The aim of this study is to assess the safety in a real-world cohort of patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
MethodsObservational, retrospective and single-center study with patients on vericiguat treatment from the Cardiology and Internal Medicine outpatient clinic of the Valencia General University Hospital Consortium during 2023 year and with minimum follow-up of 6 months. Patients with HFpEF diagnosis and optimized treatment according to the ESC 2021 clinical practice guidelines were included, to whom treatment with vericiguat was started.
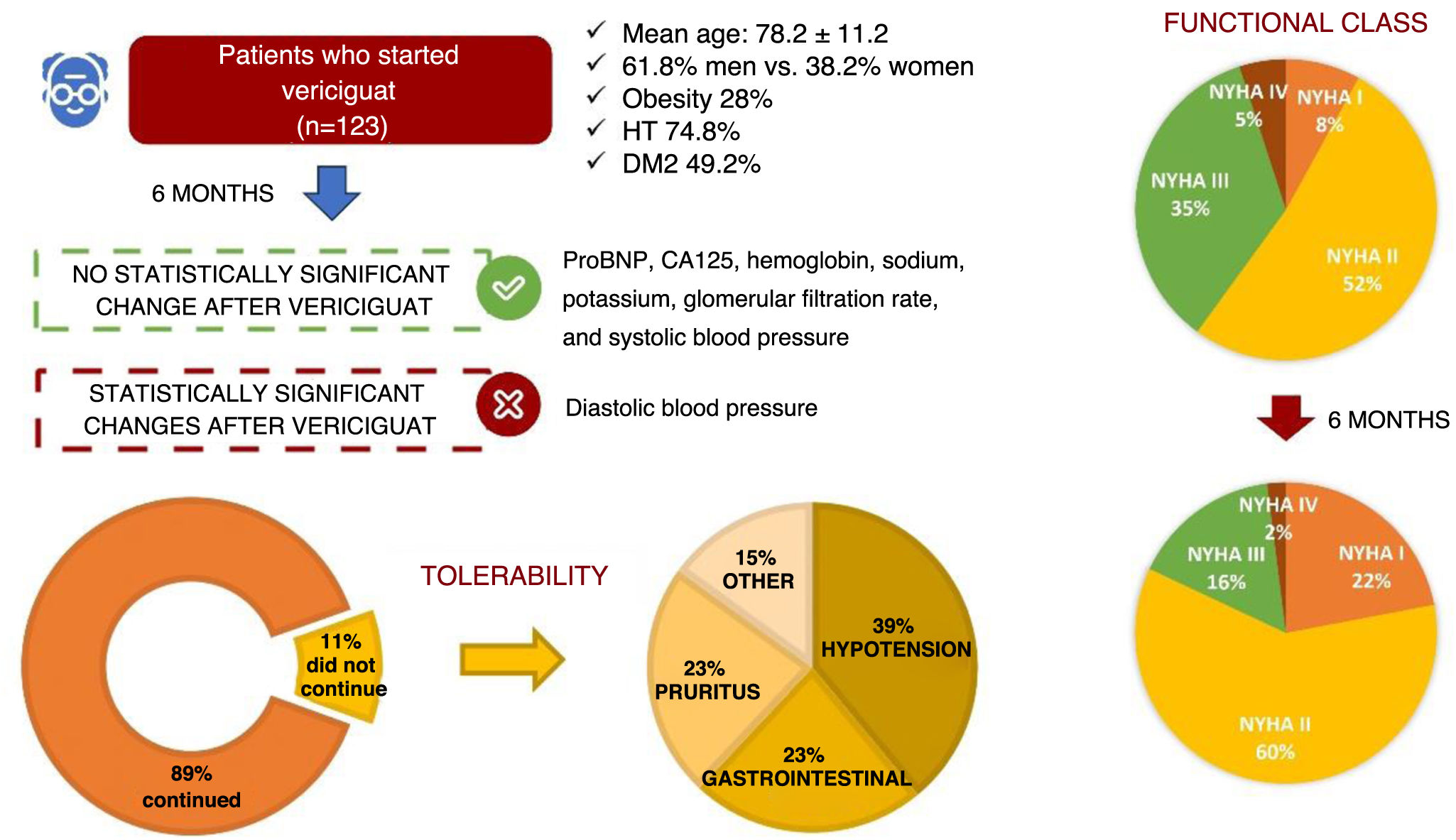
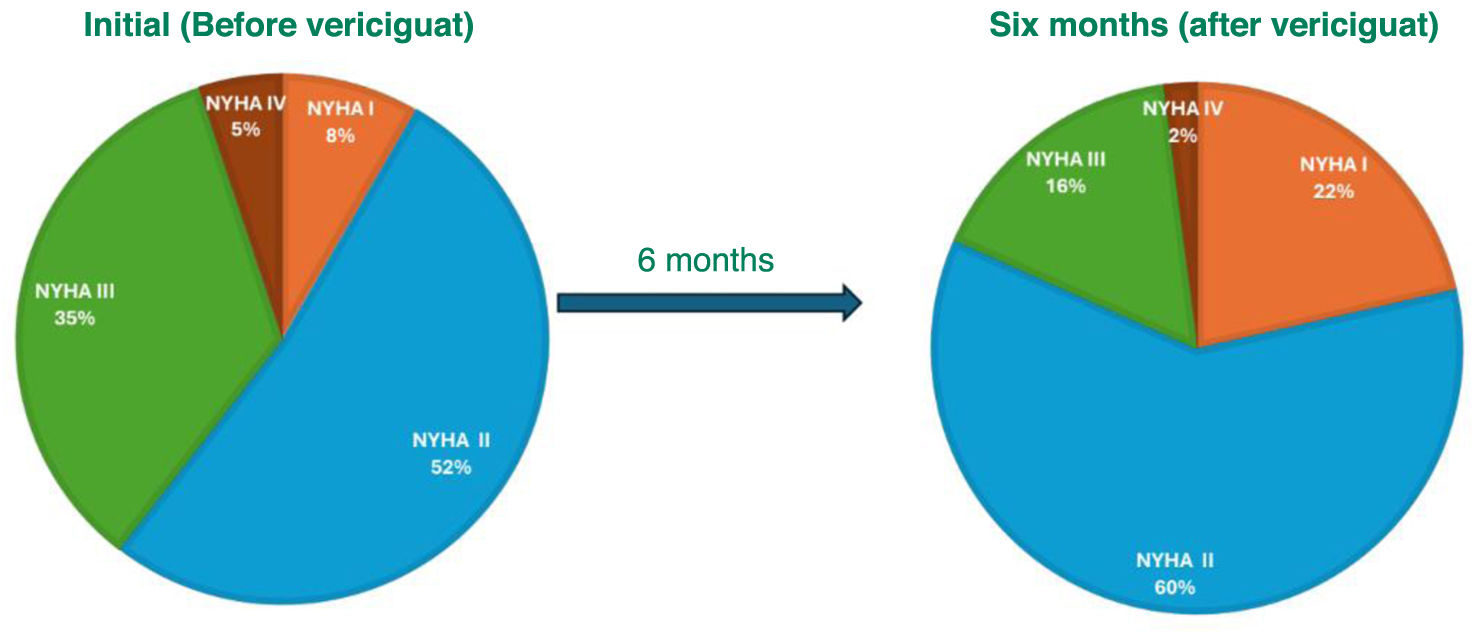
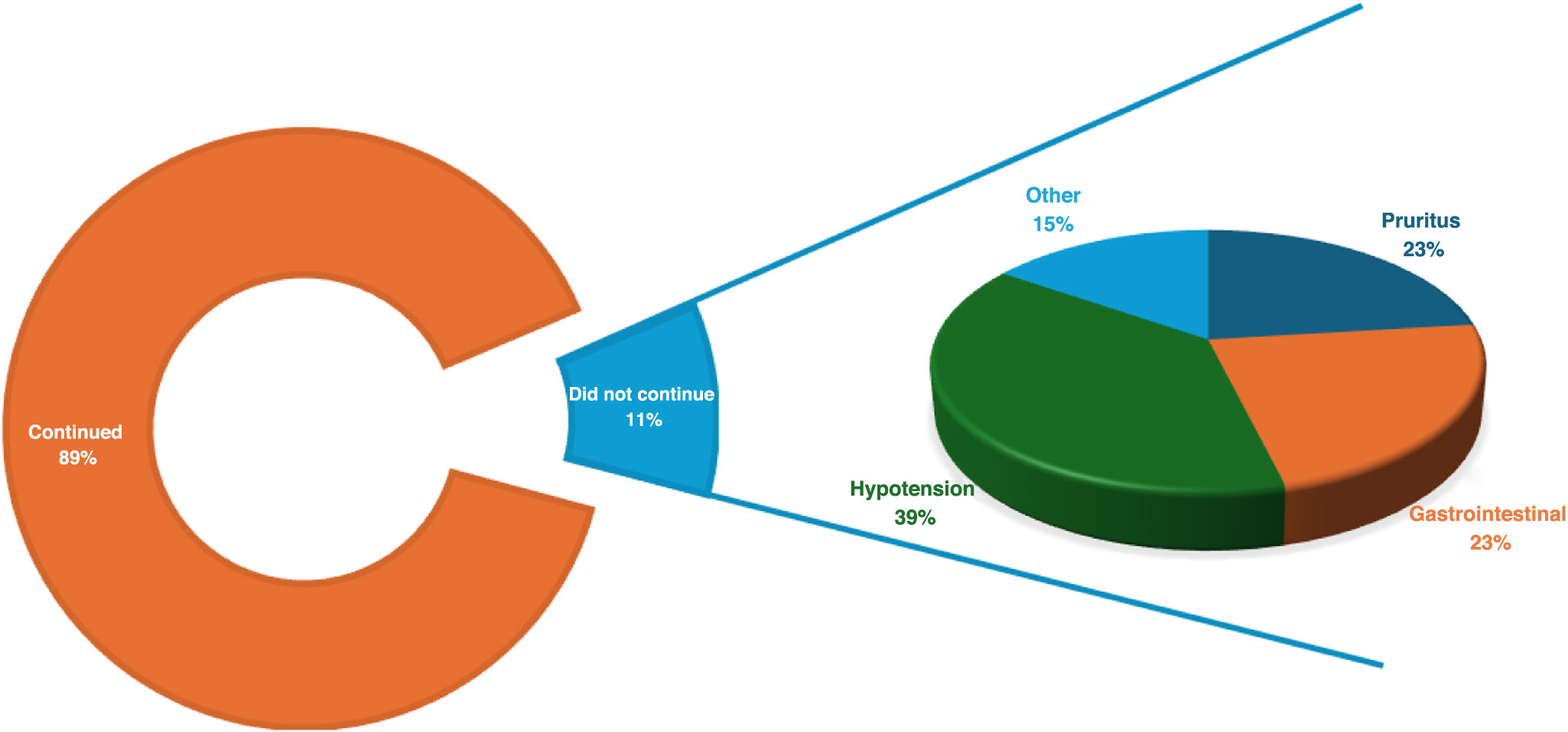
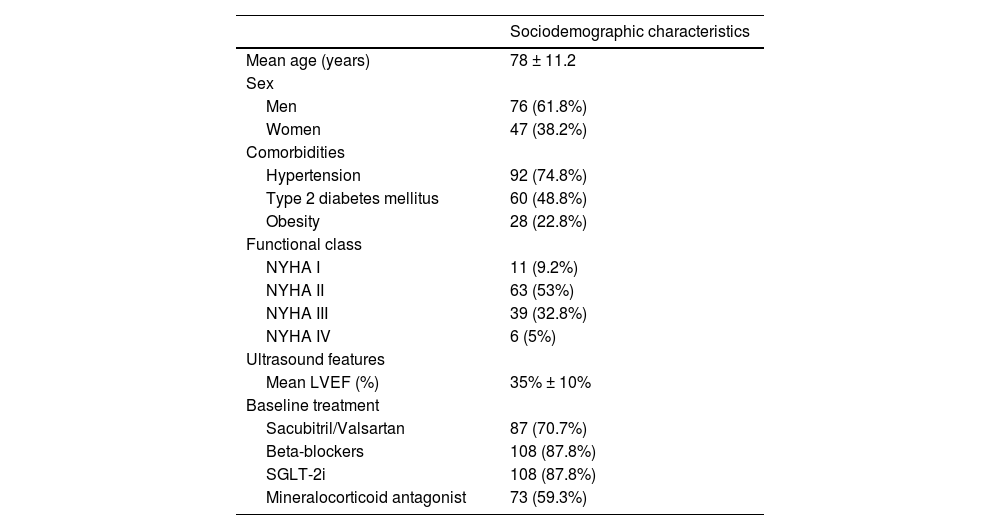
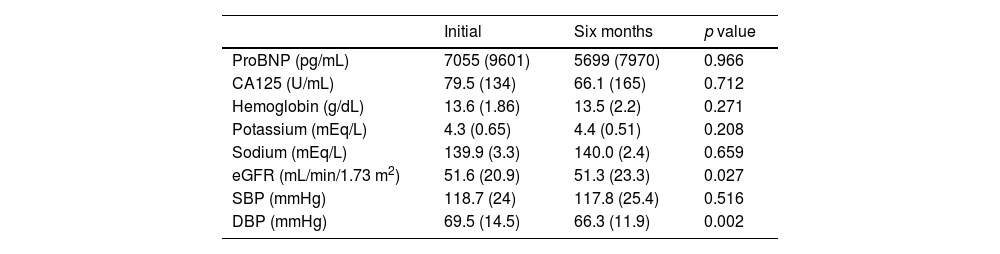
ResultsWe included 123 patients with a mean age of 78 years, mostly men (62%) and with NYHA II functional status (52%). 98 patients completed follow-up after a median follow-up of 162 days (IQR 13–343). The average dose of vericiguat used was 8,3 ± 2,7 mg and 75 patients achieved the target dose of 10 mg (71%). At the end of follow-up, no significant changes were observed in the values of proBNP (pg/mL), CA125, hemoglobin (mg/dl), electrolytes, glomerular filtration rate (mL/min/m2) and systolic blood pressure (mmHg). Of all the patients who completed follow-up, 11 (11%) discontinued treatment due to adverse effects, mostly symptomatic hypotension, digestive symptoms and pruritus; 25 died (20%).
ConclusionsThe use of vericiguat is safe, if used according to the technical data sheet, in terms of the established parameters. Further long-term studies are needed to evaluate the impact of vericiguat as a potential disease-modifying treatment.
El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar en condiciones de vida real la seguridad de vericiguat en pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca y fracción de eyección reducida (IC-FEVIr).
MétodosEstudio observacional, retrospectivo y unicéntrico con pacientes de los servicios de Cardiología y Medicina Interna del Consorcio Hospital General Universitario de Valencia que iniciaron tratamiento con vericiguat durante el año 2023 con seguimiento mínimo de 6 meses. Se incluyeron pacientes con diagnóstico de IC-FEVIr y tratamiento optimizado según guías de práctica clínica de la ESC 2021, tras haber iniciado vericiguat según ficha técnica.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 123 pacientes con edad media de 78 años, predominantemente varones (62%) y en situación funcional NYHA II (52%). 98 pacientes finalizaron el seguimiento tras una mediana de seguimiento de 162 días (RI 13–343). La dosis media utilizada de vericiguat fue de 8,3 ± 2,7 mg y en 75 pacientes (71%) se consiguió la dosis objetivo de 10 mg. Al finalizar el seguimiento, no se observaron cambios significativos en los valores de proBNP (pg/mL), CA125, hemoglobina (mg/dl), electrolitos, filtrado glomerular (mL/min/m2) y presión arterial sistólica (mmHg). De los pacientes que finalizaron el seguimiento, 11 (11%) descontinuaron el tratamiento por efectos adversos, mayoritariamente hipotensión sintomática, síntomas digestivos y prurito; 25 (20%) fallecieron.
ConclusionesEl uso de vericiguat es seguro, si es empleado según ficha técnica, en cuánto a los parámetros establecidos. Son necesarios más estudios a largo plazo para evaluar el impacto del vericiguat como potencial tratamiento modificador de la enfermedad.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<