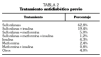
Context. To know the characteristics, related risk factors, and degree of control in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 (DM2) in our country. Methods. Observational, unrandom, opened, and multicenter study. Anthropometric characteristics, substance abuse, medication, control of diabetes, cholesterol, and triglycerides were analyzed in 5,395 patients. The patients were classified according to the length of the diagnosis: recent diabetes (RD) and known diabetes (KD). The chi-square test was utilized in order to compare the categorical variables, and the Student's «t» test for compare the continuous variables. The relationship between these variables was analyzed through the Pearson's correlation coefficient, and an analysis of multiple correspondence was carried out. Results. Median age, 63 years; obese, 34%; smokers, 11%; drinkers, 24%; hypertensives, 44%; lipemic, 42%. Control degree: HbA1c > 6.5% in 79%, LDLc > 115 mg/dl in 80%. Hypoglycemic treatment: sulfonylureas, 62.8%; antidiabetics combination, 5%; only insulin, 4.3%; insulin combined with antidiabetics, 20.6%. Control of diabetics, of lipids, and of weight was lower in the patients with KD that in the patients with RD (HbA1c, 7.6% versus 7%; LDLc 148 mg/dl versus 136 mg/dl; percentage of obese, 27.2% versus 38.62%). A relationship between the lenght of evolution of diabetes and the deterioration of the control of blood glucose and of lipids was detected. Conclusion. DM2 and its associated risk factors are insufficiently controlled in our country. The drug combination and insulin are utilized scarcely.
Keywords:
diabetes mellitus type 2, Primary Care, cardiovascular risk factors, diabetes treatment