La prevalencia de disfunción (DT) y autoinmunidad (AT) tiroideas en la población laboral hospitalaria en nuestro país no se conoce.
ObjetivoEstudiar la prevalencia de DT y AT en una población laboral hospitalaria.
Individuos estudiados y métodosEstudiamos la función (tirotropina [TSH], tiroxina [T4] libre y triiodotironina [T3] libre) y autoinmunidad (anti-tiroglobulina, [antiTg] y anti-peroxidasa tiroidea, [antiTPO]) tiroideas en 310 individuos adultos trabajadores del Hospital General de Segovia durante 2007.
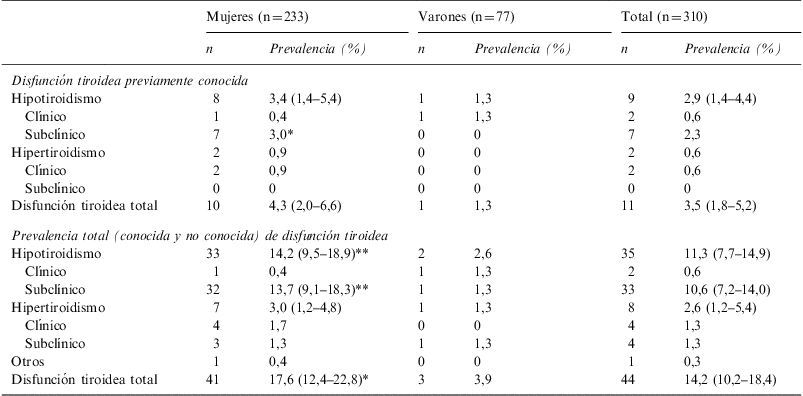
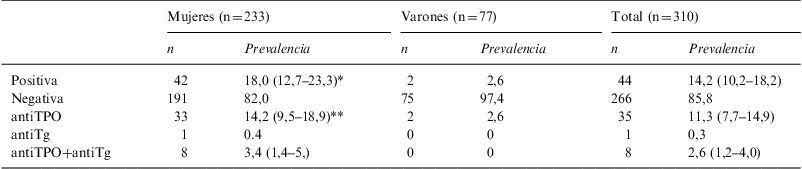
ResultadosOnce sujetos (3,5%, 10 mujeres) presentaban DT conocida. Treinta y tres (11%) fueron diagnosticados de DT no conocida, fundamentalmente hipotiroidismo subclínico (8,4%). La DT total fue del 14,2%. La AT fue positiva en 44 (14,2%) individuos. Tanto la DT (p<0,05) como la AT (p<0,05) se asociaron al sexo femenino y los niveles de antiTPO lo hicieron con la presencia de DT no conocida (OR 1,007; IC 95%, 1,004–1,010; p<001).
ConclusiónEn esta población, la prevalencia total de DT y AT es similar (14%). Los títulos elevados de anti-TPO predicen la DT no conocida.
The prevalence of thyroid dysfunction (TD) and thyroid autoimmunity (TA) in hospital employees in our country is unknown.
ObjectiveTo study the prevalence of TD and TA in a group of hospital employees.
Study subjects and methodsWe studied thyroid function (thyrotropin, TSH, free thyroxine, T4, and free triiodothyronine, T3) and thyroid autoimmunity (anti-thyroglobulin, antiTg and anti-thyroid peroxidase, antiTPO) in 310 adult subjects (18–70 years) from the hospital General, Segovia, Spain during 2007.
ResultsEleven subjects (3.5%, 10 women) had previously known TD. Thirty-four subjects (11.0%) were diagnosed of unknown TD, mainly subclinical hypothyroidism (8.4%). Prevalence of total TD was 14.2%. TA was positive in 44 (14.2%) subjects. Both TD (P<0.05) and TA (P<0.05) were associated with female sex, and antiTPO levels were related to the presence of unknown TD (OR 1.007; 95% CI, 1.004–1.010; P<0.001).
ConclusionIn this population, total prevalence of TD and TA is similar (14%). Increased antiTPO titers are predictors of unknown TD.
Artículo
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<