Analizar los indicadores de actividad asistencial de una unidad de corta estancia (UCE) y comparar estos indicadores con los de otros servicios de hospitalización convencional.
Material y métodosEstudio descriptivo retrospectivo de los pacientes ingresados en la UCE durante el período 2003–2007. Se analizó el número de ingresos, la estancia media, la mortalidad y el destino. Se comparó la estancia media y el número de ingresos de los principales grupos relacionados con el diagnóstico (GRD) de la UCE en relación con otros servicios de hospitalización convencional.
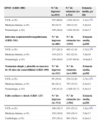
ResultadosUn 15,3% de los enfermos que acudieron a la urgencia fue ingresado en la UCE. La estancia media fue significativamente menor en la UCE que en el resto del hospital (año 2003: UCE 3,2 días, resto del hospital 10,2 días; año 2007: UCE 3,3 días, resto del hospital 8,6 días). Los cuatro GRD más comunes (el 71,3% de todos los ingresos en la UCE) fueron enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica, infección respiratoria/bronquitis/asma, neumonía simple y pleuritis en mayores de 18 años sin comorbilidad y fallo cardíaco y shock. Para los cuatro GRD, la estancia media en la UCE fue significativamente menor (p<0,01) que en Medicina Interna, Neumología y Cardiología («fallo cardíaco y shock»).
ConclusionesLa UCE maneja con mayor agilidad sus patologías más prevalentes en relación con otros servicios de hospitalización convencionales.
To analyze the health care activity indicators of a short-stay unit (SSU) and compare them with those of other services in a Conventional Hospital.
Material and methodsA descriptive, retrospective study was conducted of the patients admitted to SSU during 2003–2007. Number of admissions, mean stay (MS), mortality and destination were analyzed. Mean stay and number of admissions of the main diagnosis-related groups (DRGs) in the SSU were compared with other services of conventional hospitalization.
ResultsA total of 15.3% of the patients who came to the Emergency Service were admitted to the SSU. Mean stay was significantly lower in the SSU than in the rest of the hospital (year 2003, SSU 3.2 days, rest of the hospital 10.2 days; year 2007, SSU 3.3 days, rest of the hospital 8.6 days). The 4 most common DRGs (71.3% of all those admitted to the SSU) were COPD, respiratory infection/bronchitis, simple pneumonia/pleuritis and heart failure/shock. Mean stay for the 4 DRGs in the SSU was significantly lower (p<0.01) than in Internal Medicine, Pneumology and Cardiology (heart failure/shock).
ConclusionsThe SSU handles its most prevalent diseases with greater agility compared to other conventional hospitalization services.
Artículo
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<