Given the proven protective effect of the Mediterranean Diet, adherence to it by healthcare personnel and the influence of different factors on dietary compliance were evaluated.
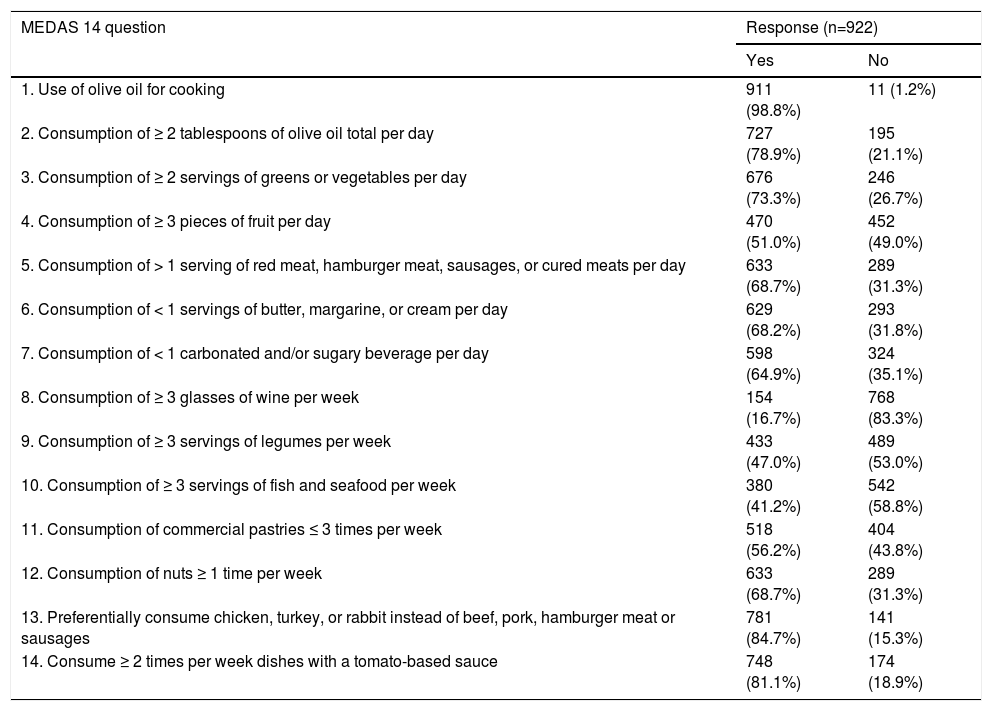
MethodsA cross-sectional study was conducted on healthcare personnel, obtaining the data through anonymous surveys that collected demographic characteristics, professional activity, history of cardiovascular risk factors, alcohol, and tobacco consumption, physical activity, and adherence to the Mediterranean Diet, using the 14-point Mediterranean Diet Adherence Score (MEDAS). Adherence and related factors were measured.
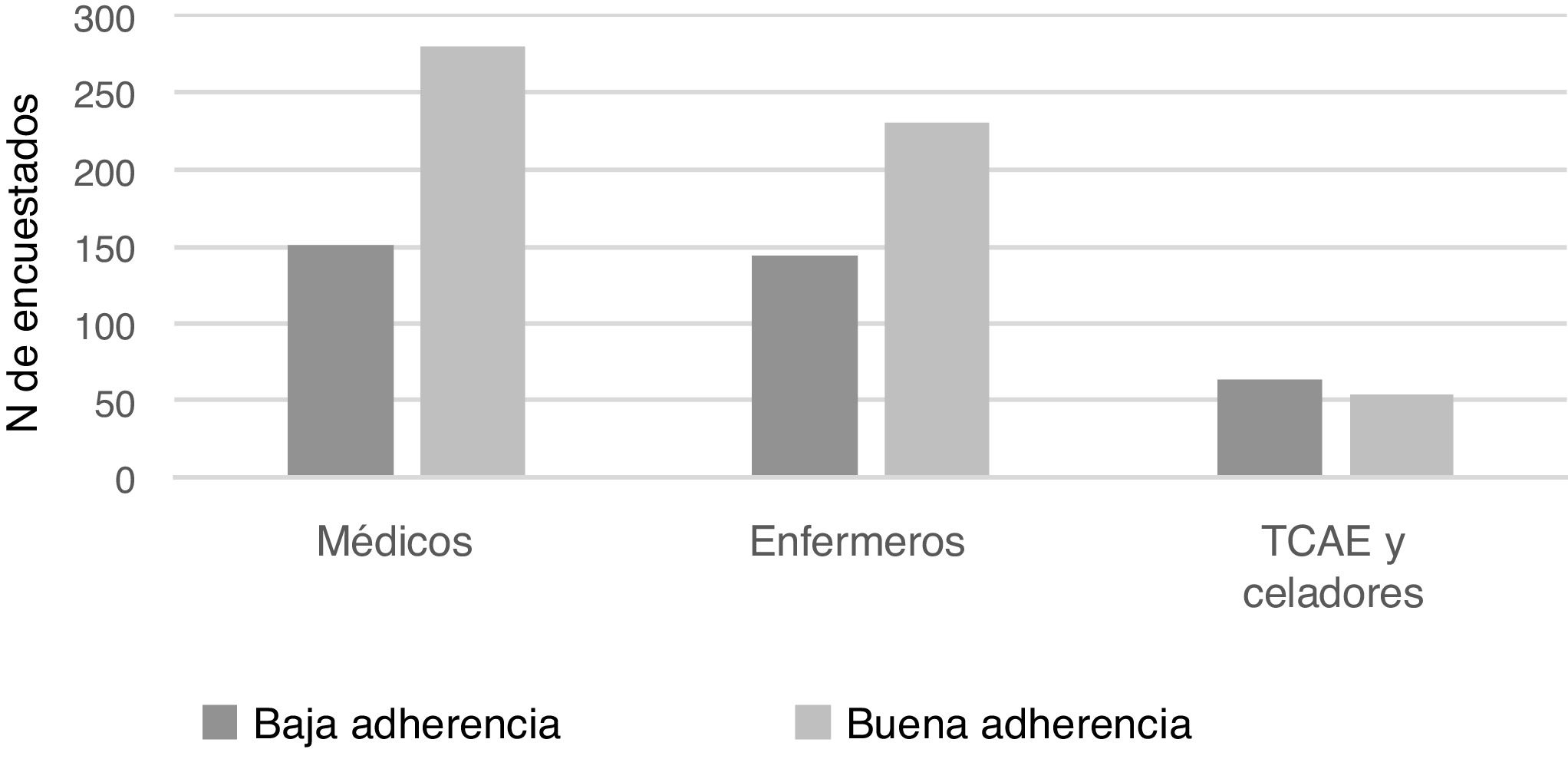
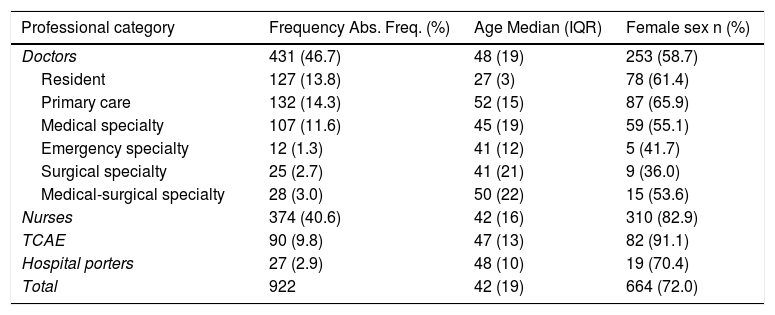
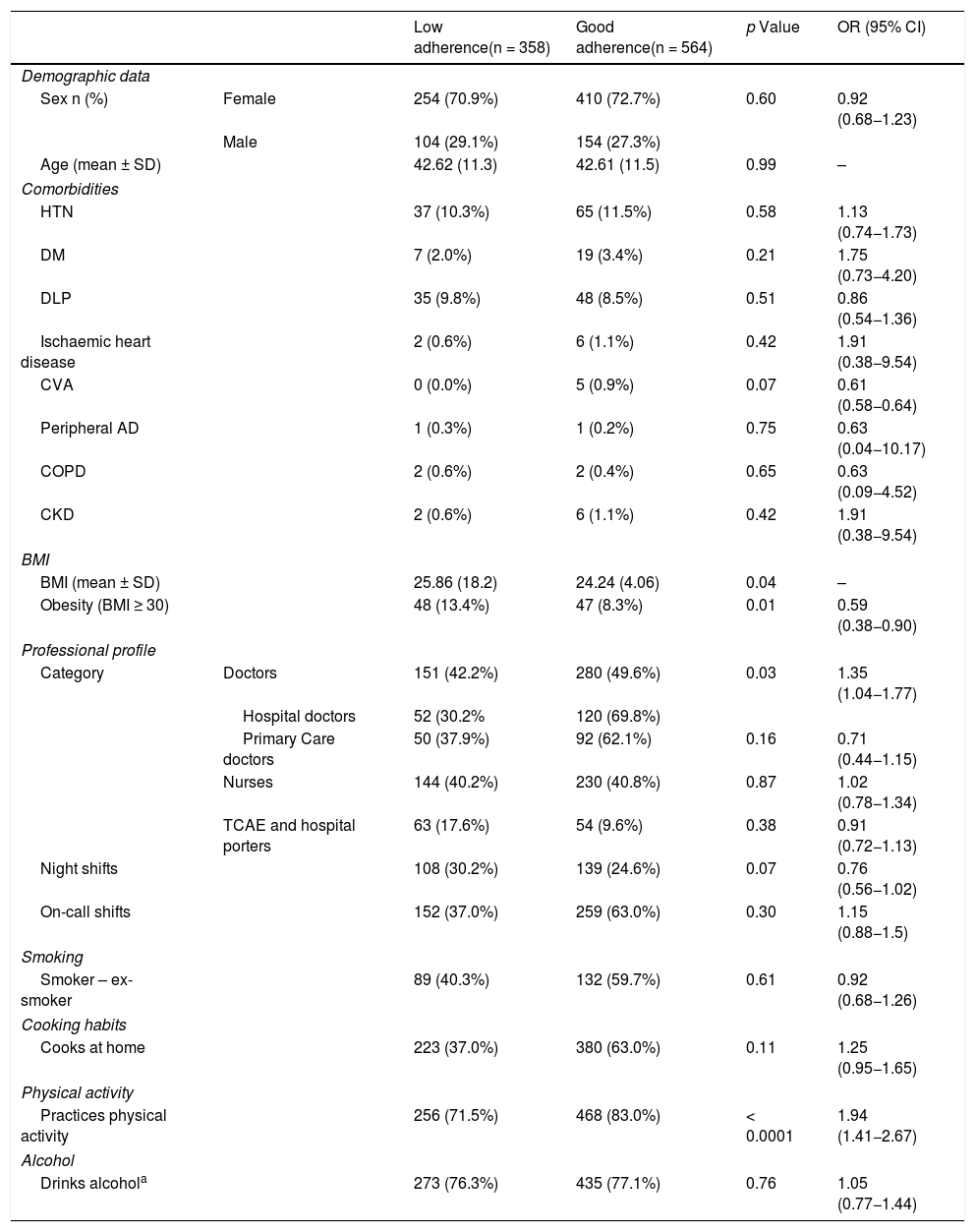
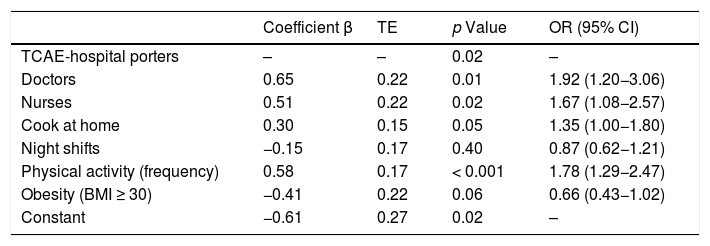
Results and conclusionsOf a total of 922 respondents (664 women) mean aged 42.61 years (range 20–69), 61.2% showed a good adherence to the Mediterranean Diet. Adherence was significantly associated with the professional categories of physicians (OR = 1.92; 95% CI: 1.20−3.06; p = 0.01) and nurses (OR = 1.67; 95% CI: 1.08−2.57). Furthermore, it was associated with physical exercise (OR = 1.78; 95% CI: 1.29–2.47; p < 0.001) and cooking at home (OR = 1.35; 95% CI: 1.00–1.80; p = 0.05). However, adherence was not significantly associated with age or sex, comorbidities, working hours, alcohol, or tobacco consumption. Quantifying knowledge of the diet would be useful, as well as increasing educational programs, promoting physical exercise and cooking habits.
Demostrado efecto protector de la dieta mediterránea, se evaluó su seguimiento y la influencia de distintos factores en el cumplimiento dietético.
Material y métodosSe realizó un estudio transversal con encuestas anónimas para obtener datos sobre características demográficas, actividad laboral, antecedentes de factores de riesgo cardiovascular, consumo de alcohol y tabaco, actividad física y consumo de dieta mediterránea. Se evaluó el cumplimiento por medio del cuestionario 14-point Mediterranean Diet Adherence Score (MEDAS) y los factores estadísticamente relacionados con el mismo.
Resultados y conclusionesDe 922 personas encuestadas (664 mujeres) de edad media 42,61 años (rango: 20 a 69 años), un 61,2% mostró buen cumplimiento. De manera independiente, el consumo de la dieta mediterránea se asoció con la categoría profesional, siendo superior en el personal médico (OR = 1,92; IC 95%: 1,20 a 3,06; p = 0,01) y de enfermería (OR = 1,67; IC 95%: 1,08 a 2,57) comparado con los técnicos auxiliares en cuidados de enfermería. Además, se relacionó con realizar actividad física (OR = 1,78; IC 95%: 1,29 a 2,47; p < 0,001) y cocinar en casa (OR = 1,35; IC 95%: 1,00 a 1,80; p = 0,05). Sin embargo, no se asoció significativamente con la edad, el sexo ni con la presencia de comorbilidades, con las características de la jornada laboral, ni con el consumo de alcohol ni tabaco. Convendría cuantificar el conocimiento sobre la dieta e incrementar los programas educativos, fomentando el ejercicio y el hábito culinario.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<