The COPD-LUCSS-DLCO score had been validated as a predictive tool capable of identifying patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and a high mortality risk associated with lung cancer (LC); however, studies have not been conducted yet on its use in standard clinical practice. The aim of this study was to estimate the COPD-LUCSS-DLCO scores for patients with COPD treated in Pulmonology consultations and to determine the incidence of LC in each of the subgroups.
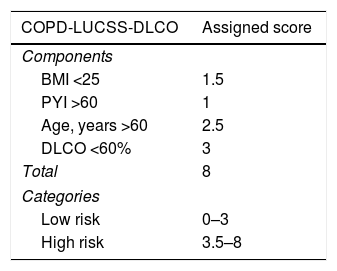
Material and methodsA retrospective observational study was conducted with a cohort of 159 patients with COPD in Pulmonology outpatient follow-up consultations. We calculated the COPD-LUCSS-DLCO score (0–8) for each patient, with low risk considered at 0–3 points and high risk at ≥3.5 points. We calculated the incidence rate of LC in each of the subgroups.
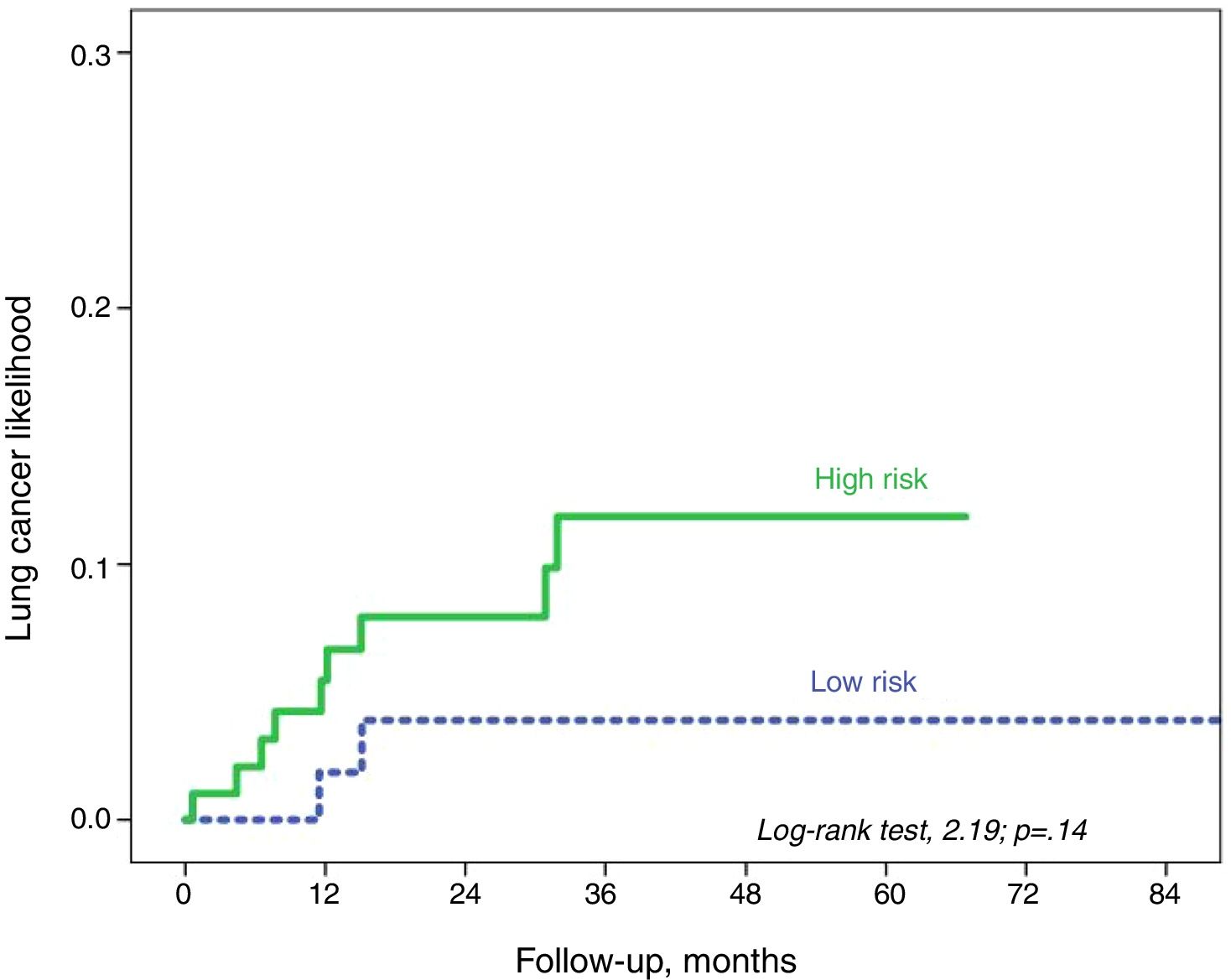
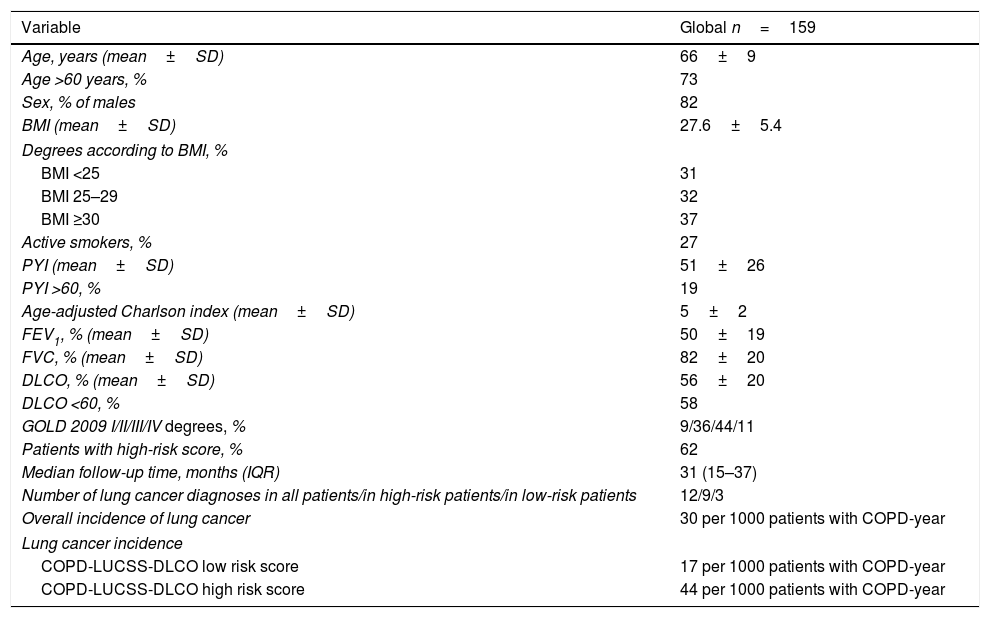
ResultsSixty-two percent of the patients had a high-risk score. We estimated an overall LC rate of 30 per 1000 patients with COPD-year (95% CI: 16–53), 44 per 1000 patients with COPD-year (95% CI: 18–76) among those categorized as high risk and 17 per 1000 patients with COPD-year among those categorized as low risk (95% CI: 4–50).
ConclusionsThe use of the COPD-LUCSS-DLCO score in standard clinical practice could help detect patients with a greater risk of developing LC, which could help to better manage cases in an LC screening program.
El score COPD-LUCSS-DLCO ha sido validado como una herramienta predictiva capaz de identificar pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica (EPOC) y alto riesgo de fallecer por cáncer de pulmón (CP). No obstante, hasta la fecha no se han realizado estudios acerca de su uso en la práctica clínica habitual. El objetivo del estudio fue estimar las puntuaciones del score COPD-LUCSS-DLCO en pacientes con EPOC atendidos en consultas de Neumología, así como determinar la incidencia de CP en cada uno de los subgrupos.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional retrospectivo de una cohorte de 159 pacientes con EPOC en seguimiento en consultas ambulatorias de Neumología. Se calculó la puntuación del score COPD-LUCSS-DLCO (puntuación de 0-8) a cada uno de los sujetos, considerando bajo riesgo (BR) entre 0-3 puntos y alto riesgo (AR) ≥ 3,5 puntos. Se estimó la incidencia del CP en cada uno de los subgrupos.
ResultadosEl 62% presentaban un score de AR. Se estimó una tasa global de CP de 30 por 1.000 pacientes con EPOC-año (IC 95%:16-53), de 44 por 1.000 pacientes con EPOC-año (IC 95%: 18-76) entre los catalogados de AR y de 17 por 1.000 pacientes con EPOC-año (IC 95%: 4-50).
ConclusionesEl uso del score COPD-LUCSS-DLCO en la práctica clínica habitual podría permitir detectar pacientes con un mayor riesgo de desarrollar CP, lo cual ayudaría a una mejor gestión de casos en un programa de screening de CP.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<