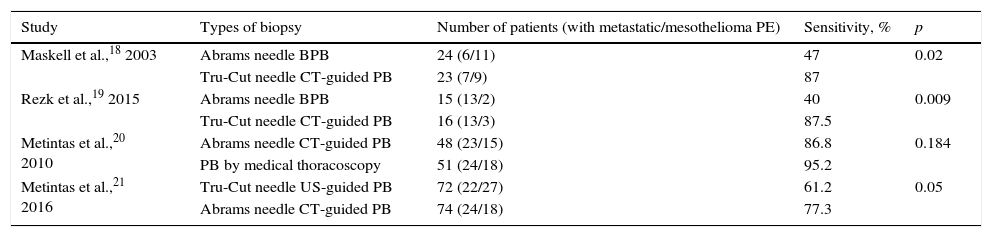
In most cases, the etiological diagnosis of pleural exudates does not require a pleural biopsy. However, when it is considered necessary, the biopsy should seldom be conducted using invasive methods such as thoracoscopy. Two paradigmatic examples are pleural tuberculosis and malignant effusions. In many centers, pleural fluid adenosine deaminase measurement has replaced closed pleural biopsies in the diagnosis of tuberculosis. Similarly, pathological and molecular studies on pleural fluid cell blocks or alternatively, image-guided pleural biopsies have drastically reduced the need for thoracoscopy.
En la mayoría de las ocasiones, el diagnóstico etiológico de un exudado pleural no requiere de una biopsia pleural y, si esta finalmente se considera imprescindible, excepcionalmente hay que recurrir a procedimientos invasivos como la toracoscopia. Dos ejemplos paradigmáticos son el derrame pleural tuberculoso y el maligno. En muchos centros, la medición de adenosina deaminasa en líquido pleural ha sustituido a la biopsia pleural cerrada para diagnosticar tuberculosis. Del mismo modo, el análisis anatomopatológico y molecular de los bloques celulares del líquido pleural o, en su defecto, de las biopsias pleurales dirigidas por técnicas de imagen ha reducido drásticamente la necesidad de una toracoscopia.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<