Myelomatous pleural effusion (MPE) is rare in multiple myeloma, and therefore its characteristics are not well defined.
MethodsA systematic review (4 online databases) was conducted of articles describing the clinical characteristics of patients with MPE, pleural effusion's biochemical characteristics and treatment efficacy. We analyzed isolated cases and small retrospective series.
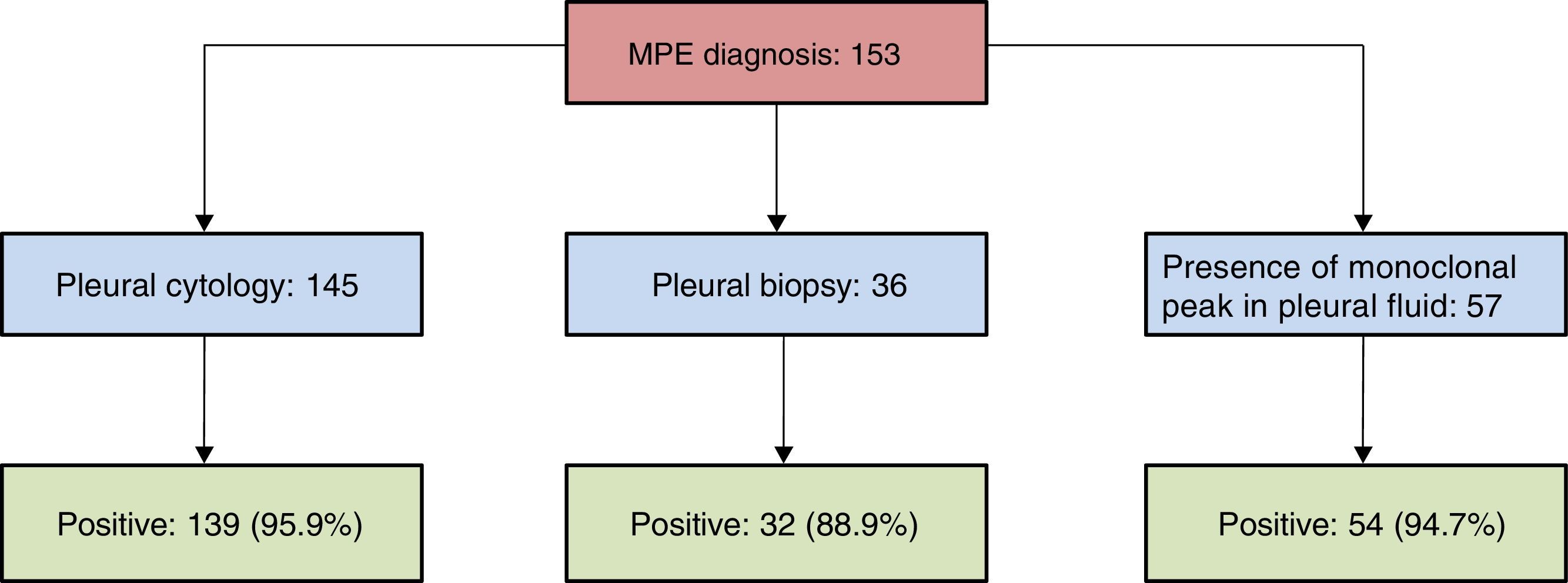
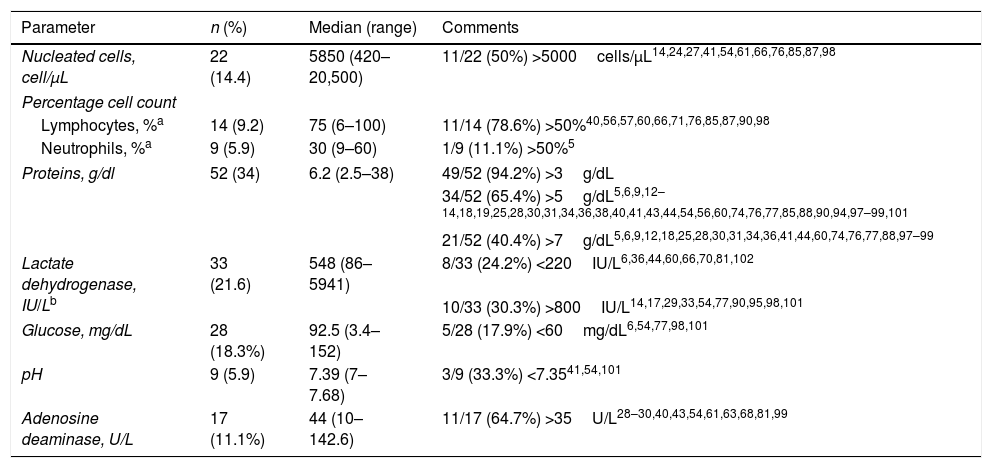
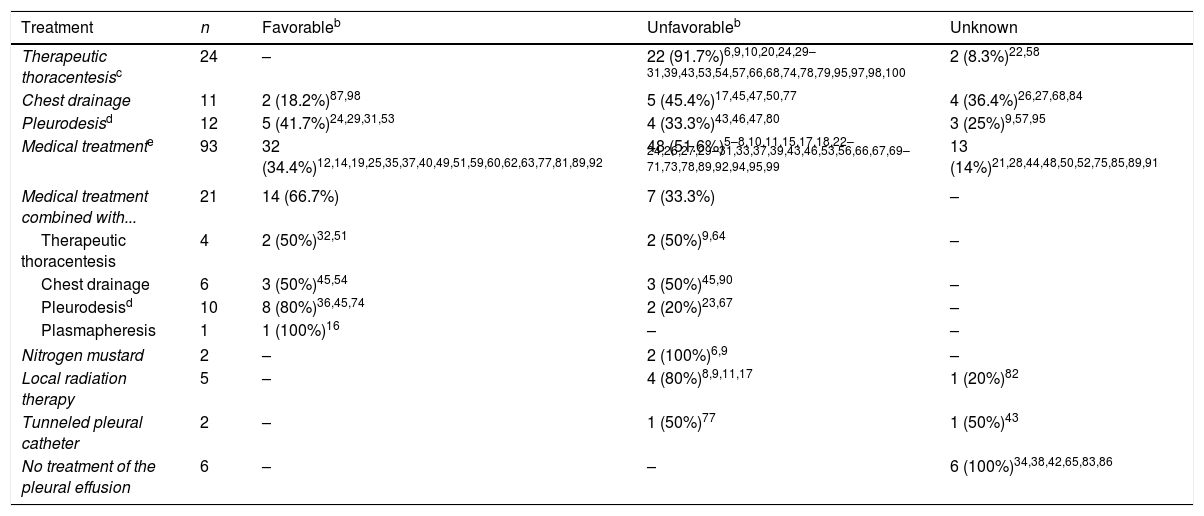
ResultsWe included 98 articles with a total of 153 patients with MPE. The median age was 62 years, and the ratio of males to females was 1.7:1. The most common symptoms were dyspnea (98.8%), bone pain (100%) and chest pain (95.3%), and the most relevant abnormal laboratory test results were anemia (90.1%) and renal failure (53.8%). MPE was predominantly unilateral (63.9%) and covered more than two-thirds of the hemithorax (54.5%). The pleural fluid (PF) had a haematologic/serohaematologic appearance (87%) and met the criteria for lymphocytic (78.6%) exudate (94.7%). The most cost-effective diagnostic procedures were pleural cytology (95.9%) and the observation of a monoclonal peak in the PF (94.7%). In a significant proportion of patients (54.7%), the MPE did not respond to treatment, and the best response was achieved when chemotherapy (with/without corticosteroids) was combined with therapeutic thoracentesis, chest drainage or pleurodesis.
ConclusionsMPE predominates in middle to older age men, is symptomatic and is usually unilateral. PF is an exudate with a hemorrhagic appearance, and the most cost-effective diagnostic procedure is pleural cytology. Treatment response is unfavorable in more than half of patients.
El derrame pleural mielomatoso (DPM) es raro en el mieloma múltiple, por lo que sus características no están bien definidas.
MétodosRevisión sistemática (cuatro bases de datos electrónicas) de los artículos que describen las características clínicas de estos pacientes, las características bioquímicas del derrame pleural y la eficacia de los tratamientos instaurados. Se analizaron casos aislados y pequeñas series retrospectivas.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 98 artículos con un total de 153 pacientes con DPM. La mediana de edad fue de 62 años y la razón hombre/mujer, de 1,7/1. La sintomatología más frecuente consistió en disnea (98,8%), dolor óseo (100%) y dolor torácico (95,3%); las alteraciones analíticas más relevantes fueron la anemia (90,1%) y la insuficiencia renal (53,8%). El DPM fue predominantemente unilateral (63,9%) y mayor de 2/3 del hemitórax (54,5%). El líquido pleural (LP) tuvo aspecto hemático/serohemático (87%) y cumplió criterios de exudado (94,7%) linfocitario (78,6%). Los procedimientos diagnósticos más rentables fueron la citología pleural (95,9%) y la observación en el LP de un pico monoclonal (94,7%). En una proporción significativa de pacientes (54,7%) el DPM no respondió al tratamiento y la mejor respuesta se obtuvo cuando la quimioterapia (con/sin corticoesteroides) se asoció a toracocentesis terapéuticas, drenaje torácico o pleurodesis.
ConclusionesEl DPM predomina en varones de edad media/alta, es sintomático y suele ser unilateral. El LP es un exudado de aspecto hemorrágico y el procedimiento diagnóstico más rentable es la citología pleural. La respuesta al tratamiento no es favorable en más de la mitad de los pacientes.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<