Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis can be a medical emergency in which a delay in correct diagnosis and therapeutic management can cause serious complications.
With the aim of improving the care of patients with these pathologies in the Community of Madrid, a study was designed to identify the causes and possible solutions to address the problems related to the diagnosis of these pathologies.
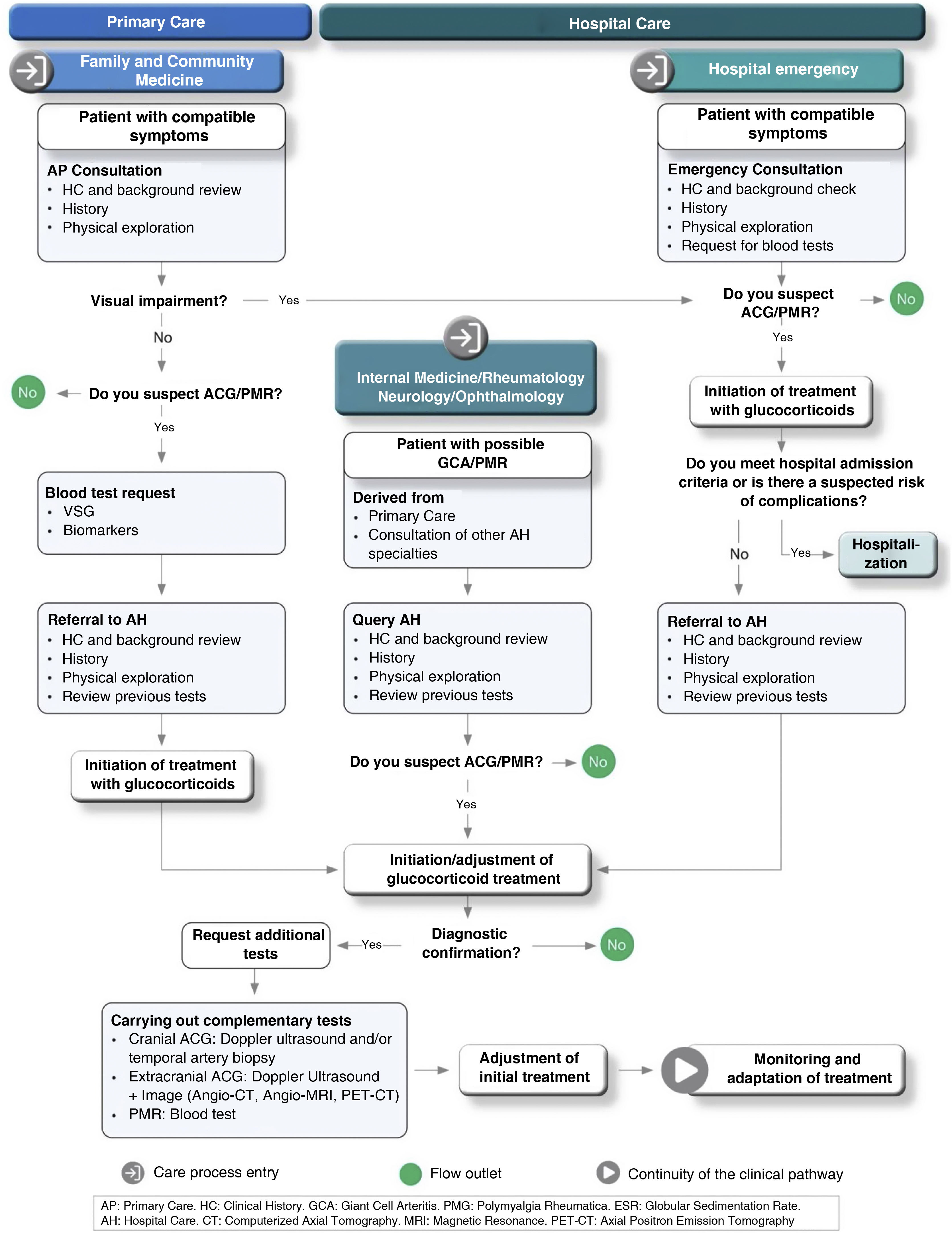
After the analysis, 11 areas of improvement related to four different aspects of the care process were identified: coordination and protocols, equipment, training and awareness of pathologies, and patient experience. Of all the areas identified, it was considered a priority to resolve those related to the generation of protocols for the comprehensive management of the pathologies, which include all the specialties and levels of care involved. Another crucial aspect is the increase in the degree of clinical suspicion of these pathologies.
La Polimialgia reumática y la arteritis de células gigantes pueden suponer una emergencia médica en la que el retraso en su correcto diagnóstico y manejo terapéutico pueden asociar complicaciones graves.
Con el objetivo de mejorar la atención de los pacientes con estas patologías en el entorno de la Comunidad de Madrid, se diseñó un estudio para identificar las causas y posibles soluciones para hacer frente los problemas relacionados con el diagnóstico de estas patologías.
Tras un análisis preliminar, se identificaron 11 áreas de mejora relacionadas con cuatro aspectos diferenciados del proceso asistencial: coordinación y protocolos, equipamientos, formación y concienciación sobre las patologías y experiencia del paciente. De todas ellas, se priorizó resolver aquellas relacionadas con la generación de protocolos de abordaje integral de las patologías, que contemplen a todas las especialidades y niveles asistenciales implicados. Otro aspecto crucial es el incremento del grado de sospecha clínica de estas patologías.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<