To study the temporal evolution of the bibliometric indices of internists with established research experience in order to predict the future behavior of researchers and to assess whether output focused on a specific area of internal medicine helps obtain greater visibility than in general internal medicine.
Materials and methodsWe analyzed a representative group of members of the Spanish Society of Internal Medicine (SEMI) based on data obtained from the Web of Science. As an indicator of productivity, we analyzed the number of articles published. As impact indicators, we studied the impact factor (IF), the number of citations and the h-index.
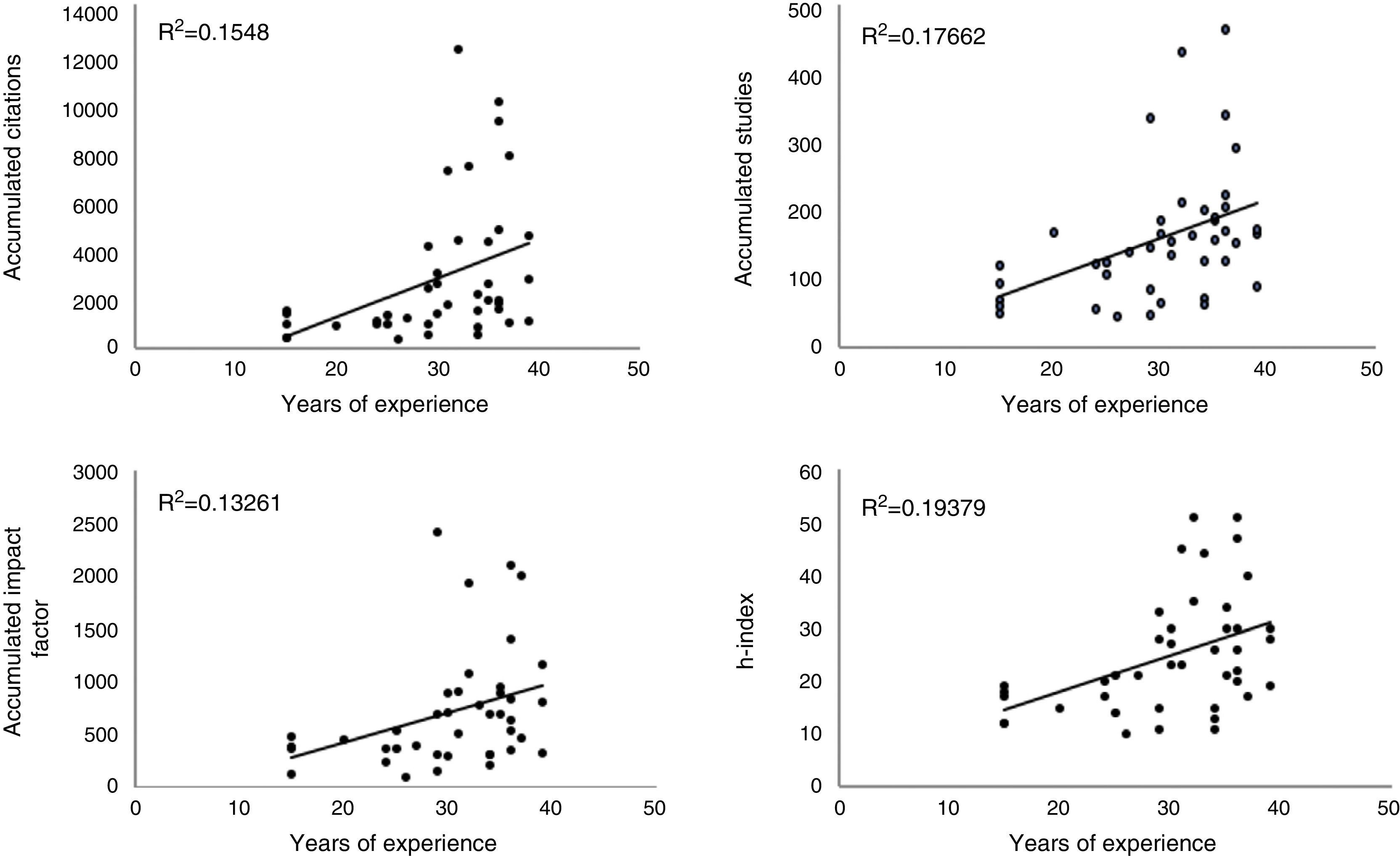
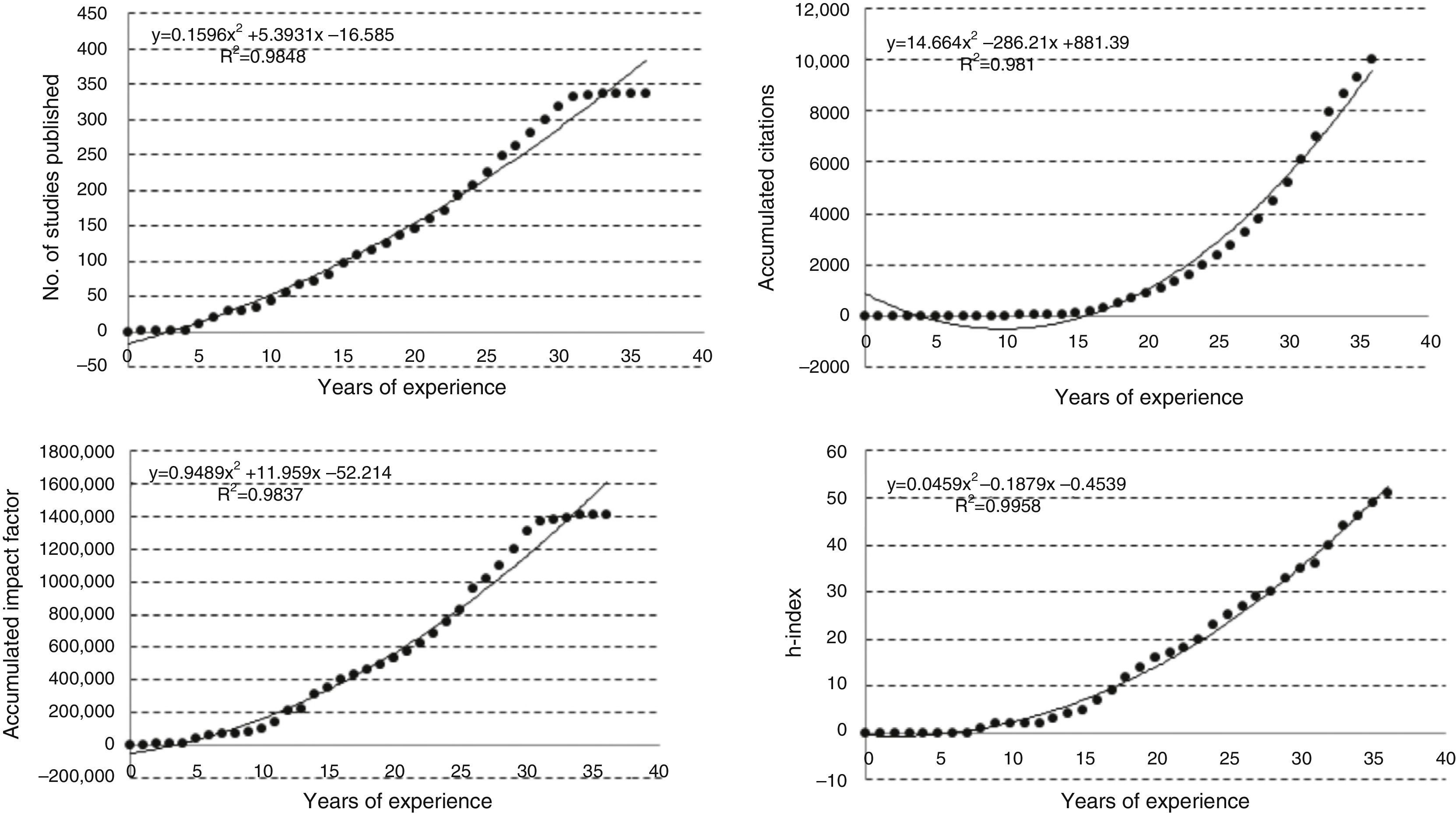
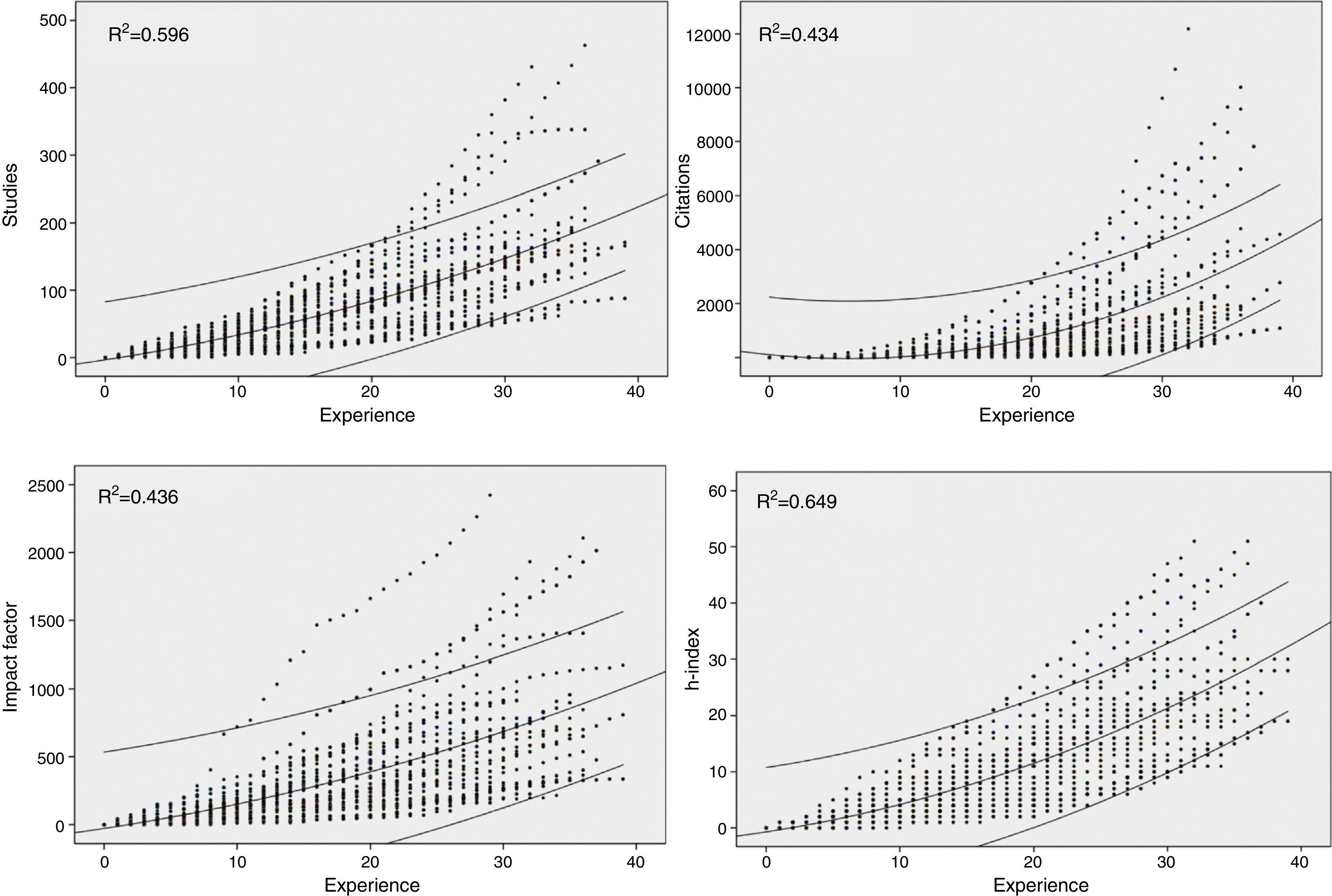
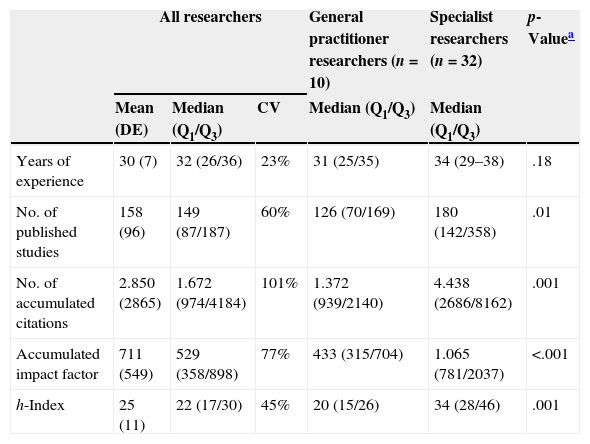
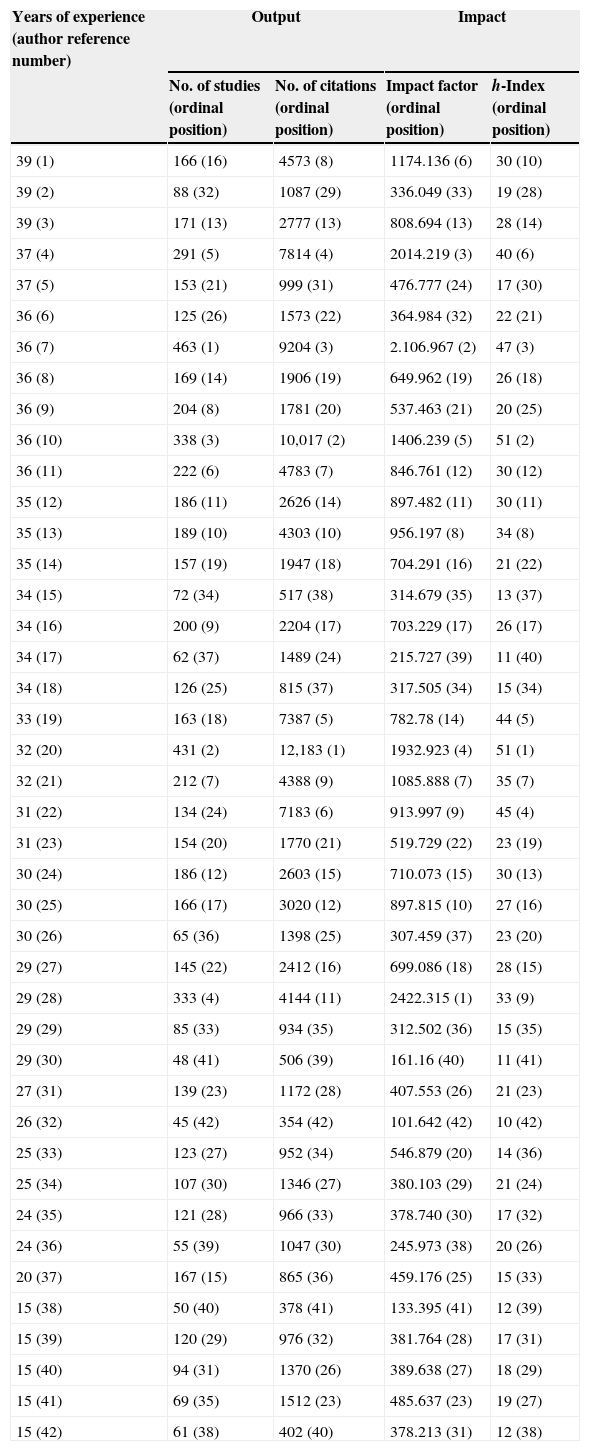
ResultsWe analyzed 42 internists, with a mean experience of 30 years and a total of 6655 publications. The mean (SD) number of studies was 158 (96), the number of citations was 2850 (2865), the IF was 711 (549) and the h-index was 25 (11). These figures were higher for the specialist internists than for the general internists. There was a good relationship between the impact and productivity indicators (R2=0.61–0.89) and a poor relationship between these indicators and the years of experience (R2=0.13–0.19). The temporal evolution of these indicators for each individual researcher and for all researchers as a whole was adjusted to a second-degree polynomial model, with the h-index having the highest R2 values.
ConclusionsThe h-index is the factor that had the best adjustment and least variability and could therefore help predict the future scientific output and impact of internists. The specialist researchers achieved greater visibility than the general internists.
Estudiar la evolución temporal de los índices bibliométricos de internistas con una trayectoria investigadora consolidada, con el fin de predecir el comportamiento futuro de un investigador y evaluar si la producción centrada en un área concreta de la medicina interna permite obtener mayor visibilidad que en medicina interna general.
Material y métodoSe analizó un grupo representativo de miembros de la Sociedad Española de Medicina Interna a partir de los datos obtenidos de la Web of Science. Como indicador de productividad se analizó el número de artículos publicados y como indicadores de repercusión el factor de impacto, el número de citas y el índice h.
ResultadosSe analizó a 42 internistas, con una media de 30 años de experiencia y un total de 6.655 publicaciones. La media (DE) del número de trabajos fue de 158 (96), el número de citas 2.850 (2.865), el factor de impacto 711 (549) y el índice h 25 (11), siendo superiores estos datos en los internistas especializados respecto a los generalistas. Hubo buena relación entre indicadores de repercusión y de productividad (R2=0,61–0,89) y poca entre estos y los años de experiencia (R2=0,13–0,19). La evolución temporal de estos indicadores para cada investigador individual, y para todos ellos en conjunto, se ajustó a un modelo polinomial de segundo grado, teniendo el índice h las R2 más altas.
ConclusionesEl índice h es el que mejor se ajusta y menos variabilidad presenta, lo cual podría permitir predecir la producción e impacto científico futuro de los internistas. Los investigadores especializados obtienen más visibilidad que los generalistas.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<