To estimate the prevalence of obesity in patients treated by departments of Internal Medicine and to classify the patients according to the Edmonton Obesity Staging System (EOSS).
Material and methodsAn observational, descriptive cross-sectional study included outpatients older than 18 years, with a body mass index (BMI)>30, from 38 hospitals between the 1st and 14th of February, 2016. We classified the patients according to the EOSS and analyzed their clinical, laboratory and demographic variables. A value of p<.05 was considered statistically significant.
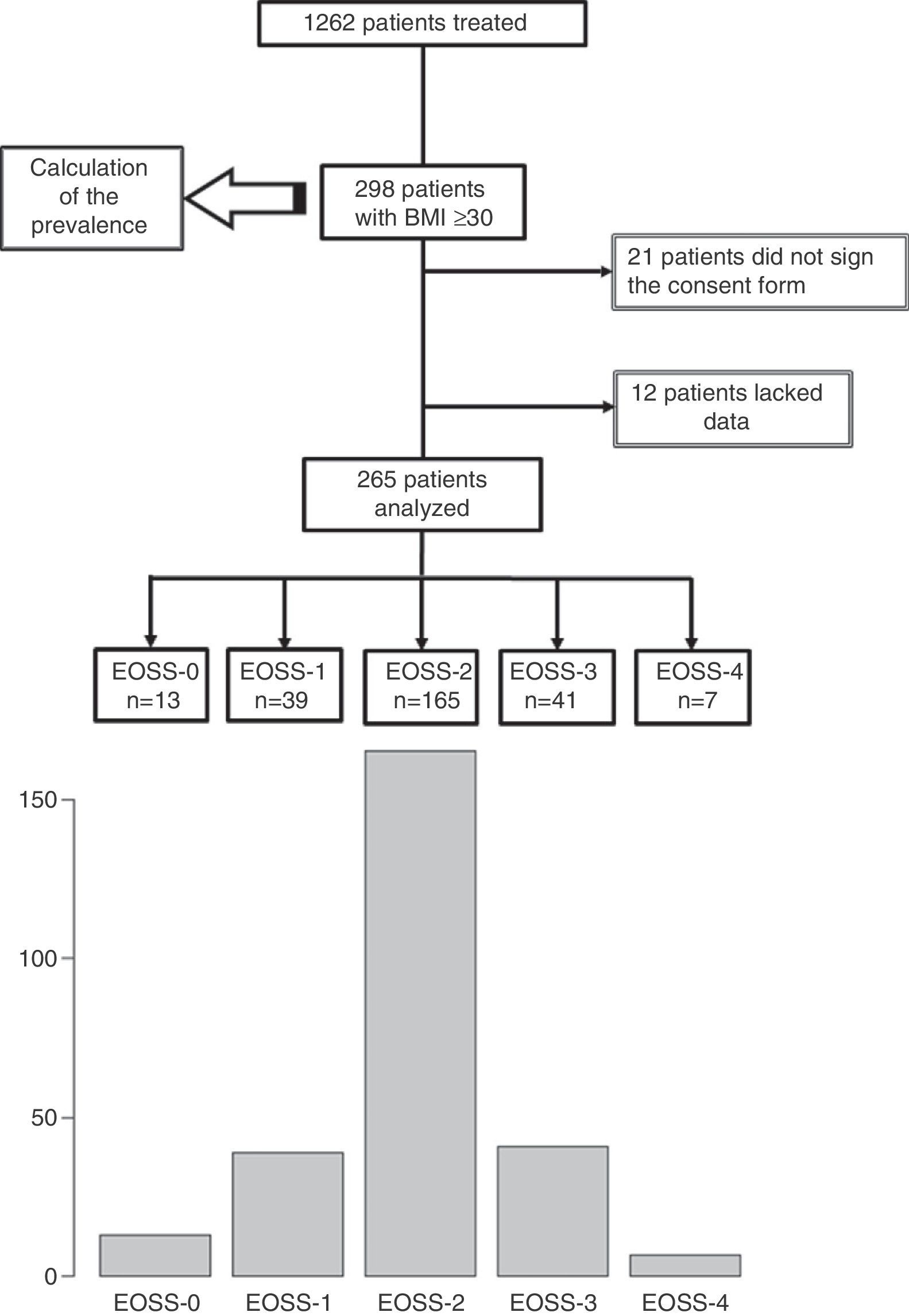
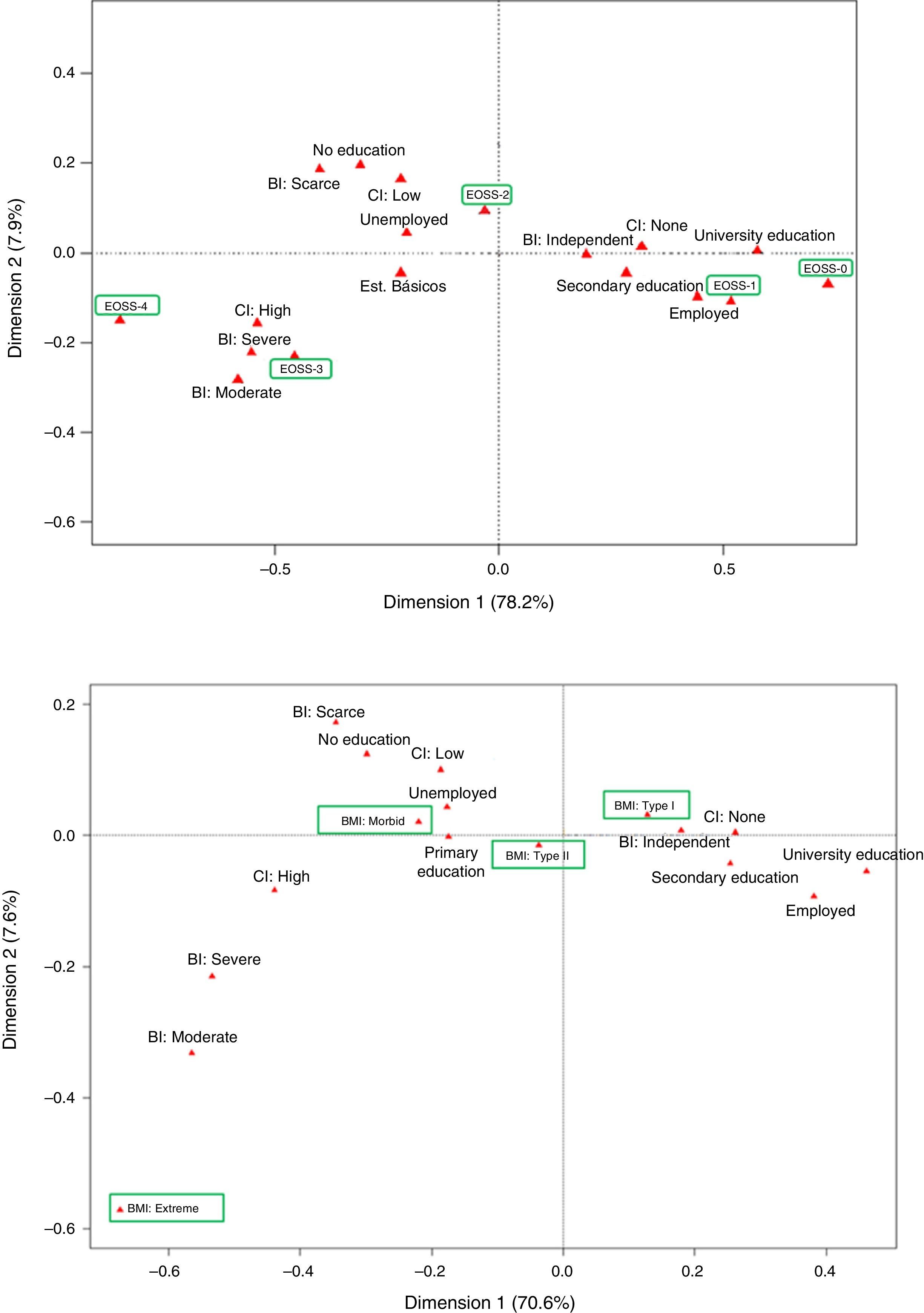
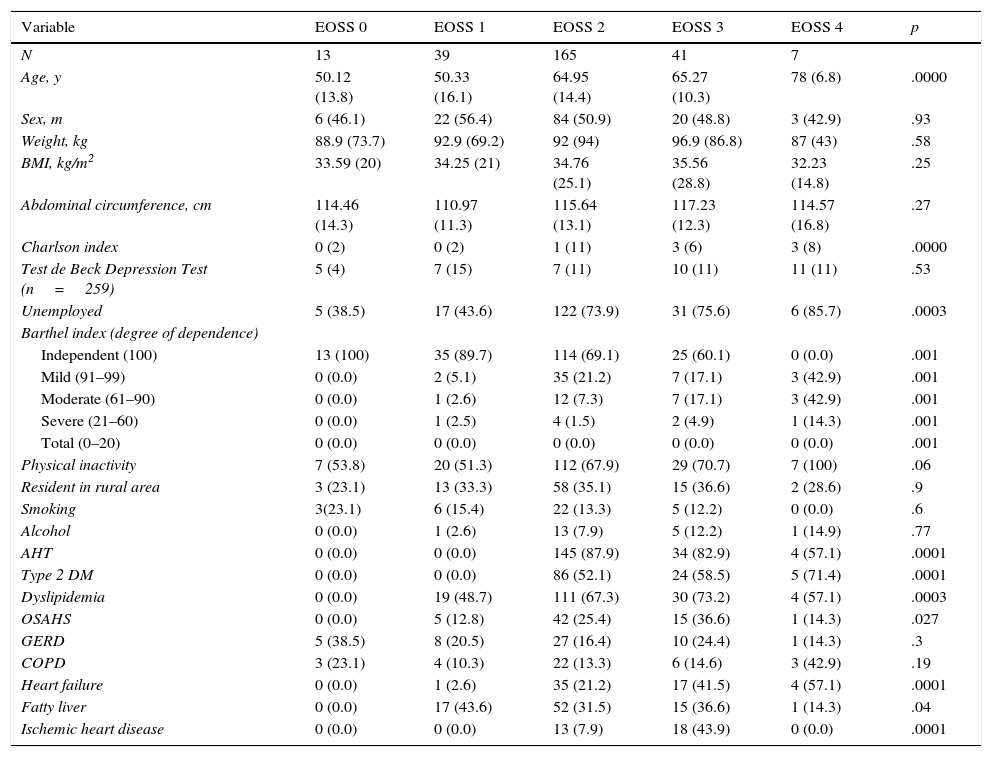
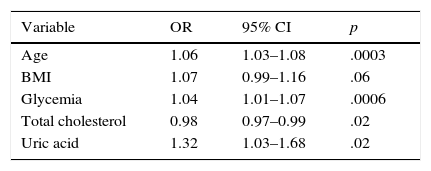
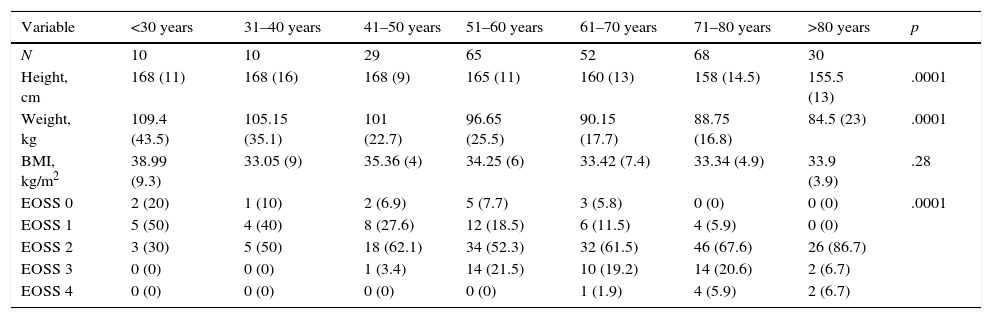
ResultsOf the 1262 patients treated in consultations, we recruited 298 and analyzed 265. The prevalence of obesity was 23.6%, the mean age was 62.47±15.27 years, and the mean BMI was 36.1±5.3kg/m2. According to EOSS stage (0, 1, 2, 3 and 4), the prevalence was 4.9, 14.7, 62.3, 15.5 and 2.64%, respectively. Those patients with EOSS>2 were significantly older and had significantly more comorbidities. The multivariate analysis related age (OR 1.06; p<.0003), blood glucose (OR 1.04; p<.0006), total cholesterol (OR 0.98; p<.02) and uric acid (OR 1.32; p<.02) levels with an EOSS>2. An analysis of correspondence grouped, with an explanatory percentage of 78.2%, the patients according to their EOSS, comorbidity, education level, employment status and functional capacity.
ConclusionsThe prevalence of obesity in the patients treated by Internal Medicine departments is similar to that of the general population, although the patients are older and have a higher BMI. EOSS is useful for implementing a comprehensive approach for patients with obesity, regardless of the BMI, which can help achieve better health and quality-of-life results.
Estimar la prevalencia de obesidad y clasificarla según la estadificación de Edmonton (EOSS) en pacientes atendidos por Medicina Interna.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional, descriptivo y transversal. Incluyó pacientes ambulatorios mayores de 18 años con un índice de masa corporal (IMC) > 30, procedentes de 38 hospitales, entre el 1 y el 14 de febrero de 2016. Se clasificaron según EOSS y se analizaron variables clínicas, analíticas y sociodemográficas. Se consideró significación estadística con p < 0,05.
ResultadosDe 1.262 pacientes vistos en las consultas se seleccionaron 298 y se analizaron 265. La prevalencia de obesidad fue del 23,6%, la edad, de 62,47 ± 15,27 años y el IMC, de 36,1 ± 5,3 kg/m2. Por EOSS (0, 1, 2, 3 y 4) la prevalencia fue de 4,9, 14,7, 62,3, 15,5 y 2,64%, respectivamente. Aquellos pacientes con EOSS > 2 tenían significativamente más edad y comorbilidades. El análisis multivariante relacionó la edad (OR 1,06, p < 0,0003), la glucemia (OR 1,04, p < 0,0006), el colesterol total (OR 0,98, p < 0,02) y el ácido úrico (OR 1,32, p < 0,02) con un EOSS > 2. Un análisis de correspondencias agrupó, con un porcentaje explicativo del 78,2%, a los pacientes según su EOSS, comorbilidad, nivel de estudios, situación laboral y capacidad funcional.
ConclusionesLa prevalencia de obesidad en pacientes atendidos por Medicina Interna es similar a la de la población general, aunque los pacientes son de mayor edad e IMC. El EOSS es útil para hacer una aproximación integral de los pacientes obesos, independientemente del IMC, lo que puede posibilitar la obtención de mejores resultados en salud y en calidad de vida.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<