The purpose of this study was to learn about the clinical practice of specialists who care for patients with giant cell arteritis, to verify whether they follow the diagnosis and treatment recommendations for this disease, and to identify areas for improvement.
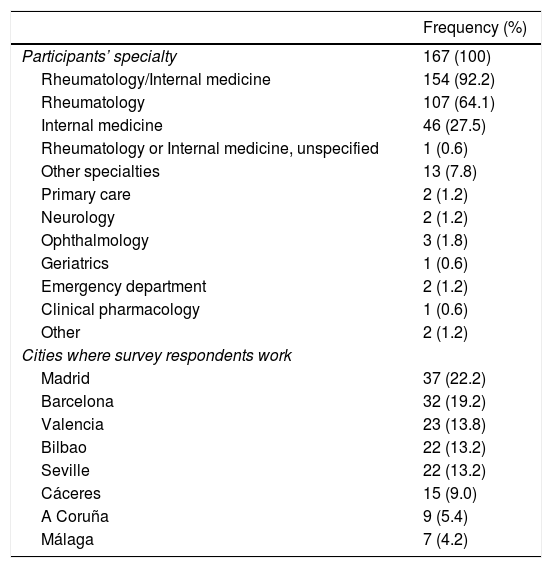
MethodsA cross-sectional survey on clinical practice in 2019. The survey was completed by 167 physicians (64% rheumatologists, 27% internal medicine specialists, and 9% other specialists) who attended a course on updating giant cell arteritis treatment. We compared the clinical practice collected in the study with the latest recommendations approved by the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR).
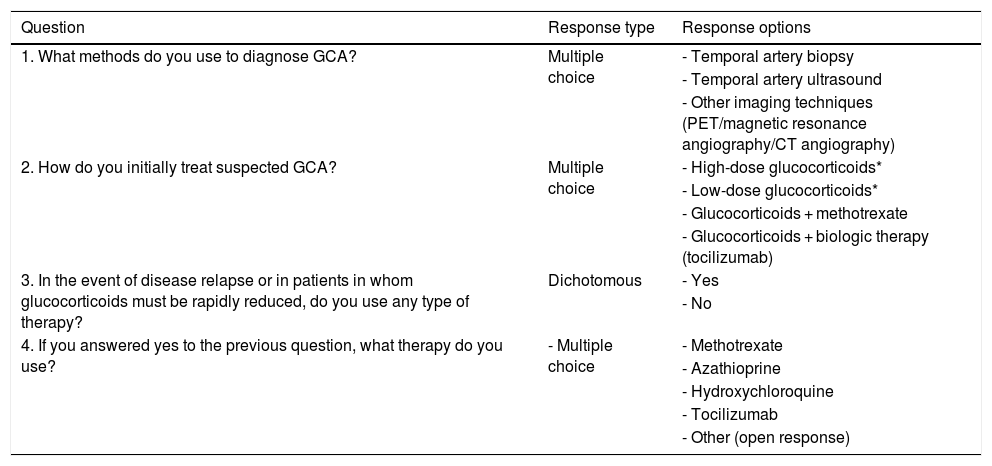
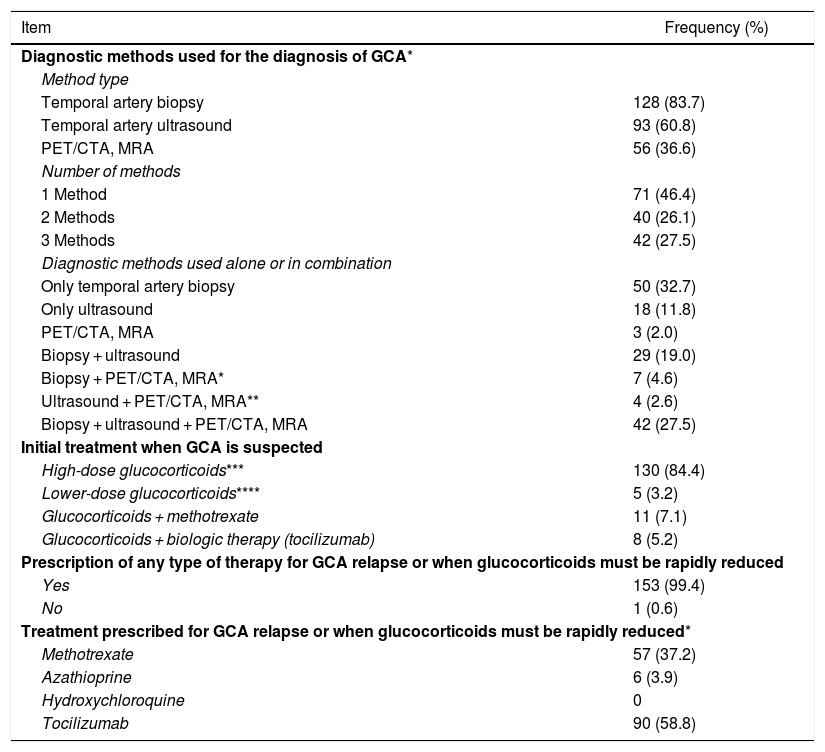
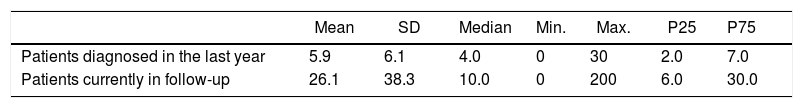
ResultsThe physicians surveyed cared for a median of 10 patients (interquartile range 6–30) with giant cell arteritis during their practice. As a diagnostic method, respondents used temporal artery biopsy (84%), temporal artery ultrasound (61%) or other imaging techniques (37%). As first-line therapy, respondents used high-dose glucocorticoids (at least 40 mg of prednisone, or equivalent, per day) (84%), glucocorticoids with methotrexate (7%) and glucocorticoids with tocilizumab (5%). The most frequent drugs used for relapse were methotrexate (37%) and tocilizumab (58%).
ConclusionOur results indicate that the medical specialists surveyed follow the recent EULAR recommendations for giant cell arteritis diagnosis and therapy.
El propósito de este estudio fue conocer la práctica clínica de especialistas que atienden a pacientes con arteritis de células gigantes, para comprobar si siguen las recomendaciones para el diagnóstico y tratamiento de esta enfermedad e identificar áreas de mejora.
MétodosEncuesta transversal de prácticas clínicas realizada en 2019. Ciento sesenta y siete médicos (64% reumatólogos, 27% especialistas en medicina interna, 9% otros especialistas) que asistieron a un curso de actualización del tratamiento de la arteritis de células gigantes completó la encuesta. Comparamos la práctica clínica recogida en el estudio con las últimas recomendaciones aprobadas por la Liga Europea Contra el Reumatismo (EULAR).
ResultadosLos médicos encuestados atendían a una mediana de 10 pacientes (rango intercuartílico 6–30) con arteritis de células gigantes en su práctica clínica. Como método de diagnóstico, los encuestados utilizaron biopsia de arteria temporal (84%), ecografía de arteria temporal (61%) u otras técnicas de imagen (37%). Como terapia de primera línea, los encuestados utilizaron glucocorticoides en dosis altas (al menos 40 mg de prednisona o equivalente por día) (84%), glucocorticoides con metotrexato (7%) y glucocorticoides con tocilizumab (5%). Los fármacos más utilizados para la recaída fueron el metotrexato (37%) y tocilizumab (58%).
ConclusiónLos resultados de esta encuesta indican que los médicos especialistas encuestados siguen las recomendaciones recientes de EULAR sobre diagnóstico y tratamiento de la arteritis de células gigantes.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<