Acute hepatic porphyria is a genetic disorder affecting enzymes involved in heme biosynthesis. The most common subtype is acute intermittent porphyria, accounting for 80% of cases. Other types include hereditary coproporphyria, variegate porphyria, and delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase deficiency.
Attacks in acute hepatic porphyria are triggered by the induction of hepatic ALA synthase 1, leading to the accumulation of neurotoxic heme intermediates, delta-aminolevulinic acid, and porphobilinogen. Women experience attacks more frequently than men.
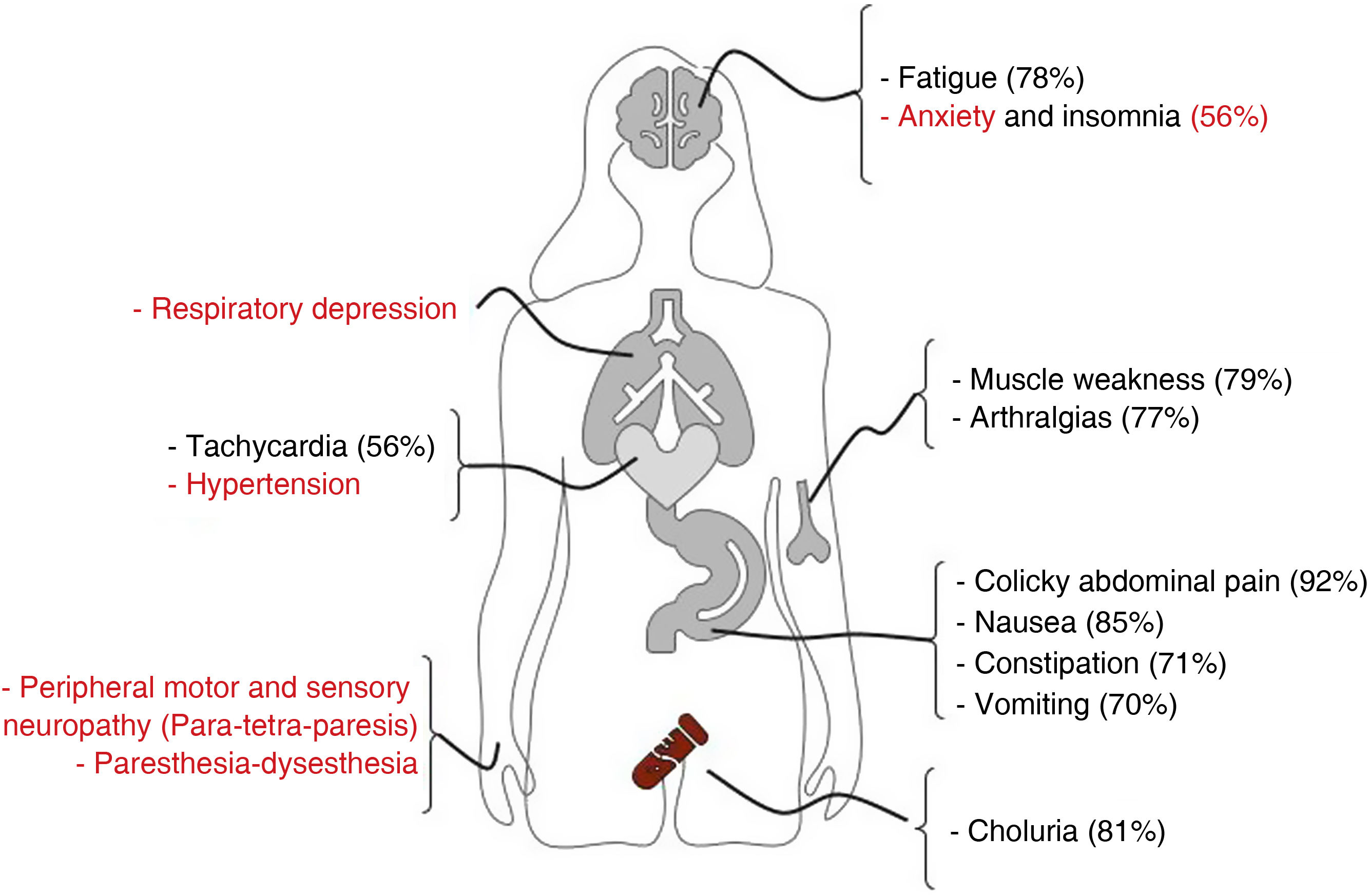
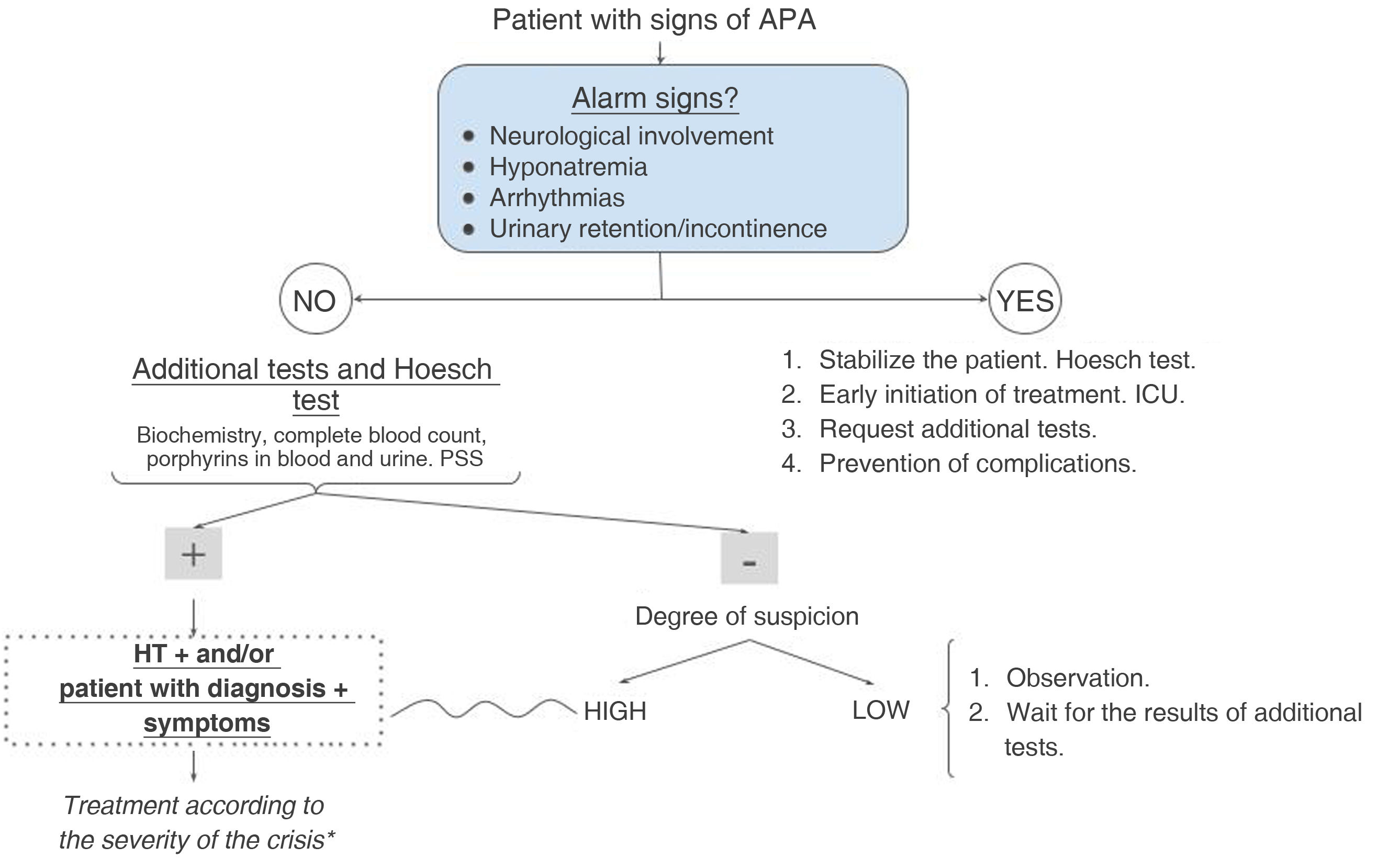
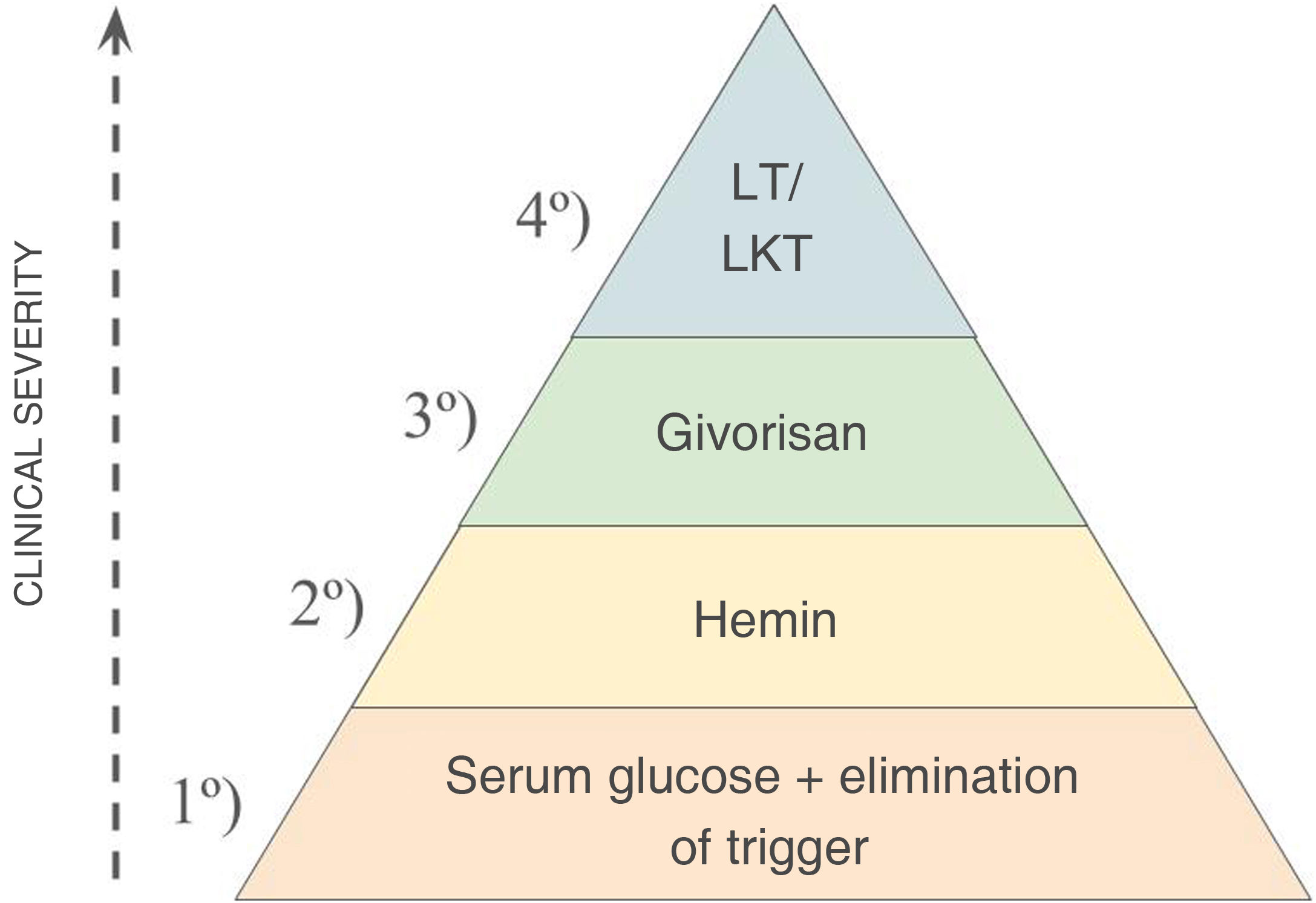
Acute porphyria attacks are characterized by severe, diffuse abdominal pain, muscle weakness, autonomic neuropathy (including hypertension, tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, and constipation), and changes in mental status. Early recognition of the disease is crucial as it requires urgent medical attention and treatment. Management includes intravenous opioids, glucose, hemin, and the removal of triggering factors.
Preventive treatment options include hormone suppression therapy, off-label prophylactic hemin, Givosiran, and exceptionally liver transplantation.
La porfiria hepática aguda es un trastorno genético que afecta a las enzimas implicadas en la biosíntesis del hemo. El subtipo más común es la porfiria aguda intermitente (PAI), que representa el 80% de los casos. Otros tipos incluyen coproporfiria hereditaria, porfiria variegata y deficiencia de ácido delta-aminolevulínico (ALA) deshidratasa.
Las crisis agudas de porfiria (CAPs) se desencadenan por la inducción de la ALA sintasa 1 hepática, lo que lleva a la acumulación de intermediarios neurotóxicos, ácido delta-aminolevulínico y porfobilinógeno (PBG). Las mujeres sufren ataques con más frecuencia que los hombres.
Los ataques agudos de porfiria se caracterizan por dolor abdominal intenso y difuso, debilidad muscular, neuropatía autonómica (que incluye hipertensión, taquicardia, náuseas, vómitos y estreñimiento) y cambios en el estado mental. El reconocimiento temprano de la enfermedad es crucial ya que requiere atención y tratamiento médicos urgentes. El tratamiento incluye opioides intravenosos, glucosa, hemina y la eliminación de factores desencadenantes.
Las opciones de tratamiento preventivo incluyen terapia de supresión hormonal, hemina profiláctica (indicación no autorizada), Givosiran y, excepcionalmente trasplante hepático.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<