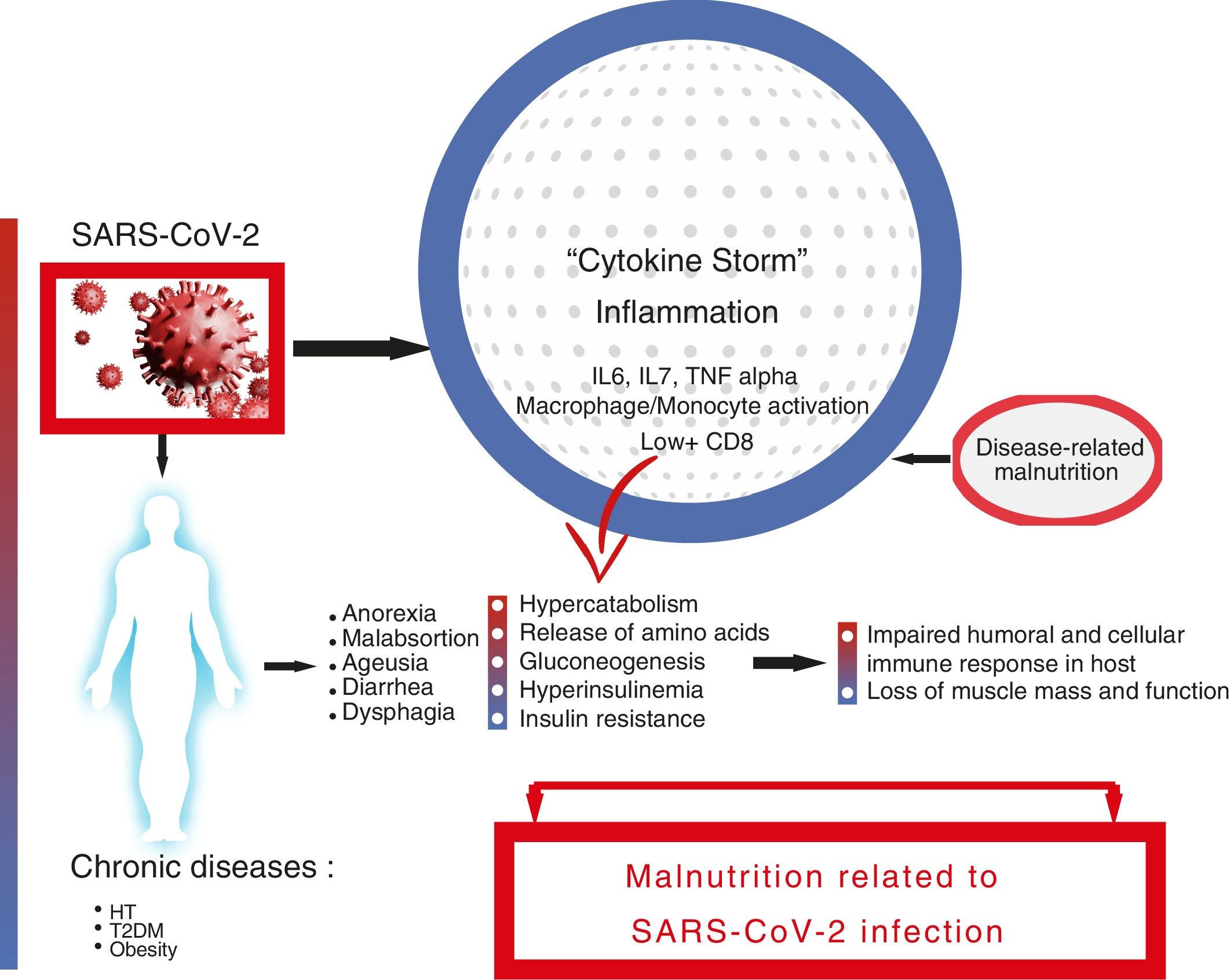
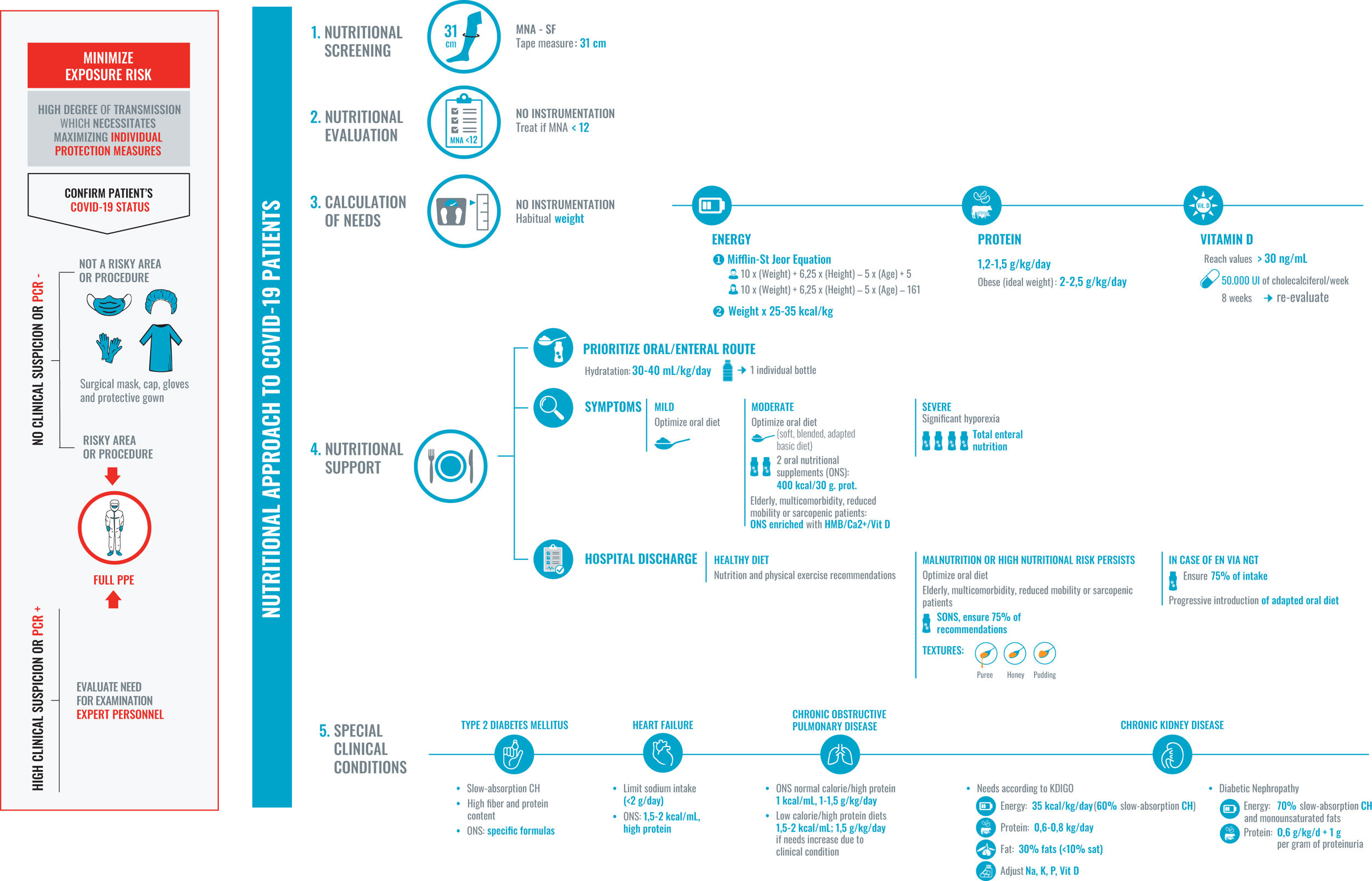
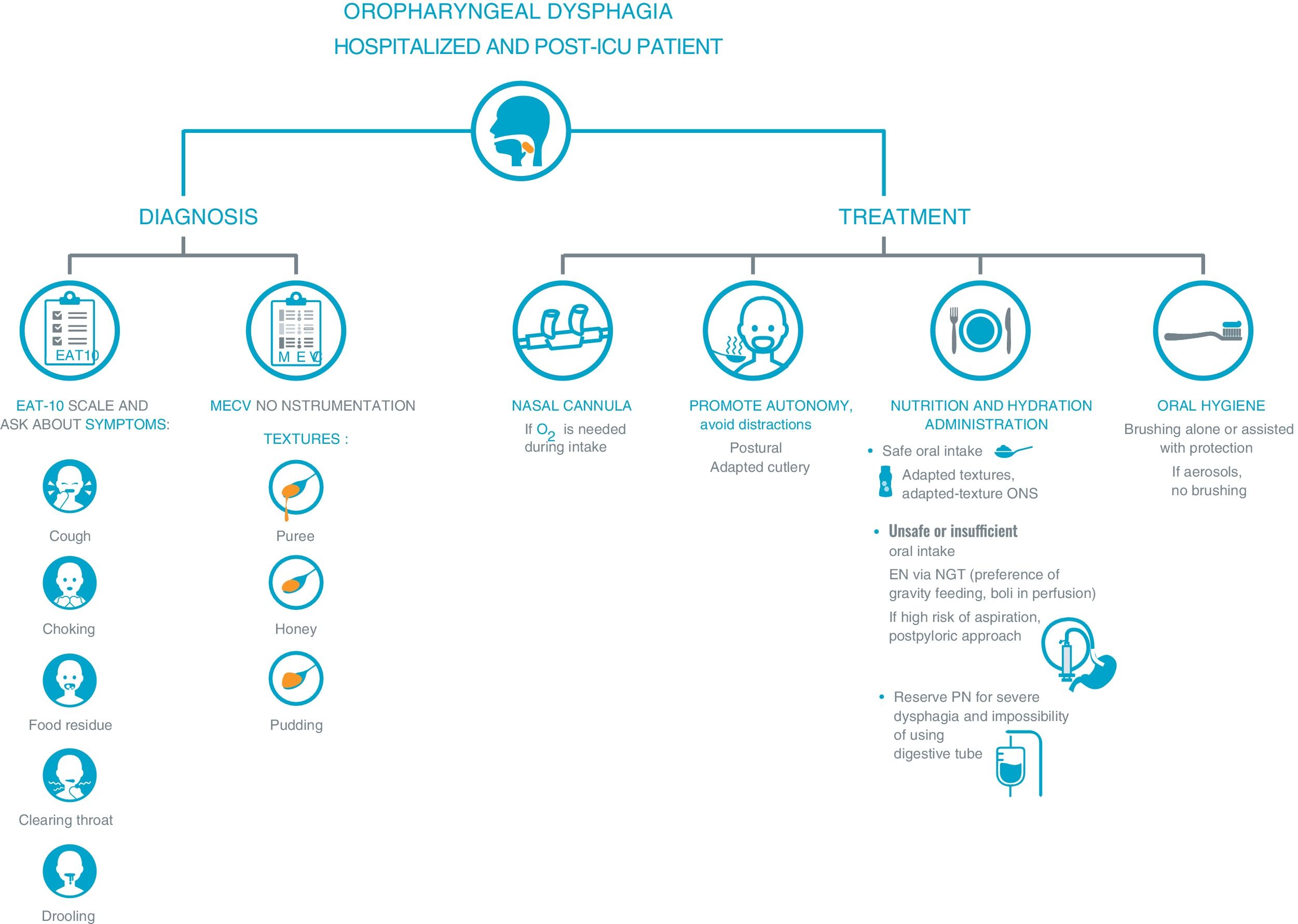
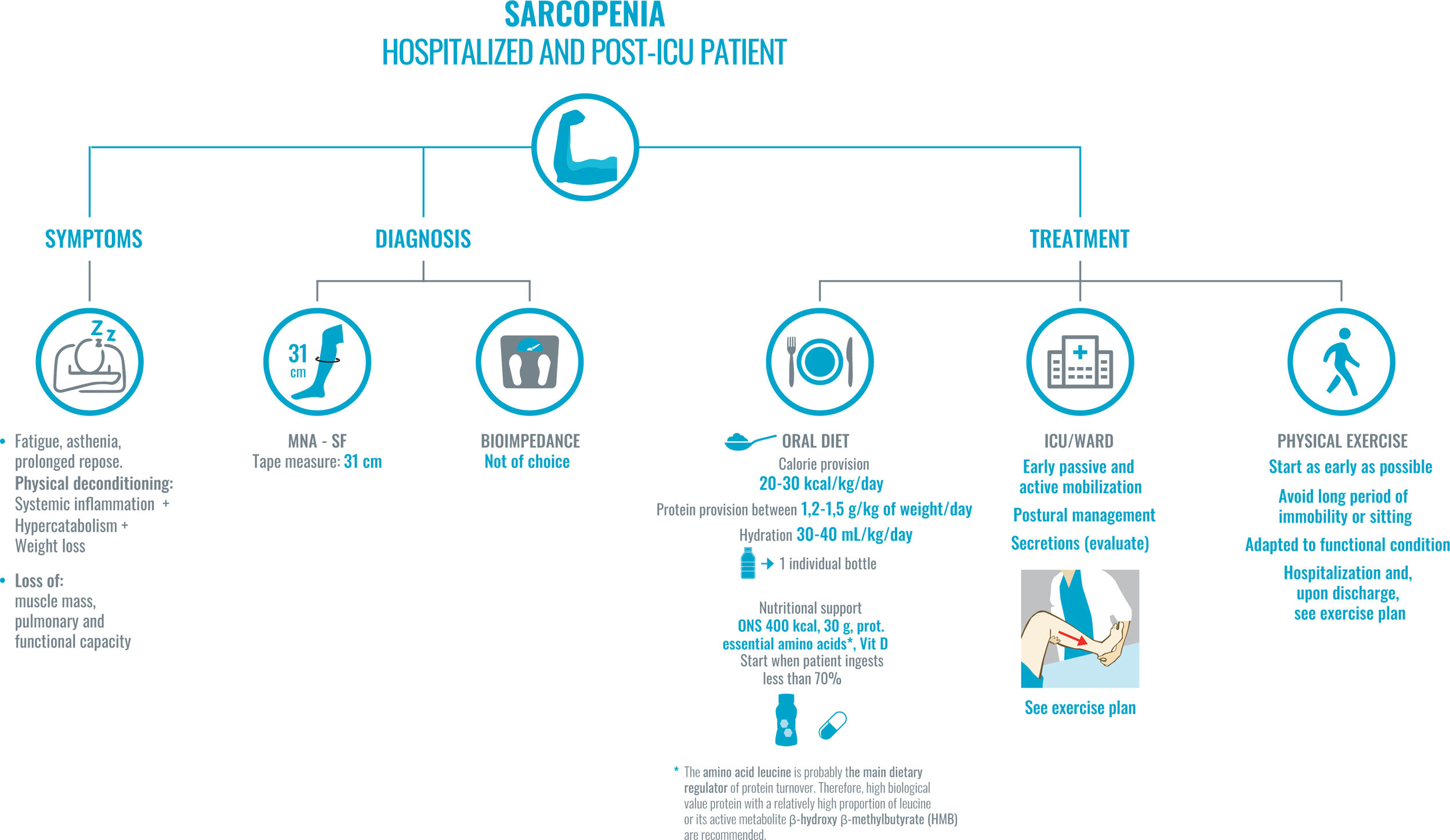
SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with a high risk of malnutrition, mainly due to increased nutritional requirements and the presence of a severe and universal inflammatory state. Associated symptoms contribute to hyporexia, which perpetuates the negative nutritional balance. Furthermore, dysphagia, especially post-intubation, worsens, and makes intake unsafe. This risk is greater in elderly and multimorbid patients. Inflammation to varying degrees is the common link between COVID-19 and the onset of malnutrition, and it is more correct to refer to disease-related malnutrition (DRM). DRM worsens the poor prognosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection, especially in the most severe cases. Therefore, it is necessary to identify and treat people at risk early, avoiding overexposure and direct contact with the patient. We cannot forget the role that a healthy diet plays in both prevention and recovery after discharge.
La infección por SARS-CoV-2 se relaciona con un riesgo alto de malnutrición, principalmente por el aumento de los requerimientos nutricionales y la presencia de un estado inflamatorio severo y universal. Los síntomas asociados contribuyen a la hiporexia, que perpetua el balance nutricional negativo. Además, la disfagia, especialmente posintubación, empeora y hace poco segura la ingesta. Este riesgo es mayor en pacientes ancianos y multimórbidos. La inflamación en distinto grado es el nexo común entre la COVID-19 y la aparición de desnutrición, siendo más correcto hablar de desnutrición relacionada con la enfermedad (DRE). La DRE empeora el mal pronóstico de la infección por SARS-CoV-2, sobre todo, en los casos más severos. Por ello es necesario identificar y tratar precozmente a las personas en riesgo evitando la sobreexposición y el contacto directo con el paciente. No podemos olvidarnos del papel que juega la dieta saludable tanto en la prevención como en la recuperación tras el alta.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<