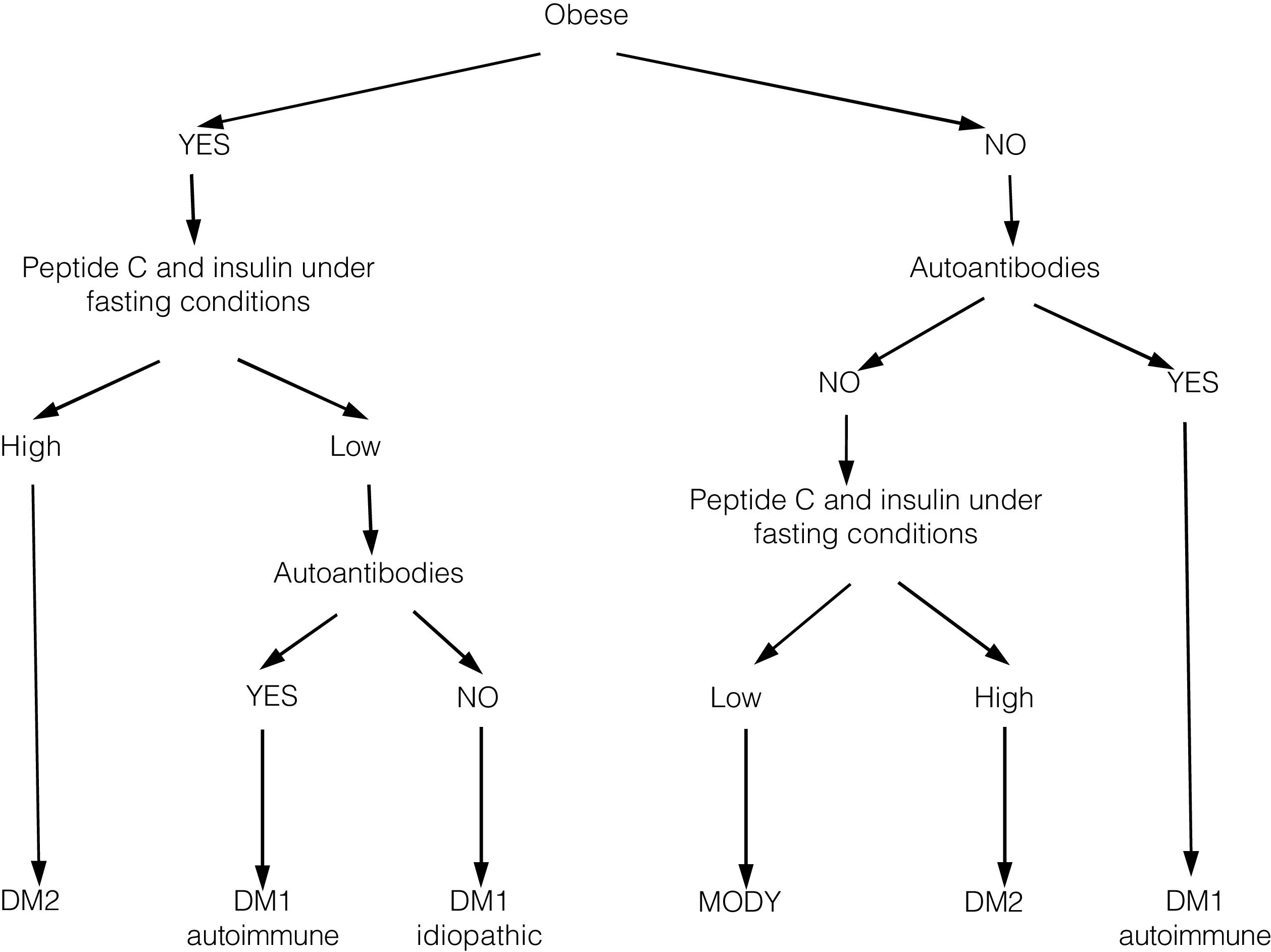
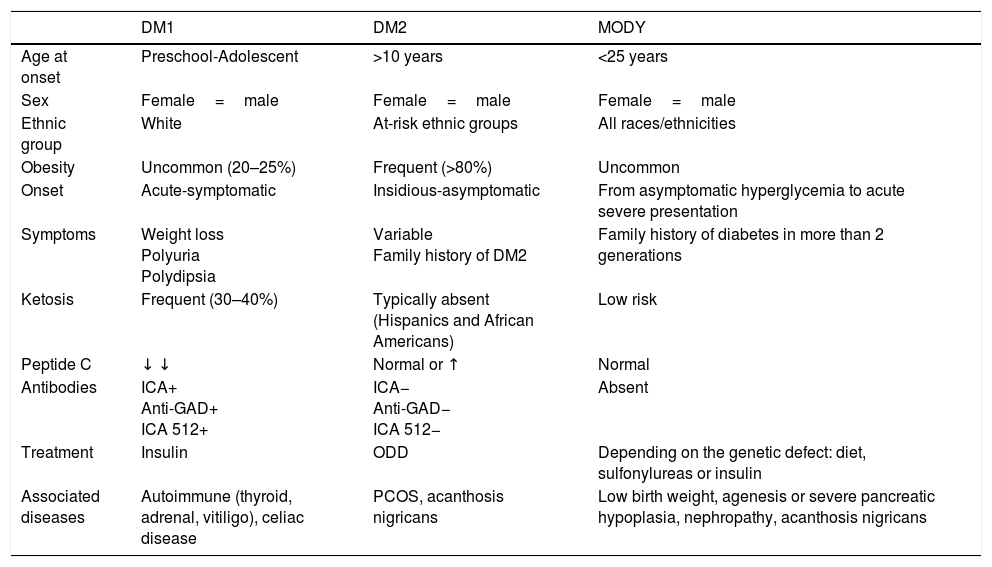
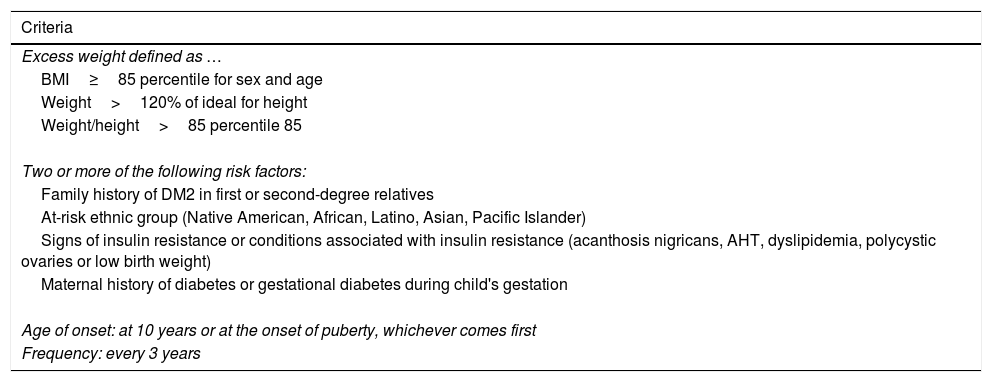
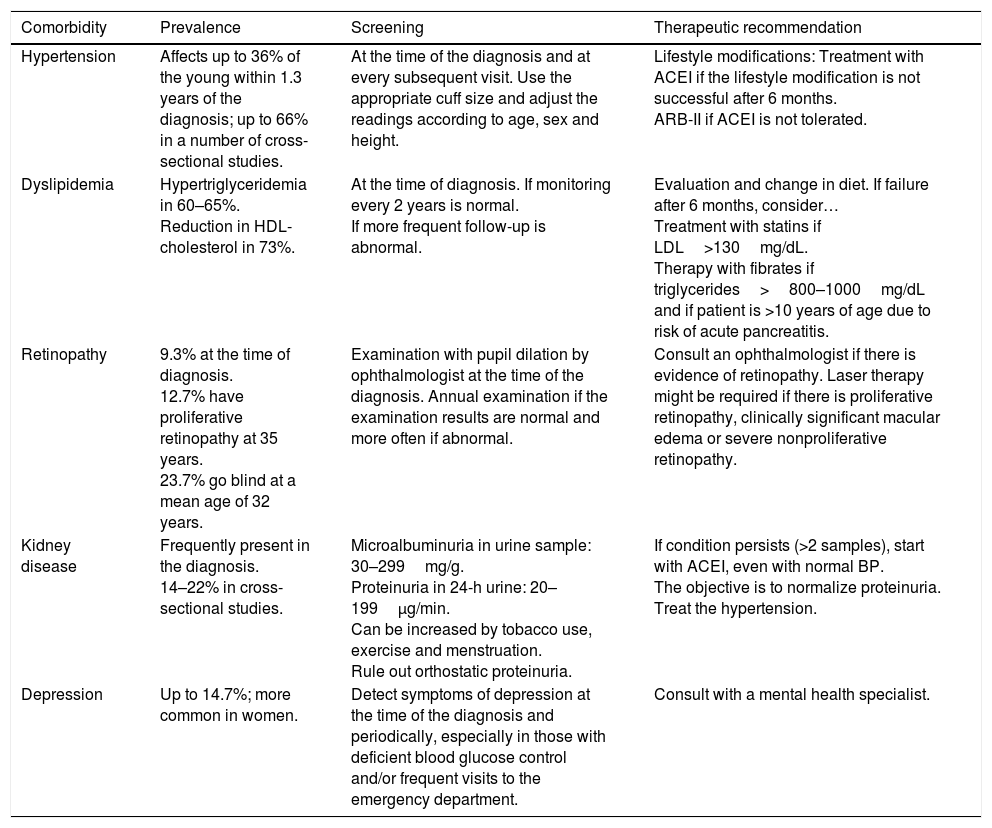
In recent years, we have witnessed an increase in the number of cases of type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2) in children and adolescents, which has paralleled the increase in the worldwide prevalence of obesity. Although screening the general population does not appear to be cost-effective, special attention should be paid to children with excess weight, obesity or other factors that predispose them to a state of insulin resistance. When faced with the diagnosis of childhood DM2, the presence of comorbidities (such as hypertension, dyslipidemia and microalbuminuria) should be assessed, and appropriate treatment and follow-up should be administered to prevent the onset of complications, given that the DM2 in this population group will last longer than that started in adulthood.
En los últimos años asistimos a un aumento en el número de casos de diabetes mellitus tipo 2 (DM2) en niños y adolescentes, que ocurre de forma paralela al aumento de la prevalencia de obesidad en todo el mundo. A pesar de que un cribado de la población general no parece coste-efectivo, debería prestarse especial atención a los niños con sobrepeso, obesidad u otros factores que predispongan a un estado de resistencia a la insulina. Ante el diagnóstico de DM2 en la infancia debe evaluarse la presencia de comorbilidades, como la hipertensión, la dislipidemia y la microalbuminuria, así como llevar a cabo un adecuado tratamiento y seguimiento para evitar la aparición de complicaciones, pues en este grupo de población la duración de la DM2 será mayor que en la iniciada en el adulto.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<