This work aims to assess the effect of weekly subcutaneous semaglutide on biomarkers of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), namely the hepatic steatosis index (HSI) and the fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index, at 24 weeks in outpatients attended to in internal medicine departments.
MethodsThis study analyzed patients in an ongoing, multicenter, prospective, pre-post, uncontrolled cohort registry that enrolls unique, consecutive patients with type 2 diabetes treated with weekly subcutaneous semaglutide. Steatosis/fibrosis were determined by HSI (<30 ruled out, >36 steatosis) and FIB-4 (<1.3 ruled out, >2.67 fibrosis), respectively.
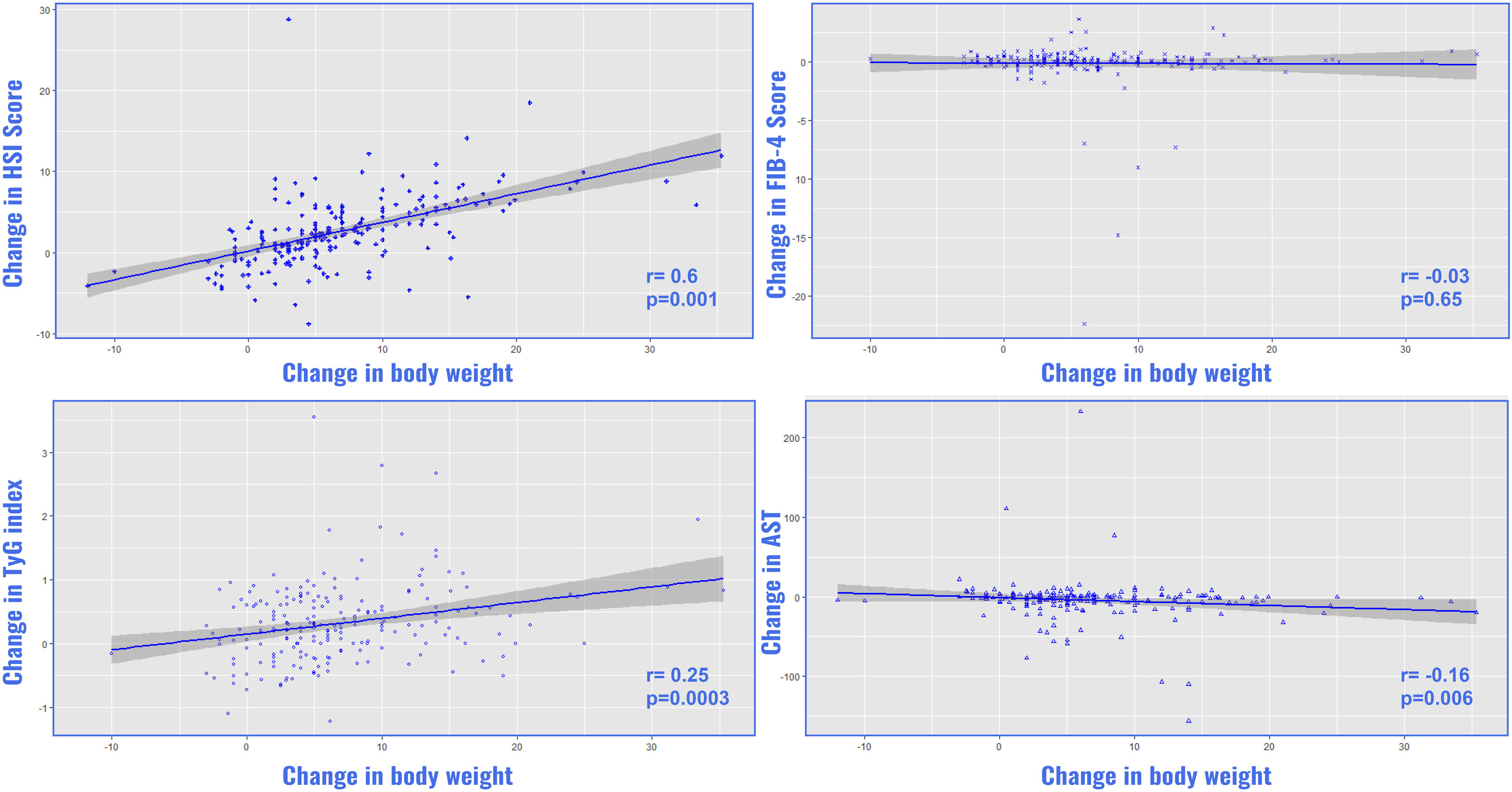
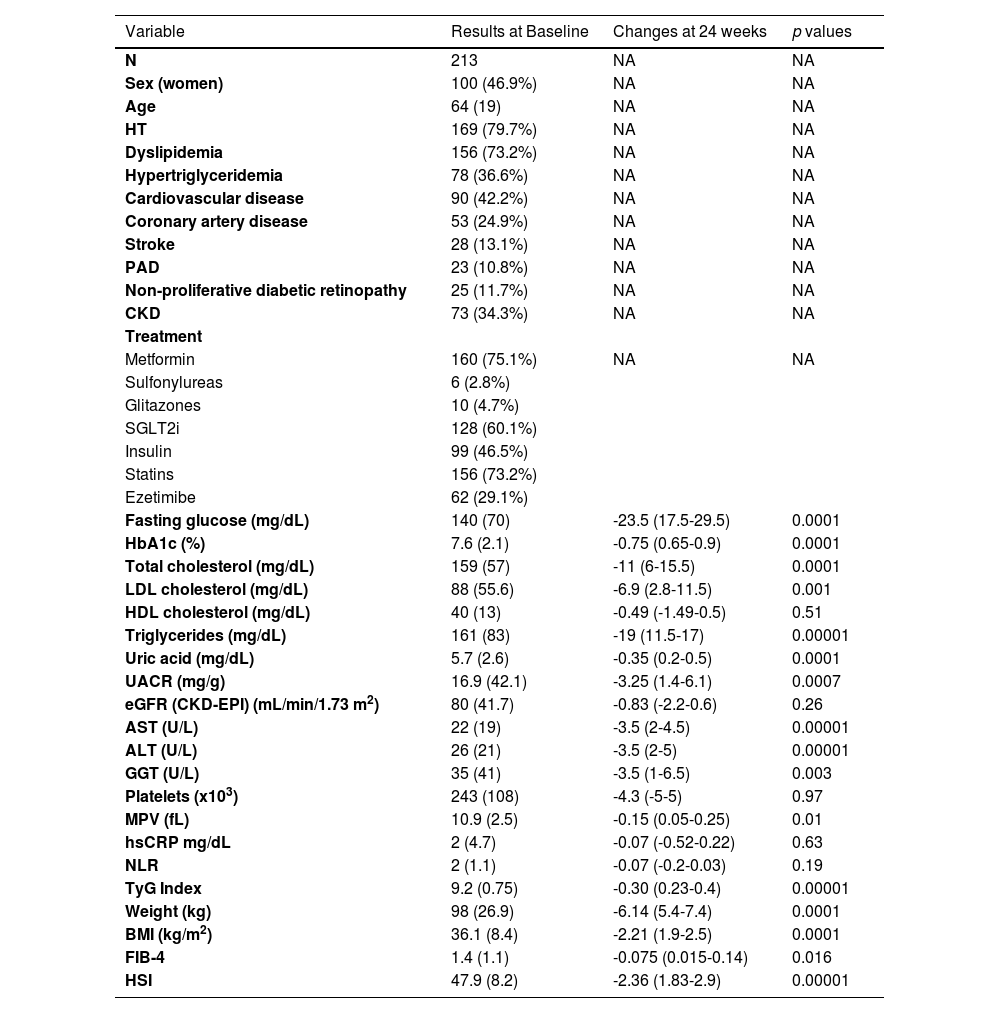
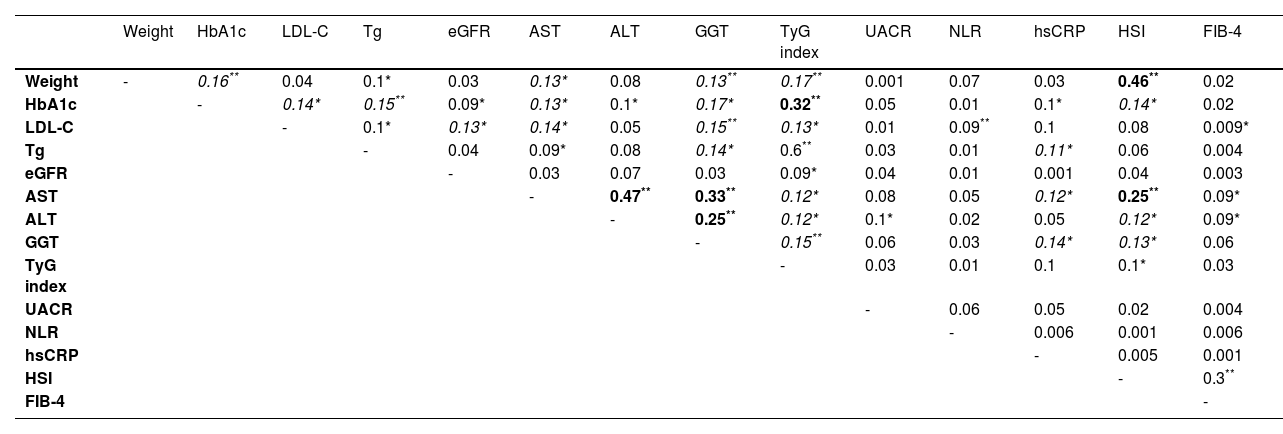
ResultsThe sample included 213 patients (46.9% women) with a median age of 64 (19) years. The median baseline body mass index and weight were 36.1 (8.4) kg/m2 and 98 (26.9) kg, respectively. A total of 99.9% had HSI values indicating steatosis, with a mean HSI of 47.9 (8.2). Additionally, 10.8% had fibrosis (FIB-4 > 2.67) and 42.72% had values in intermediate ranges (FIB-4 1.3-2.67). At 24 weeks, there was a significant reduction in HSI (-2.36 (95%CI 1.83-2.9) p < 0.00001) and FIB-4 (-0.075 (95%CI 0.015-0.14) p < 0.016), mainly related to declines in body weight, triglyceride levels, insulin resistance (estimated by the triglyceride-glucose index), and liver enzymes.
ConclusionThese results show that weekly subcutaneous semaglutide had a beneficial effect on liver steatosis that went beyond glucose control. Its effects were mainly related to weight loss, a decline in biomarkers, and improvements in insulin sensitivity. For many patients, early detection is essential for improving MAFLD outcomes and may allow for selecting the most efficient treatment options.
El objetivo de este trabajo es evaluar el efecto de semaglutida subcutánea sobre los biomarcadores de la enfermedad metabólica hepática (MAFLD, por sus siglas en inglés), a saber, el índice de esteatosis hepática (HSI) y el índice de fibrosis-4 (FIB-4), a las 24 semanas en pacientes ambulatorios atendidos en los servicios de Medicina Interna.
MétodosEn este estudio se analizaron pacientes de un registro de cohortes en curso, multicéntrico, prospectivo, pre-pos y no controlado que inscribe a pacientes únicos y consecutivos con diabetes tipo 2 tratados con semaglutida subcutánea. La esteatosis/fibrosis se determinó mediante HSI (<30 descartada, >36 esteatosis) y FIB-4 (<1,3 descartada, >2,67 fibrosis), respectivamente.
ResultadosLa muestra incluyó 213 pacientes (46,9% mujeres) con una mediana de edad de 64 (19) años. El índice de masa corporal y el peso basales medios fueron de 36,1 (8,4) kg/m2 y 98 (26,9) kg, respectivamente. El 99,9% presentaba valores de HSI indicativos de esteatosis, con un HSI medio de 47,9 (8,2). Además, el 10,8% presentaba fibrosis (FIB-4 > 2,67) y el 42,72% tenía valores en rangos intermedios (FIB-4 1,3-2,67). A las 24 semanas, se produjo una reducción significativa del HSI (-2,36 [IC 95%: 1,83-2,9] p < 0,00001) y del FIB-4 (-0,075 [IC 95%: 0,015-0,14] p < 0,016), relacionada principalmente con descensos del peso corporal, los niveles de triglicéridos, la resistencia a la insulina (estimada mediante el índice triglicéridos-glucosa) y las enzimas hepáticas.
ConclusionesEstos resultados muestran que la semaglutida subcutánea tuvo un efecto beneficioso sobre la esteatosis hepática que fue más allá del control de la glucosa. Sus efectos estaban relacionados principalmente con la pérdida de peso, la disminución de los biomarcadores y la mejora de la sensibilidad a la insulina. Para muchos pacientes, la detección precoz es esencial para mejorar los resultados de la MAFLD y puede permitir seleccionar las opciones terapéuticas más eficaces.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<