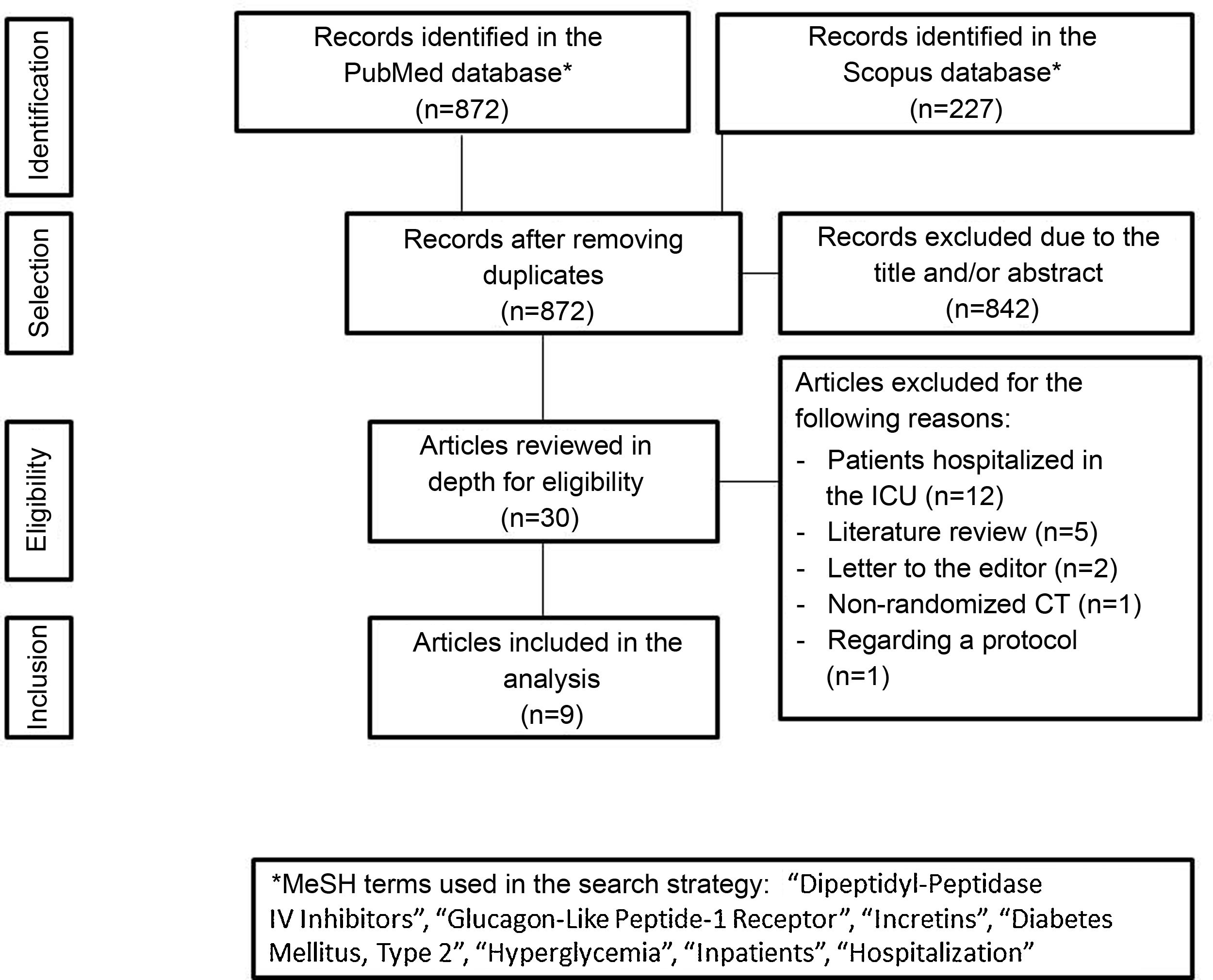
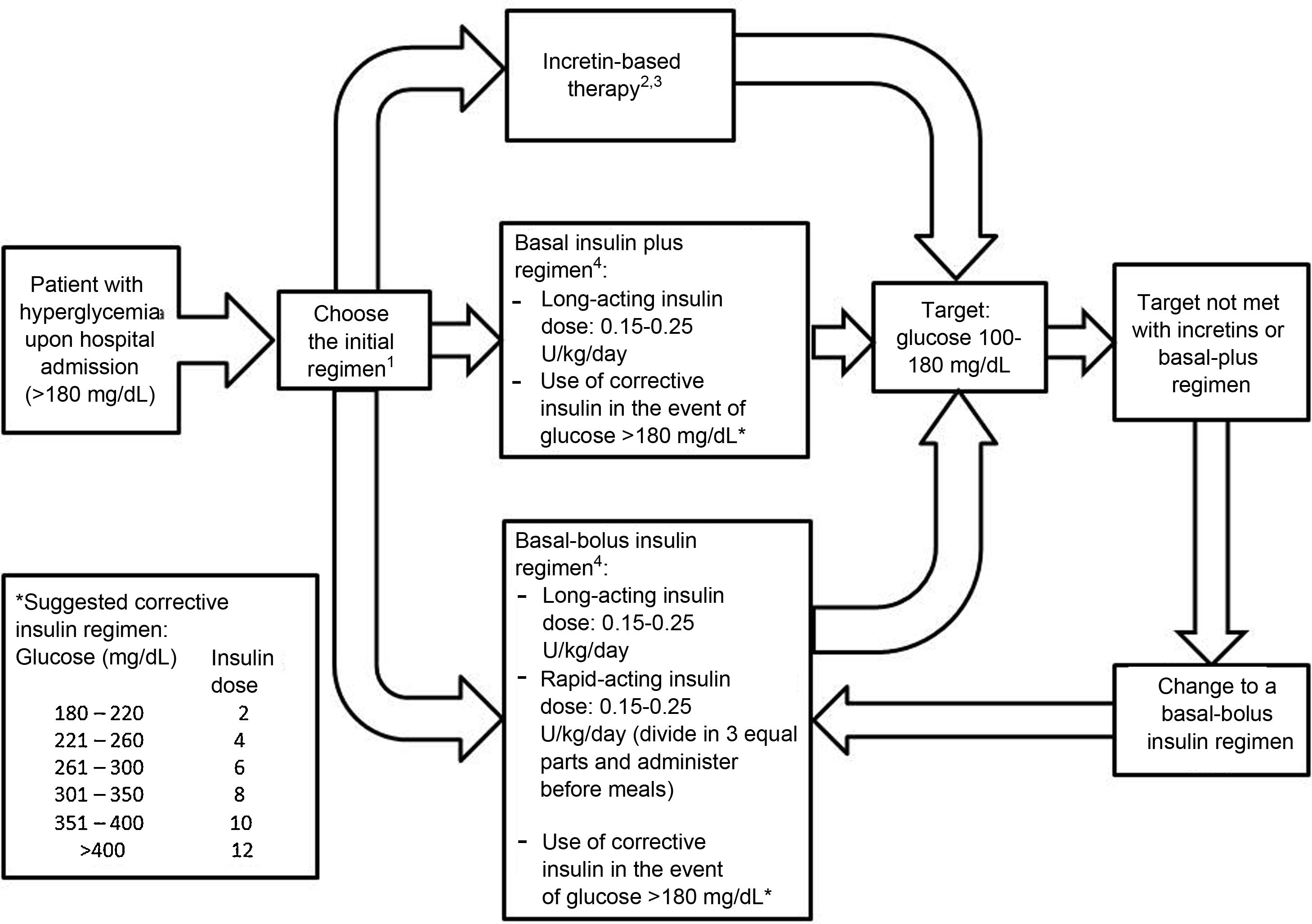
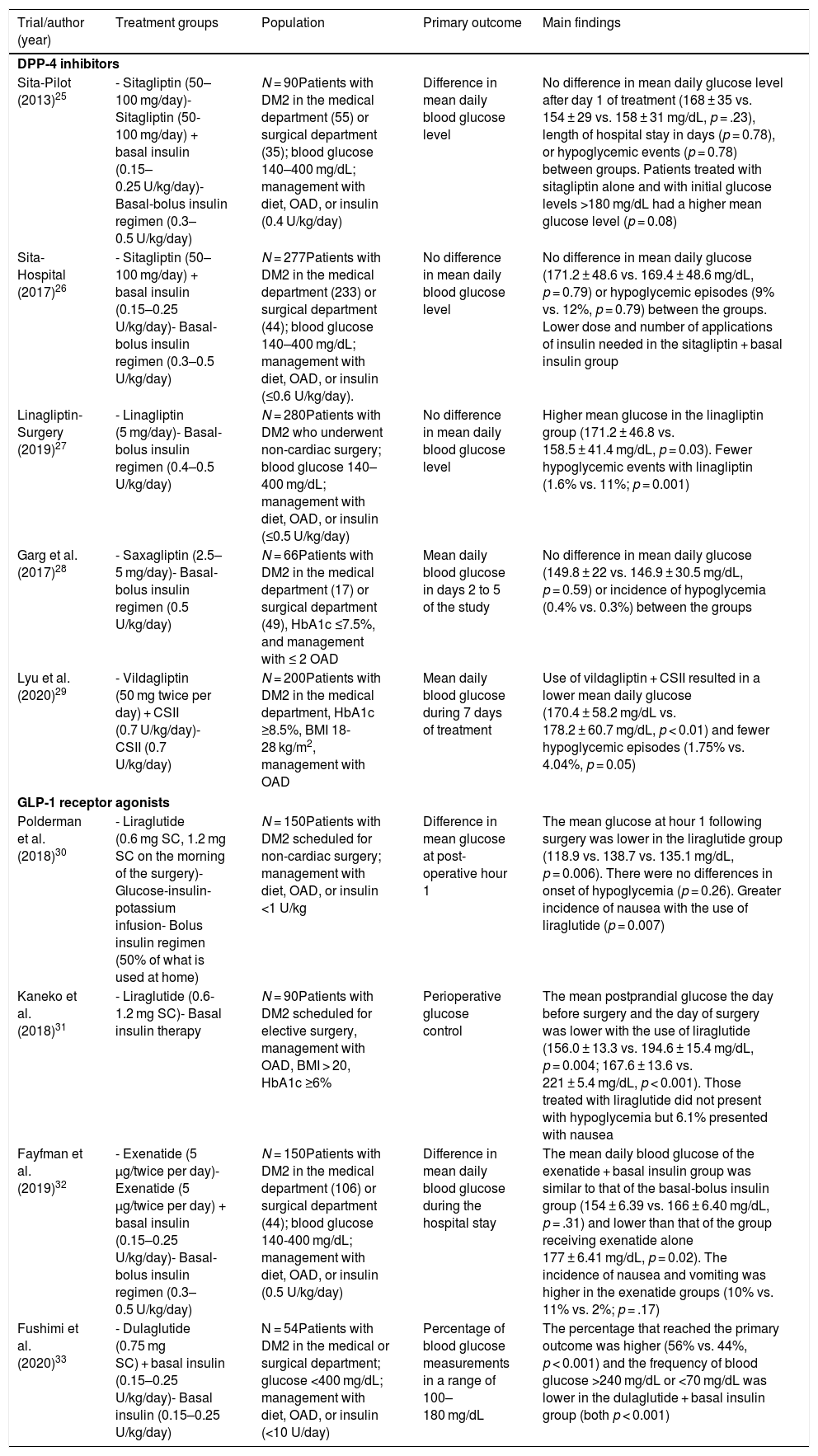
Incretin-based therapy leads to glycemic control in a glucose-dependent manner with a low risk of hypoglycemia, making it appealing for use in the hospital. The aim of this systematic review was to assess the benefits of incretin-based therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes hospitalized outside of the intensive care unit. We searched for studies published up to August 2021 in the PubMed and Scopus databases. Clinical trials comparing incretin-based therapy (alone or in combination with insulin) versus an insulin regimen were selected. The results of the included studies showed that incretin-based therapy showed mean blood glucose values, a percentage of records within the therapeutic target, and a percentage of treatment failure similar to insulin management, particularly in patients with mild to moderate hyperglycemia. Furthermore, incretin-based treatment was associated with a lower total insulin dose and a lower incidence of hypoglycemia. In conclusion, incretin-based therapy achieved glycemic control similar to insulin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes hospitalized outside the intensive care unit and has the advantages of reducing the insulin requirement and a lower risk of hypoglycemia.
La terapia basada en incretinas lleva al control glucémico de una manera dependiente de glucosa con un bajo riesgo de hipoglucemia, por lo que resulta atractiva para su uso hospitalario. El objetivo de esta revisión sistemática fue evaluar los beneficios de la terapia basada en incretinas en pacientes con diabetes tipo 2 hospitalizados fuera de la unidad de cuidados intensivos. Se buscaron estudios publicados hasta agosto de 2021 en las bases de datos PubMed y Scopus. Se seleccionaron los ensayos clínicos que comparaban la terapia basada en incretinas (sola o en combinación con insulina) versus el régimen con insulina. Los resultados de los estudios incluidos mostraron que la terapia basada en incretinas registró un promedio de glucosa sanguínea, un porcentaje de registros dentro de meta terapéutica y un porcentaje de falla al tratamiento similar al manejo con insulina, particularmente en pacientes con hiperglucemia leve a moderada. Además, el tratamiento basado en incretinas se asoció con una menor dosis total de insulina y una menor incidencia de hipoglucemia. En conclusión, la terapia basada en incretinas logró un control glucémico similar al tratamiento con insulina en los pacientes con diabetes tipo 2 hospitalizados fuera de la unidad de cuidados intensivos, con la ventaja de disminuir el requerimiento insulínico y con menor riesgo de hipoglucemia.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<