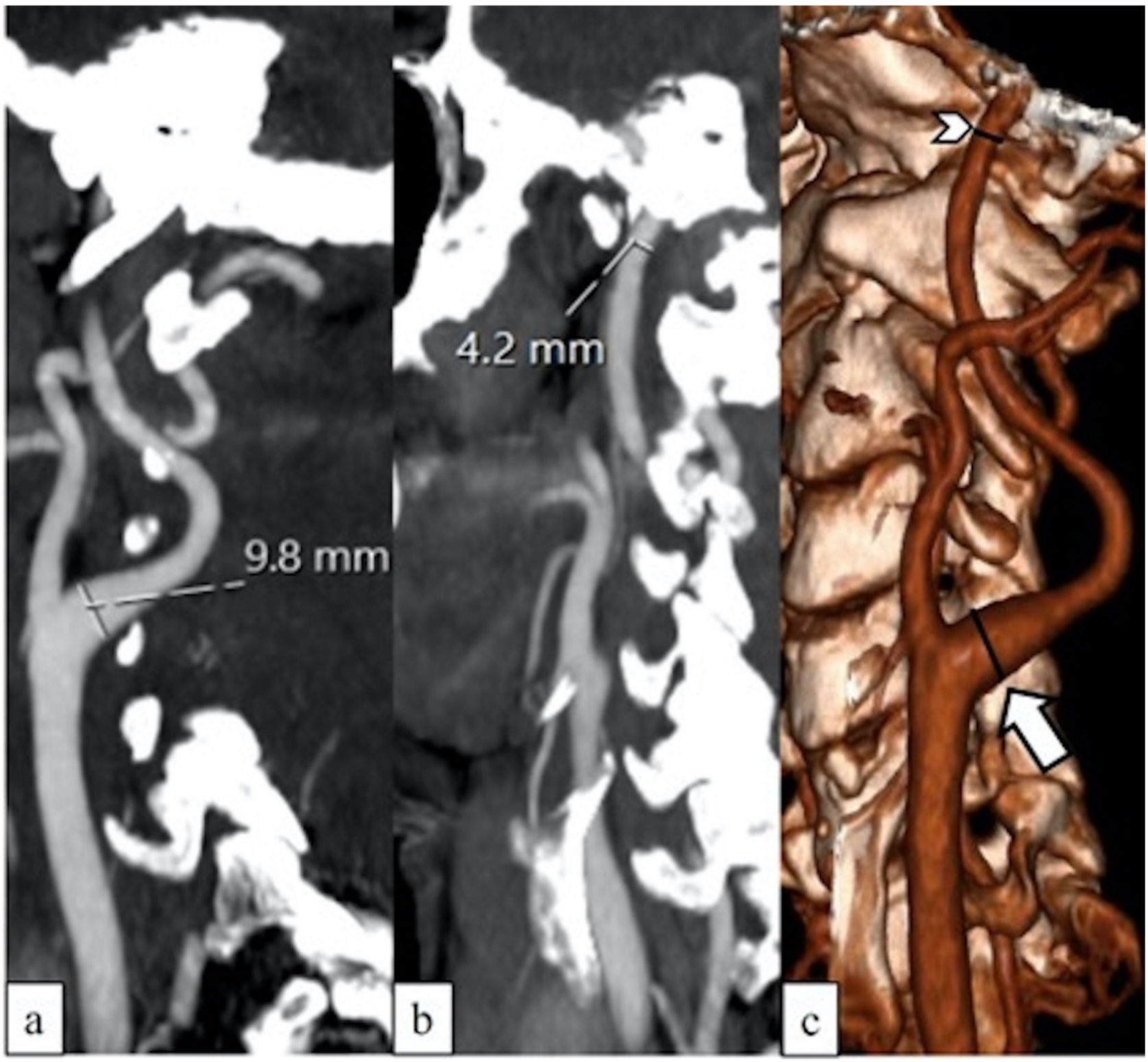
To investigate the relationship between the width of the internal carotid artery (ICA) bulb and cerebral vascular diseases including stroke and intracranial aneurysms.
Material and methodsIn total 300 patients who had supra-aortic computed tomography angiography (CTA) were enrolled in this study from 2015 to 2021. The study groups consisted of 100 ischemic stroke patients, 100 patients with intracranial aneurysms, and 100 control subjects. The intracranial aneurysm patient group was divided into two subgroups according to the presence of subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). The largest diameters of the ICA C1 (cervical) and C2 (petrous) segments in all individuals were measured bilaterally on CTA images. The ICA diameter ratios of the cases were measured using the formula C1-C2C1. The relationship between the age and ICA vessel analysis was evaluated as well.
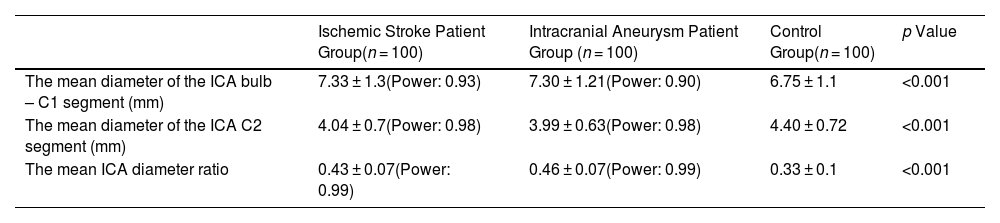
ResultsThe mean ICA bulb width values in the ischemic stroke patient group and the intracranial aneurysm patient group were significantly higher than the control group (p < 0.001). The ICA C1 and C2 segment diameter values and ICA diameter ratio were smaller in the intracranial aneurysm patients with SAH than those who had not (p = 0.7). There was a statistically significant but weak relationship between the age and ICA diameter ratios in all study groups (R-squared value of 0.26, p = 0.03).
ConclusionICA bulb width is a parameter that can be easily evaluated with neuroimaging modalities and is a successful method that may be used for predicting the risk of ischemic stroke or the presence of an intracranial aneurysm.
Investigar la relación entre la anchura del bulbo de la arteria carótida interna (ACI) y las enfermedades vasculares cerebrales, incluidos el ictus y los aneurismas intracraneales.
Material y métodosEn total, 300 pacientes a los que se les realizó una angiografía por tomografía computarizada (ATC) supraaórtica se inscribieron en este estudio entre 2015 y 2021. Los grupos de estudio consistieron en 100 pacientes con ictus isquémico, 100 pacientes con aneurismas intracraneales y 100 sujetos control. El grupo de pacientes con aneurisma intracraneal se dividió en dos subgrupos según la presencia de hemorragia subaracnoidea (HSA). Los diámetros mayores de los segmentos ACI C1 (cervical) y C2 (petroso) de todos los individuos se midieron bilateralmente en imágenes de ATC. Las proporciones de los diámetros ACI de los casos se midieron mediante la fórmula (C1-C2)/C1. También se evaluó la relación entre la edad y el análisis de los vasos ACI.
ResultadosLos valores medios de anchura del bulbo ACI en el grupo de pacientes con ictus isquémico y en el grupo de pacientes con aneurisma intracraneal fueron significativamente superiores a los del grupo control (p < 0,001). Los valores del diámetro de los segmentos C1 y C2 de la ACI y el cociente del diámetro de la ACI fueron menores en los pacientes con aneurisma intracraneal y HSA que en los que no lo tenían (p = 0,7). Existía una relación estadísticamente significativa pero débil entre la edad y los cocientes de diámetros de la ACI en todos los grupos de estudio (Valor R-cuadrado de 0,26; p = 0,03).
ConclusionesLa anchura del bulbo de la ACI es un parámetro que puede evaluarse fácilmente con modalidades de neuroimagen y es un método satisfactorio que puede utilizarse para predecir el riesgo de ictus isquémico o la presencia de un aneurisma intracraneal.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<