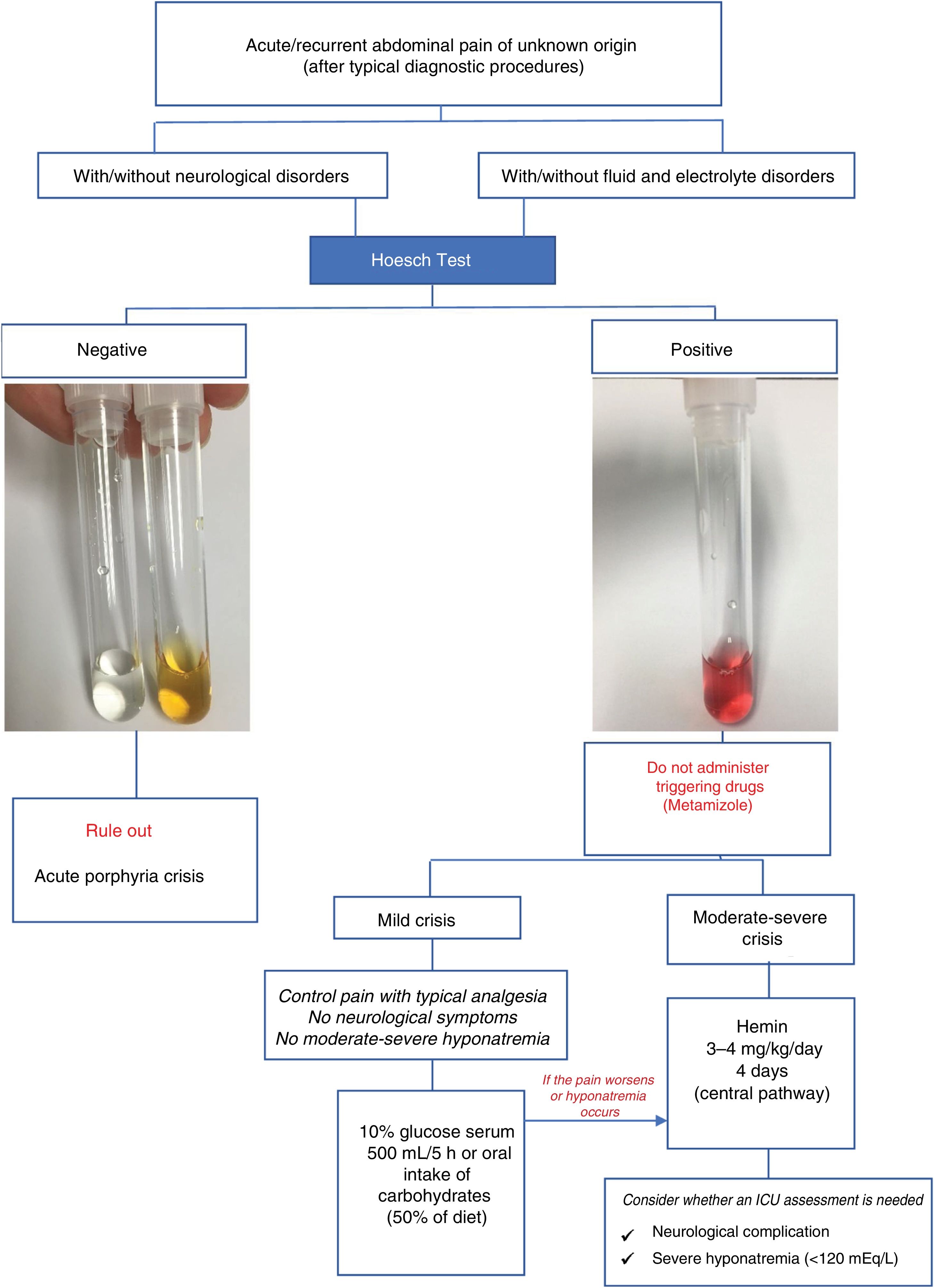
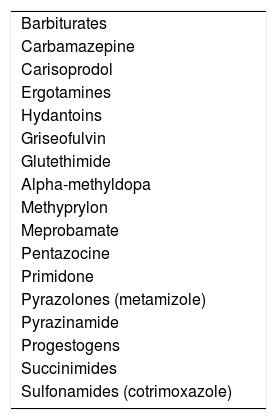
Porphyria are a group of congenital errors in porphyrin metabolism and in the heme biosynthetic pathway. Accumulation of porphyrin precursors (delta-aminolaevulinic acid and porphobilinogen) is responsible for the neurovisceral crises of acute porphyria, which, when expressed clinically, start with intense abdominal pain. During crises, the urinary elimination of porphobilinogen and delta-aminolaevulinic acid is always very high. Excessive porphobilinogen concentration in urine is easily identified using the simple Hoesch test. A negative test rules out a current porphyric crisis. The clinical protocol for patients with acute abdominal pain of unknown origin in whom a positive Hoesch test leads to the suspicion of acute porphyria is based on the following aspects: initial clinical assessment in the emergency department, suppression of potential triggers, specific treatment for the crisis with hemin and/or glucose overload and symptomatic treatment.
Las porfirias son errores congénitos del metabolismo de las porfirinas o ruta biosintética del hemo. El acúmulo de los precursores de las porfirinas, ácido delta aminolevulínico (ALA) y/o porfobilinógeno (PBG) es responsable de las crisis neuroviscerales de las porfirias agudas que cuando se expresan clínicamente se inician con intenso dolor abdominal. Durante las crisis la eliminación urinaria de PBG y ALA siempre es muy elevada. La excesiva concentración de PBG en orina es fácilmente identificable mediante el sencillo test de Hoesch. Un test negativo descarta crisis porfírica actual. El protocolo de actuación en pacientes con dolor abdominal agudo no filiado en los que el test de Hoesch positivo permite la sospecha de porfiria aguda se basa en los siguientes aspectos: valoración clínica inicial en el servicio de urgencias, supresión de los posibles factores desencadenantes, tratamiento específico de la crisis con hemina y/o sobrecarga de glucosa y tratamiento sintomático.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<