Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2) is usually accompanied by various comorbidities that can increase the cost of treatment. We are not aware of studies that have determined the costs associated with treating DM2 patients with comorbidities such as overweight (OW), obesity (OBE) or arterial hypertension (AHT). The aim of the study was to examine the health-related costs and the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in these patients.
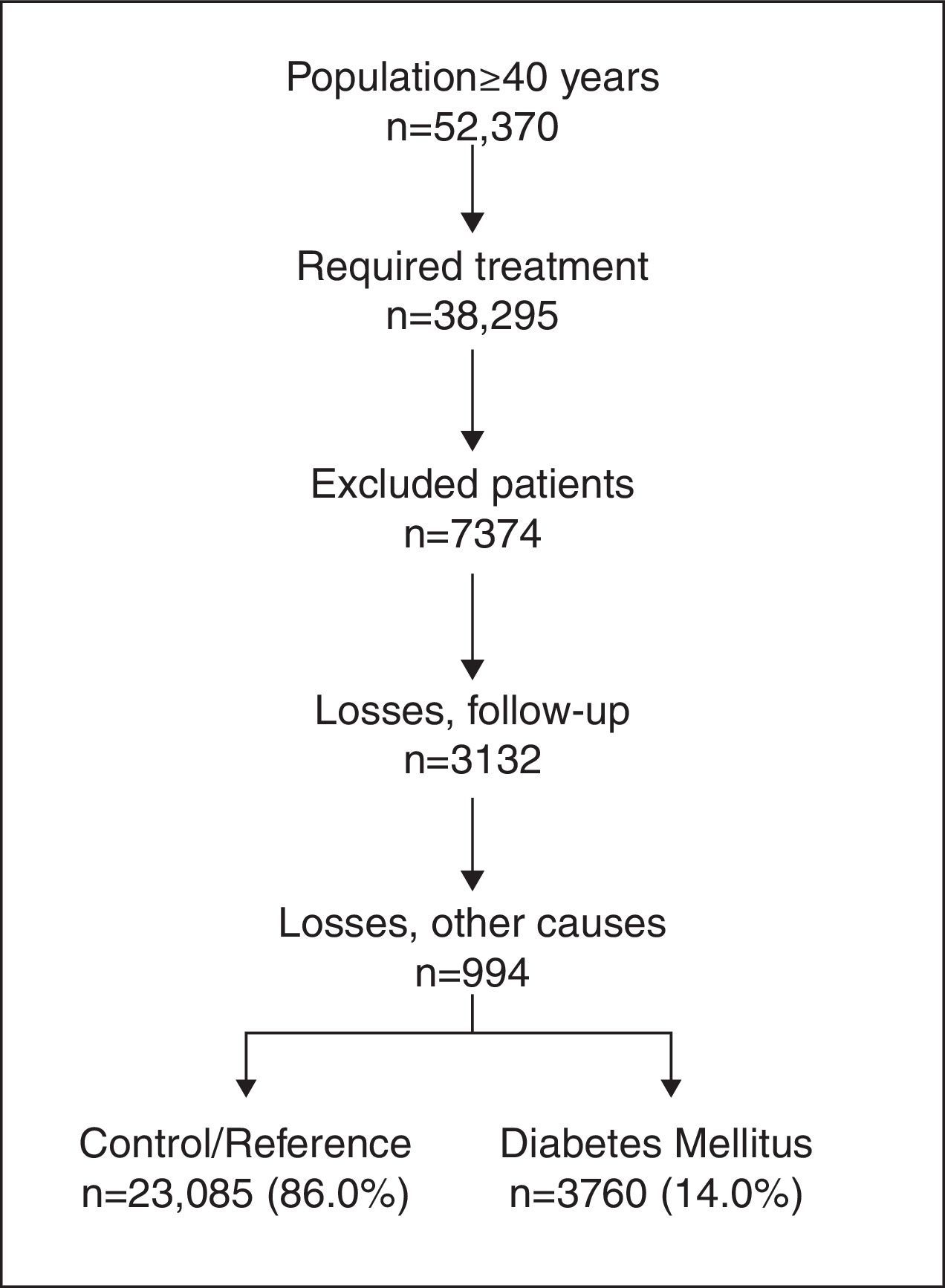
Patients and methodsMulticenter, observational retrospective design. We included patients 40–99 years of age who requested medical attention in 2010 in Badalona (Barcelona, Spain). There were two study groups: those with DM2 and without DM2 (reference group/control), and six subgroups: DM2-only, DM2–AHT, DM2–OW, DM2–OBE, DM2–AHT–OW and DM2–AHT–OBE. The main outcome measures were: comorbidity, metabolic syndrome (MS), complications (hypoglycemia, CVD) and costs (health and non-health). Follow-up was carried out for two years.
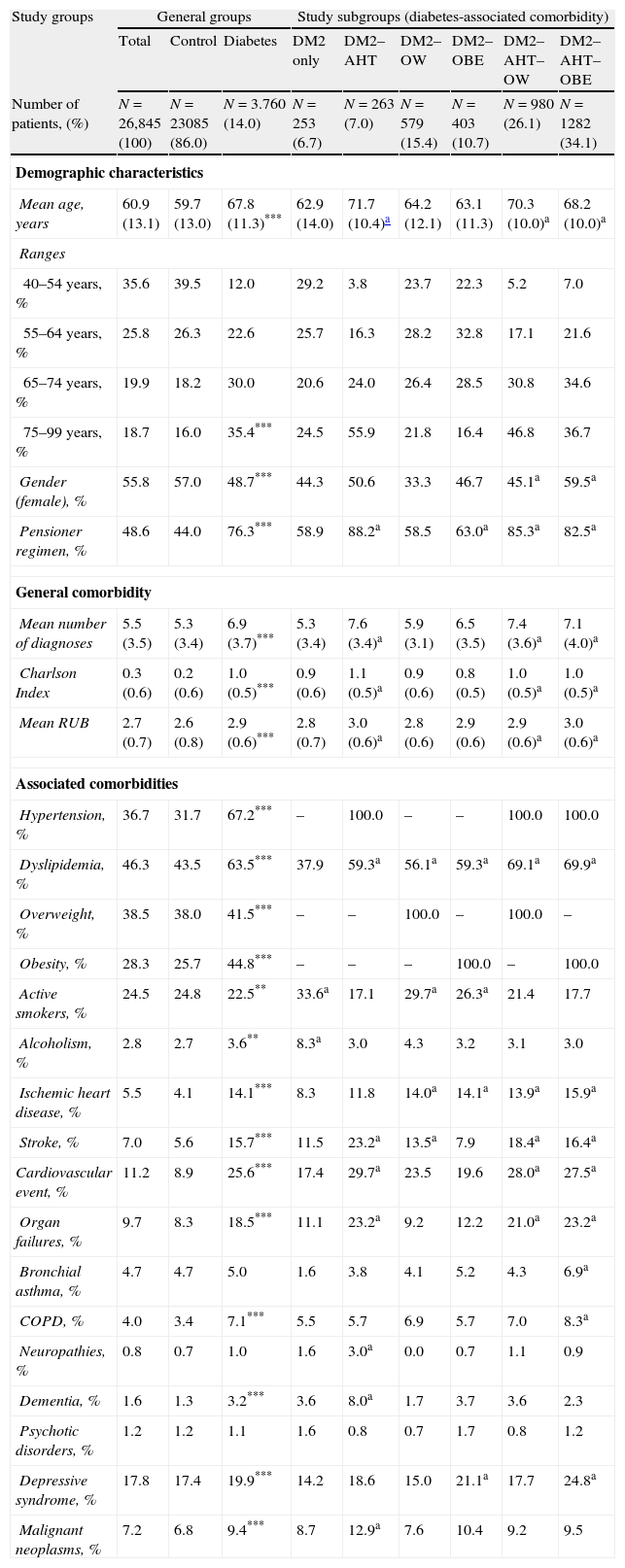
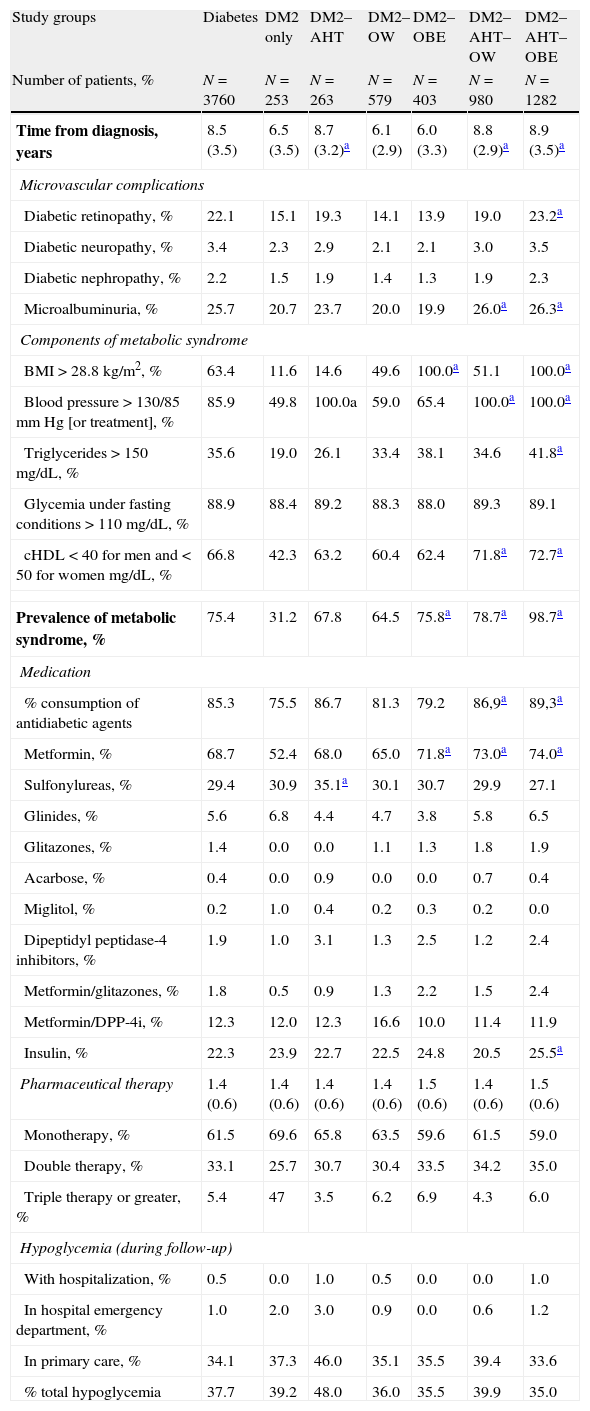
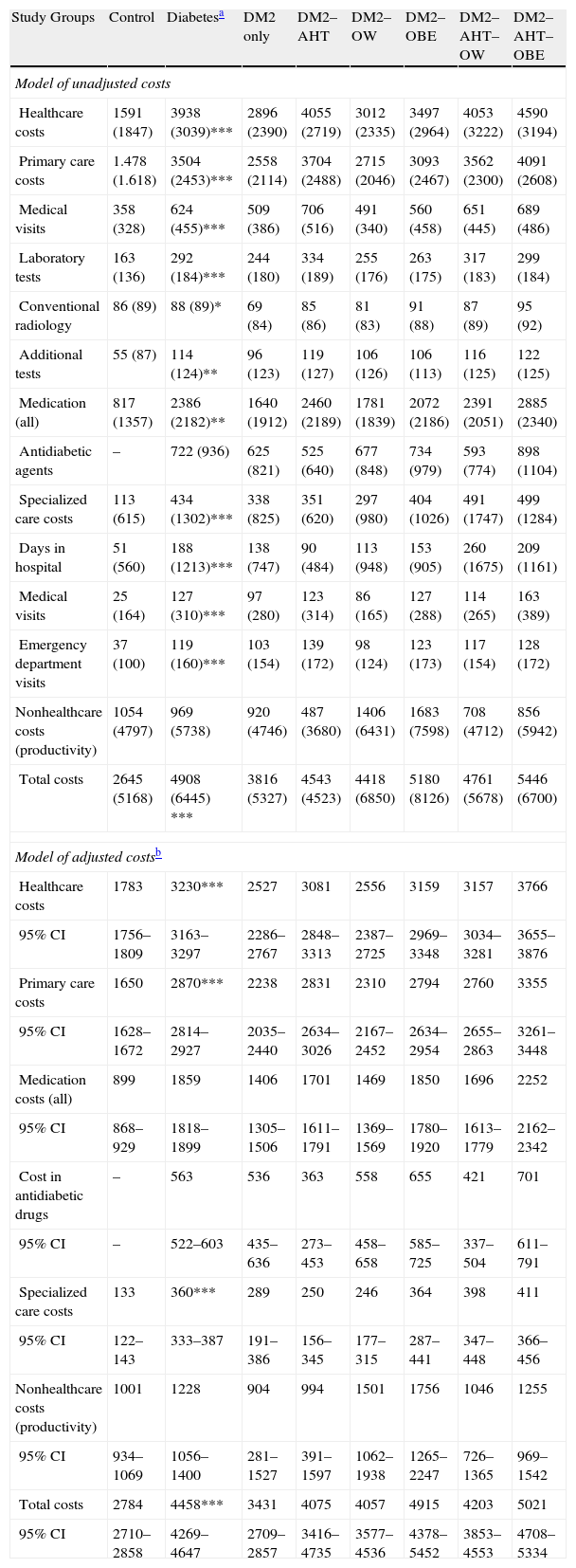
ResultsA total of 26,845 patients were recruited. The prevalence of DM2 was 14.0%. Subjects with DM2 were older (67.8 vs. 59.7 years) and more were men (51.3 vs. 43.0%), p<.001. DM2 status was associated primarily with OBE (OR=2.8, CI=2.4–3.1), AHT (OR=2.4, CI=2.2–2.6) and OW (OR=1.9, CI=1.7–2.2). The distribution by subgroups was: 6.7% of patients had only DM2, 26.1% had DM2, AHT and OW, and 34.1% had DM2, AHT, and OBE. Some 75.4% had MS and 37.5% reported an episode of hypoglycemia. The total cost/patient with DM2 was €4458. By subgroups the costs were as follows: DM2: €3431; DM2–AHT: €4075; DM2–OW: €4057; DM2–OBE: €4915; DM2–AHT–OW: €4203 and DM2–AHT–OBE: €5021, p<.001. The CVD rate among patients with DM2 was 4.7 vs. 1.7% in those without DM2 p<.001.
ConclusionsObesity is a comorbidity associated with DM2 that leads to greater healthcare costs than AHT. The presence of these comorbidities causes increased rates of CVD.
La diabetes mellitus tipo 2 (DM2) suele acompañarse de diversas comorbilidades que pueden incrementar el coste de su tratamiento. No conocemos estudios que hayan determinado los costes asociados al tratamiento de los enfermos con DM2 que, además padecen sobrepeso (SP), obesidad (OBE) o hipertensión arterial (HTA). Hemos examinado el gasto sanitario y la incidencia de enfermedad cardiovascular (ECV) en estos enfermos.
Pacientes y métodosDiseño observacional-multicéntrico de carácter retrospectivo. Se incluyeron pacientes entre 40–99 años que demandaron atención durante 2010 en Badalona (Barcelona, España). Se establecieron 2 grupos de estudio: presencia-DM2 y ausencia-DM2 (referencia/control), y 6 subgrupos: DM2-solo, DM2–HTA, DM2–SP, DM2–OBE; DM2–HTA–SP y DM2–HTA–OBE. Las principales medidas fueron: comorbilidad, síndrome metabólico (SM), complicaciones (hipoglucemias, ECV) y costes (sanitarios; no-sanitarios). El seguimiento se realizó durante 2 años.
ResultadosSe reclutaron 26.845 pacientes. La prevalencia de DM2 fue del 14,0%. Los sujetos con DM2 mostraron mayor edad (67,8 vs. 59,7 años) y porcentaje de varones (51,3 vs. 43,0%), p<0,001. La DM2 se asoció principalmente a OBE (OR: 2,8; IC 95%: 2,4–3,1), HTA (OR: 2,4; IC 95%: 2,2–2,6) y SP (OR: 1,9; IC 95%: 1,7–2,2). La distribución por subgrupos osciló entre el 6,7% para los enfermos que solo presentaban DM2, y el 26,1% para los diagnosticados de DM2–HTA–SP y el 34,1% para los que tenían DM2–HTA–OBE. El SM se identificó en el 75,4% y un 37,5% refirió algún episodio de hipoglucemia. El coste-total/paciente con DM2 al cabo de 2 años fue de 4.458€. Por subgrupos fue de DM2: 3.431€; DM2–HTA: 4.075€; DM2–SP: 4.057€; DM2–OBE: 4.915€; DM2–HTA–SP: 4.203€ y DM2–HTA–OBE: 5.02€ (p<0,001). La tasa de ECV en los enfermos con DM2 fue del 4,7%, y del 1,7% en los que no padecían esta condición (p<0,001).
ConclusionesLa OBE es una comorbilidad asociada a la DM2 que origina un mayor gasto sanitario que la HTA. La presencia de estas comorbilidades ocasiona mayores tasas de ECV.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<