Describir la distribución poblacional de la variante UGT1A1*28 (código de variante genética rs8175347) localizada en el promotor del gen UGT1A1 y correlacionar sus genotipos con los resultados de la prueba de ayuno, así como su relación con la alteración bioquímica propia del síndrome de Gilbert (SG) en población valenciana.
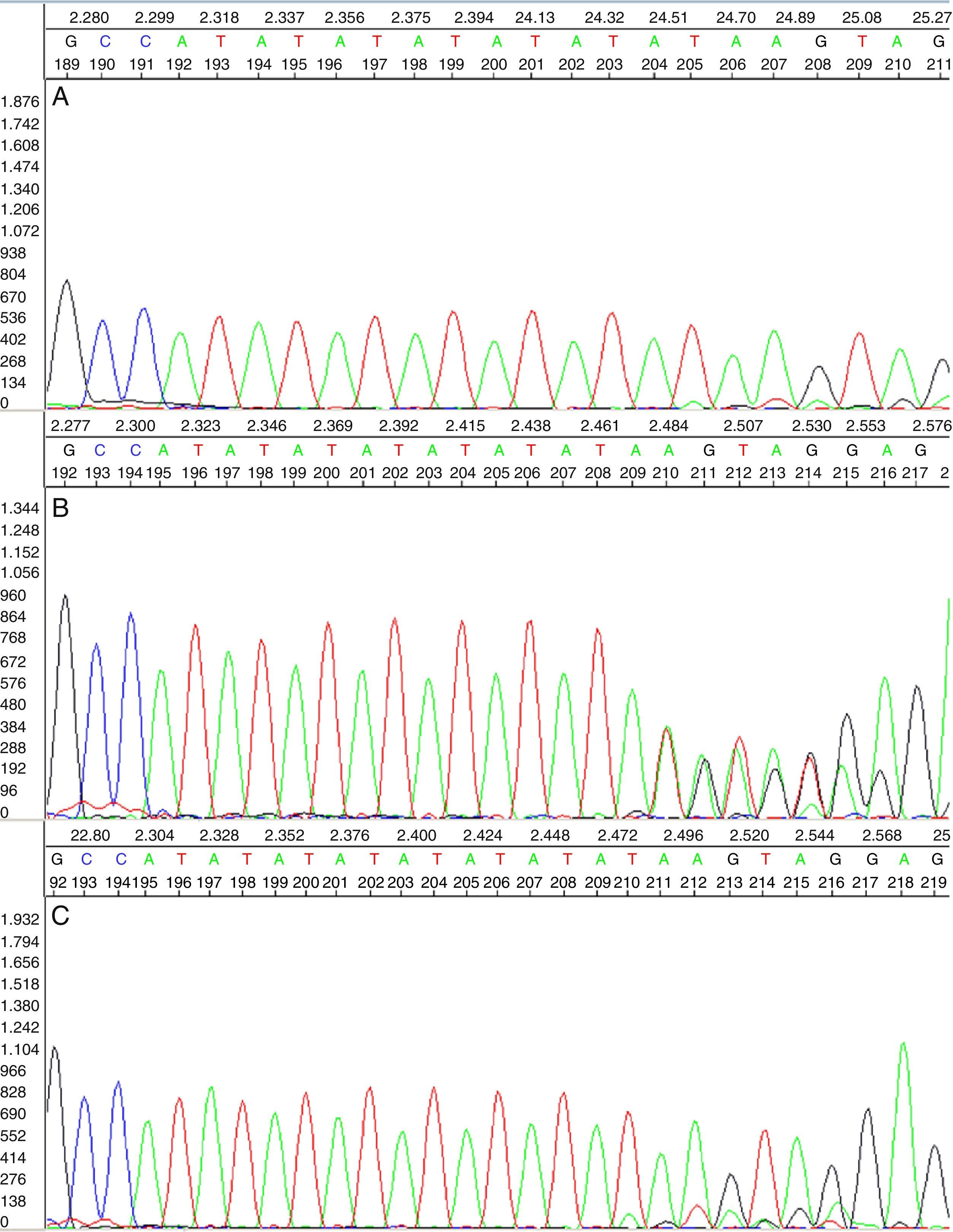
Pacientes y métodosEstudiamos la prevalencia de los genotipos (TA)6/6 (TA)6/7 y (TA)7/7 de la variante deletérea rs8175347, en 144 pacientes con hiperbilirrubinemia, de los cuales 38 habían sido sometidos previamente a la prueba del ayuno para realizar el diagnóstico de SG, y en 150 individuos control. Analizando la región genómica de la caja TATA del promotor del gen UGT1A1 mediante secuenciación Sanger, se estableció la correlación de los genotipos rs8175347 con los resultados del test del ayuno y con las alteraciones bioquímicas de los pacientes.
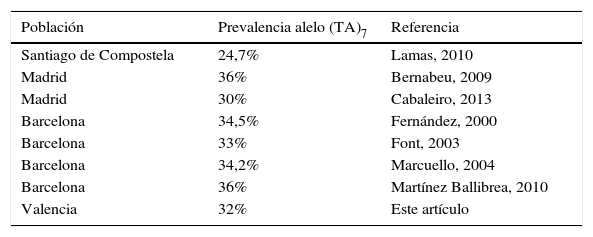
ResultadosLa frecuencia de heterocigosidad del alelo (TA)7 en población control fue 32% y ascendió al 87,59% entre pacientes con sospecha de SG. La frecuencia del genotipo TA7/7 fue del 81,94% entre los pacientes, frente a un 11,33% en controles. La prueba de ayuno mostró un 15,79% de falsos negativos y un 5,26% de falsos positivos.
ConclusionesLa elevada frecuencia del alelo (TA)7 entre individuos de población control valenciana, casi el doble del 5% descrito en individuos control europeos, corrobora la elevada frecuencia del SG descrita en población española, sin observarse diferencias significativas entre extremos geográficos del país. La eficacia y fiabilidad de la prueba del ayuno para el diagnóstico del SG es cuestionable.
To describe the populational distribution of the UGT1A1*28 variant (genetic variant code rs8175347) located in the promotor of the UGT gene and correlate its genotypes with the results of the fasting test, as well as its relationship with the biochemical disorder of Gilbert's syndrome (GS) in a Valencian population.
Patients and methodsWe studied the prevalence of the genotypes (TA)6/6 (TA)6/7 and (TA)7/7 of the deleterious variant rs8175347 in 144 patients with hyperbilirubinemia, 38 of whom had previously undergone the fasting test to diagnose GS, and in 150 control patients. By analysing the genomic region of the TATA box of the UGT1A1 gene promotor using Sanger sequencing, we established the correlation between the rs8175347 genotypes and the fasting test results and with the patients’ biochemical disorders.
ResultsThe rate of heterozygosity of allele (TA)7 in the control population was 32% and increased to 87.59% among the patients with suspected GS. The rate of genotype TA7/7 was 81.94% among the patients with hyperbilirubinemia, compared with 11.33% in the control patients. The fasting test showed a 15.79% rate of false negatives and a 5.26% rate of false positives.
ConclusionsThe high frequency of allele (TA)7 among the Valencian control population, almost double the 5% reported for European control patients, confirms the high rate of GS reported in the Spanish population, without observing significant differences between the geographical ends of the country. The efficacy and reliability of the fasting test for the diagnosis of GS is questionable.
Artículo
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<