the day of ICU discharged.
Statistical analysisQuantitative variables were tested for normal distribution using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov’s test. The associations between the diagnosis based on sepsis-3 criteria (classified into three groups) and a biomarker was evaluated using the Kruskall-Wallis test. In the study of correlation between MDW and SOFA/APACHE scores we used the Spearman correlation. The diagnostic performance of different biomarkers was evaluated by calculating the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), Sensitivity, Specificity, Positive Predictive Value (PPV), Negative Predictive Value (NPV) along with their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) (2-sided) calculated using the Score approach. Differences in AUC were used to demonstrate the added value of MDW in comparison to different biomarkers alone and combined, calculated using a one-predictor variable logistic model with one biomarker and a two-predictor variables logistic model with several biomarkers, as the predictor, and using sepsis status as the response.
To evaluate the association between the MDW value and overall mortality, a longitudinal analysis was conducted in which mortality served as the dependent variable. The key independent variables were the MDW value and the time at which the MDW measurement was taken (days 0, 3, 6, and 9 following ICU admission). As a result, each patient contributed up to four records, one for each MDW measurement. Given the correlation between the data points, a Generalized Estimating Equation (GEE) model was applied to adjust for this. To account for potential differences between the two groups (deceased vs. surviving), age, sex, and SOFA score were included as covariates in the model.
For all analyzes and comparisons, a value of P < .05 was considered as statistically significant. Software SPPS version 20 and Medcalc version 19.5.3 were used for all statistical analyses.
ResultsPatientsA total of 364 patients were enrolled in the study, of which 20 were excluded due to reasons such as not meeting the inclusion criteria, inadequate sample collection or unavailable MDW result (Fig. 1). The final analysis included 344 patients; median age was 59 years old and women represented 37.8%. Demographic features are shown in Table 1. Using Sepsis-3 criteria, 200 patients (58.1%) were categorized as non-sepsis, 76 (22.1%) as sepsis and 68 (19.8%) as septic shock. The primary cause of infection upon admission was respiratory (50%), followed by abdominal (22%), urinary (18%) and miscellaneous (10%) infections. Empirical antibiotic treatment was appropriate in 90% of patients.
Demographics and severity scales.
| Overall | Non-Sepsis | Sepsis | Septic Shock | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total subjects | 344 | 200 | 76 | 68 | P |
| Age, years-median (IQR) | 59 (47−69) | 56 (45−68) | 60 (50−70) | 66 (52−75) | <.001 |
| Female gender, no. (%) | 130 (37.8%) | 74 (37.0) | 28 (36.8) | 28 (41.2) | .857 |
| SOFA score, median (IQR) | 7.0 (3.0−9.0) | 5.0 (2.0−8.0) | 7.0 (4.0−9.0) | 9.5 (7−12) | <.001 |
| APACHE II score, median (IQR) | 16.0 (11.0−22.0) | 15.0 (9.3−20.0) | 15.0 (11.0−20.0) | 20.5 (14.0−24.0) | <.001 |
| WBC × 109/L, median (IQR) | 11.6 (8.6−16.0) | 11.7 (9.4−14.7) | 9.6 (6.9−16.0) | 12.9 (7.7−20.2) | <.001 |
| MDW, median (IQR) | 22.7 (19.6−29.5) | 20.4 (18.6−22.7) | 26.9 (23.7−31.2) | 32.6 (26.9−40.9) | <.001 |
| CRP mg/L, median (IQR) | 80.2 (15.6−201.0) | 26.5 (7.2−79.2) | 144.8 (80.6−269.8) | 249.5 (170.4−356.0) | <.001 |
| PCT ng/mL, median (IQR) | 0.46 (0.07−4.9) | 0.12 (0.04−0.85) | 1.1 (0.2−4.1) | 10.3 (1.9−30.0) | <.001 |
MDW in patients with sepsis diagnosis in ICU was notably higher than non-sepsis group [29.7 (24.7–35.7) vs 20.4 (18.6−22.7); P < .001] under the assumption of no mean difference between the groups. Related to the Sepsis-3 criteria, the MDW value increased progressively in the 3 groups studied (non-sepsis, sepsis and septic-shock) according to the severity of the patients (Table 1). The MDW at admission in ICU for the non-sepsis patients was 20.4 (18.6−22.7), for septic 26.8 (23.7−31.2) and for septic shock 32.5 (26.9−40.9) (P < .001) (Fig. 2). MDW correlated positively at admission in ICU with organ dysfunction (SOFA; r = 0.442, P < .001) and with severity of patients (APACHE; r = 0.206, P < .01) scores.
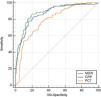
MDW performance for sepsis diagnosis: MDW demonstrated good diagnostic ability to identify sepsis patients in ICU with AUC [0.877 (95% CI: 0.841−0.914). The most accurate cut-off MDW value, calculated by Younden’s index, was 24.2, showing a sensitivity of 80.6% (95% CI: 73.1−86.7) and a specificity of 84.5% (95% CI: 78.7–89.2). The positive likelihood ratio (LR+) was 5.20 (95% CI: 3.70–7.30) and the negative (LR−) was 0.23 (95% CI: 0.20−0.30). Regarding the ROC curves for sepsis detection, the MDW demonstrated performance similar to CRP [0.871 (95% CI: 0.833−0.909)] and superior to PCT [0.787 (95% CI: 0.736−0.838)] (Fig. 3). Adding WBC determination [AUC for WBC 0.480 (95% CI: 0.414−0.547] to MDW measurement did not improve the performance [MDW + WBC: 0.877 (IC95: 0.838−0.910)] in ICU patients for Sepsis-3 diagnosis. The combination of two biomarkers with the best AUC was MDW plus CRP [MDW + CRP: 0.909 (95% CI: 0.873−0.938]). However, the combinations studied between the different biomarkers analyzed did not increase the diagnostic ability compared to the MDW alone (Table 2).
Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, PNV of MDW, CRP and PCT and combinations in predicting sepsis.
| Biomarker | AUC (95% IC) | Sensitivity (95% IC) | Specificity (95% IC) | PPV (95% IC) | NPV (95% IC) | LR+ (95% IC) | LR− (95% IC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDW | 0.877 (0.841−0.914) | 80.6 (73.1−86.7) | 84.5 (78.7–89.2) | 78.6 (72.5–83.7) | 86.0 (81.4−89.6) | 5.20 (3.7−7.3) | 0.23 (0.2−0.3) |
| WBC | 0.480 (0.414−0.547) | 84.2 (78.5–89.0) | 34.2 (26.8–42.1) | 47.9 (44.7–51.1) | 75.1 (67.3–81.6) | 1.28 (1.1–1.5) | 0.46 (0.3−0.7) |
| CRP | 0.871 (0.833−0.909) | 81.3 (74.2–87.1) | 81,44 (75,2–86,7) | 75.9 (69.9–81.0) | 85.8 (81.3–89.4) | 4,38 (3,2–5,9) | 0.23 (0.2–0.3) |
| PCT | 0.787 (0.736–0.838) | 70.6 (62.7–77.7) | 76.5 (69.7–82.4) | 68.3 (62.0–74.0) | 78.4 (73.7–82.4) | 3.00 82,3–4,0) | 0.38 (0.3–0.5) |
| MDW + WBC | 0.877 (0.838–0.910) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| MDW + CRP | 0.909 (0.873–0.938) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| MDW + PCT | 0.891 (0.852–0.923) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| CRP + PCT | 0.891 (0.852–0.922) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| MDW + CRP + PCT | 0.917 (0.881–0.945) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
The MDW cut-off of 21.5, recommended for the ED patients showed a sensitivity of 89,9% (95% CI: 82.6–93.5), specificity of 66.5% (95% CI: 59.5–73.0). The positive likelihood ratio (LR+) was 2.65 (95% CI: 2.20–3.30) and the negative (LR−) was 0.17 (95% CI: 0.10–0.30), and a negative predictive value of 91.1%. Our study showed a pretest probability of 46.4% or diagnosis of sepsis (prevalence of sepsis). A normal value (below 21.5) of MDW was associated with a 10% sepsis risk, while abnormal MDW result increased sepsis probability up to 70%.
MDW and Hospital mortality: The longitudinal analysis revealed that MDW, adjusted for age, sex, and SOFA score, was associated with sepsis-related mortality [OR 1.06 (95% CI: 1.004–1.09), P < .01]. However, the ROC analysis showed that MDW was not effective in identifying sepsis-related hospital mortality at admission, with an AUC of 0.588 (95% CI: 0.461–0.714).
The most accurate cut-off MDW value calculated by Younden’s index at admission was 27.20, showing a sensitivity of 81.2% (95% CI: 59.7–94.8) and a specificity of 46.15% (95% CI: 35.64–56.92). The MDW value on the third day showed a clear trend to identify septic patients with a low probability of death AUC [0.643 (95% CI: 0.523–0.763). The MDW cut-off value calculated by Younden’s index at third day was below 25.1 demonstrated a sensitivity of 83.33% (95% CI: 58.58–96.42) and a specificity of 48.28% (95% CI: 37.42–59.25) to identify patients who will survive.
Non-septic hyperinflammatory states associated with abnormal MDW values: In our cohort 5 patients had a diagnosis of acute pancreatitis and another 7 patients required ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation). All patients with pancreatitis were male, median age was 63 years old. The median values measured at admission for the most important parameters were APACHE II: 15 (7–16) points, CRP: 318 (55–434) mg/L, MDW 36.4 (29–48) and PCT: 5.5 (4.3–7) ng/mL.3 Patients under ECMO therapy were male, median age was 54 years old. The median values measured at admission for the most important parameters were: APACHE II: 16 (12–26) points, CRP: 30 (2–431) mg/L, MDW: 24 (20–36) and PCT: 1.5 (0.03–3.99) ng/mL.
DiscussionIn our prospective study, the MDW value showed notable differences between patients without sepsis, those with sepsis, and those with septic shock on the first day after ICU admission. We also found that the cut-off point for MDW value from which critically ill patients have a high probability of sepsis was 24.2. On the other hand, MDW value below 21.5 (is a validated cut-off value in patients admitted to the emergency department)4 has a very low probability of sepsis. In addition, the severity of sepsis was consistent with a higher MDW value and associated with hospital mortality.
Changes in the morphology of circulating monocytes are a well-recognized early sign of infection.5 It has been postulated that these changes are the expression of monocyte activation or the appearance of young forms of monocytes caused by pathogenic microorganisms.3 Crouser et al., demonstrated that changes in volumetric size of monocytes involved in the early response to bacterial infections correlated with patients with sepsis in an emergency department (ED) setting. As in our study, they found that the value of MDW correlates with the severity of sepsis.2 Polilli et al., showed that an MDW value starting at 22 correlated with sepsis in an inpatient setting.6 Crouser in a study of ED patients showed that an increase in MDW effectively identifies septic patients and infected patients who are at increased risk of progression to sepsis. The MDW value of greater than 20 was effective for sepsis detection.7,8 As can be noted, the cutoff points for the emergency department patient population are lower than our results for critically ill patients. In this regard, two studies performed in critically ill populations showed results similar to ours. The first one is a prospective study of 505 patients admitted to the ICU, ROC analysis demonstrated that AUC was 0.785 with a sensitivity of 66.88% and specificity of 77.79% at a cut-off point of 24.63 for MDW.9 The second, conducted by Polilli et al., enrolled 211 critical care patients in which an MDW value higher than 23 was associated with sepsis.10
Several reasons are possible explanations for the difference between the MDW value in patients attended in an emergency department and patients admitted to intensive care medicine. The scenario of critically ill patients is very particular because they present organ failure and an inflammatory condition not necessarily caused by infection.11 In this context, patients under ECMO therapy and pancreatitis are clear examples of this hyperinflammatory state. As can be seen in our results, the median value in both groups of patients was high (24 and 36, respectively), despite the fact that they did not present infection on admission. This reflects that the MDW value is affected by systemic hyperinflammation.
Although PCT and CRP are widely used biomarkers to assist in the diagnosis of acute infection, their specificity and sensitivity are not sufficient by themselves to make the diagnosis of sepsis.12–16 Current guidelines position PCT to guide the duration of antibiotic treatment in patients with sepsis or discontinue empirical antibiotic treatment with limited clinical infection, rather than as a diagnostic utility.17,18 Therefore, the search for new biomarkers is necessary. Three recent meta-analyses19–21 have compared the performance of PCT and CRP with that of MDW, showing comparable results. Huang et al.19 reported that MDW is a reliable diagnostic biomarker for sepsis, with higher sensitivity but lower specificity compared to PCT. Eisinger et al.21 found a high negative predictive value (NPV) for MDW, estimated at 0.94. Their comparison of MDW and PCT also showed higher sensitivity but lower specificity for MDW, consistent with the pattern reported by Huang et al.19 In our study, however, MDW was superior both in sensitivity and specificity to discriminate septic patients compared to PCT and CRP. In contrast to the study by Polilli et al., we did not find an increase in diagnostic ability with the combination of MDW + PCT.
Regarding the sensitivity and specificity of MDW according to sepsis-2 and sepsis-3 criteria, Eisinger et al. reported higher sensitivity and lower specificity when using the sepsis-3 criteria compared to sepsis-2. This could be explained by the fact that sepsis-3 aims to improve the identification of patients at higher risk of poor outcomes associated with sepsis.
Polilli's study in critical care patients setting found that an MDW value below or equal to 20 was compatible with a low risk of sepsis [NPV: 86.4(95% CI: 65.1–97.1)].10 Our study found that an MDW value below 21.5 was associated with a low probability of sepsis [NPV: 89.9% (95% CI: 82.6–93.5)]. Although the difference is small, it could be explained by the different types of pathologies that are admitted to both centers and, therefore, by the different degree of inflammation to which they may be exposed.
Liu in a group of 252 critically ill septic patients studied the prognostic value of MDW in septic patients. The MDW value 26.2 measured on the third day of admission discriminated survivors and deceased at 28 days.22 In our study, MDW was associated with in-hospital mortality; but we were unable to find a statistically specific cut-off point value and only a clear trend. In our study, the MDW value of 25.5 on the third day was able to discriminate between the deceased and the survivors. As we can see, they are similar values and the small difference could be explained by the type of anticoagulant used (Liu's study used K2 EDTA). On the other hand, the absence of significance in our cut-off point could be explained by the fact that our sample size (144 vs 252 patients) was smaller than that of Liu's study. The differences observed in MDW values—being higher in K3-EDTA tubes compared to K2-EDTA tubes—were also reported in the meta-analysis by Eisinger et al.21 MDW appeared to perform slightly better in K3 tubes, likely due to greater specificity, which may be attributed to the higher cut-off values used in studies based on K3-EDTA. Therefore, MDW values should be interpreted in accordance with the type of EDTA tube used for analysis.
It is important to emphasize that MDW is integrated into the blood cell count that is normally done in a routine blood test and can be measured automatically within a few minutes without additional sampling. Therefore, it does not add to the cost.23 These positive properties make MDW a suitable parameter for routine analysis in daily blood samples. The discrimination of the septic state becomes relevant and in that sense the measurement of MDW can be valuable, integrating it into the sepsis protocols to improve the early detection and with it the mortality. Also, avoiding unnecessary expenses.
There are several limitations to the study. First, our study included different etiologies: bacterial, viral and fungal. Second, since this is a single-center study, additional prospective clinical studies will be required to validate the performance of MDW for early sepsis detection in other Critical Care populations, and in regions with different sepsis characteristics. Third, the exclusion of patients with immune system dysfunction may introduce selection bias. Fourth, there is a delay between the study's execution and its current publication due to the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the characteristics of septic patients before and after the pandemic are comparable, making the usefulness of MDW fully valid. Finally, since we do not employ a random selection process, the statistical measures we provide may be unreliable, and the overall uncertainty is likely to be greater than the level of error quantified by random statistical methods.
ConclusionsIn conclusion, MDW reflects a change in the volume of circulating monocytes in response to sepsis. In this study we add evidence in favor of the routine use of MDW to sepsis early detection in critically ill patients and as a factor associated with the prognosis of septic patients.
Ethics approval and consent to participateThis study was carried out following the basic ethical principles contained in the Helsinski Declaration (Fortaleza, October 2013). It was reviewed and approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee (CEIC) of the Germans Trias i Pujol University Hospital (PI-18-249). All patients included in the study have an informed consent previously approved by the CEIC.
FundingThe current investigation was conducted without utilizing any external funding.
Data availabilityThe data that support the findings of this study are not openly available due to reasons of sensitivity and are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Data are located in controlled access data storage at Germans Trias i Pujol University Hospital.
Cristian Morales Indiano, Alba Herraiz Ruiz, Fernando Arméstar Rodríguez and Beatriz Catalán Eraso have received institutional research support from Beckman Coulter since 2018.
We thank the patients and their families and caregivers for participating in this study, along with all investigators and site personnel. We thank Dr. Josep Roca for providing statistical analysis and expertise.