To analyze the importance of cardiovascular risk factors, ultrasound findings in the supra-aortic trunk and the presence of anticoagulated nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF) in patients with retinal vein occlusion (RVO) and in a control group.
Patients and methodsA cross-sectional study was conducted of all patients with RVO consecutively referred to the office of internal medicine, comparing them with a control group. We analyzed clinical, electrocardiographic and ultrasound variables.
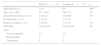
ResultsWe studied 212 patients (114 men and 98 women) with RVO and 212 controls (95 men and 117 women) of similar ages. Arterial hypertension, dyslipidaemia and diabetes mellitus were significantly more prevalent in the patients with RVO than in the controls (73.6 vs. 50%, 64.6 vs. 48.6% and 27.8 vs. 12.3%, respectively). We observed arteriosclerotic lesions in the supra-aortic trunk in 55% of the patients with RVO. The patients with RVO and NVAF had a greater burden of cardiovascular risk factors than the controls with NVAF. There were no differences in terms of the international normalized ratio or in the use of direct anticoagulants between the cases and controls with NVAF.
ConclusionsCardiovascular risk factors (especially arterial hypertension) and arteriosclerotic involvement of the supra-aortic trunk are highly prevalent in RVO. Anticoagulation does not appear to be effective in preventing RVO.
Analizar la importancia de los factores de riesgo vascular, los hallazgos ecográficos de los troncos supraaórticos, y la presencia de fibrilación auricular no valvular (FANV) anticoagulada en pacientes con obstrucción venosa retiniana (OVR) y en un grupo control.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio transversal de todos los pacientes con OVR remitidos consecutivamente a la consulta de Medicina Interna, comparándolos con un grupo control. Se analizaron variables clínicas, electrocardiográficas y ecográficas.
ResultadosSe estudiaron 212 pacientes (114 varones y 98 mujeres) con OVR y 212 controles (95 varones y 117 mujeres) de edad similar. La hipertensión arterial, la dislipidemia y la diabetes mellitus fueron significativamente más prevalentes en los pacientes con OVR que en los controles (73,6 vs. 50%, 64,6 vs. 48,6%, y 27,8 vs. 12,3%, respectivamente). Se observaron lesiones arterioescleróticas en los troncos supraaórticos en el 55% de las OVR. Los pacientes con OVR y FANV tenían una mayor carga de factores de riesgo vascular que los controles con FANV. No hubo diferencias respecto a la razón internacional normalizada o a la utilización de anticoagulantes de acción directa entre casos y controles con FANV.
ConclusionesLos factores de riesgo vascular (en especial la hipertensión arterial) y la afectación arterioesclerótica de los troncos supraaórticos son muy prevalentes en la OVR. La anticoagulación no parece eficaz para prevenir la OVR.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<