El aumento de la presión intraabdominal (PIA) que tiene lugar durante la insuficiencia cardiaca aguda parece estar directamente relacionado con un empeoramiento de la función renal, lo que conduce a peores resultados clínicos. Nuestro objetivo fue analizar la relación entre la PIA y los determinantes de la función renal para la insuficiencia cardiaca aguda descompensada (ICAD) durante el ingreso en un pabellón de medicina interna convencional.
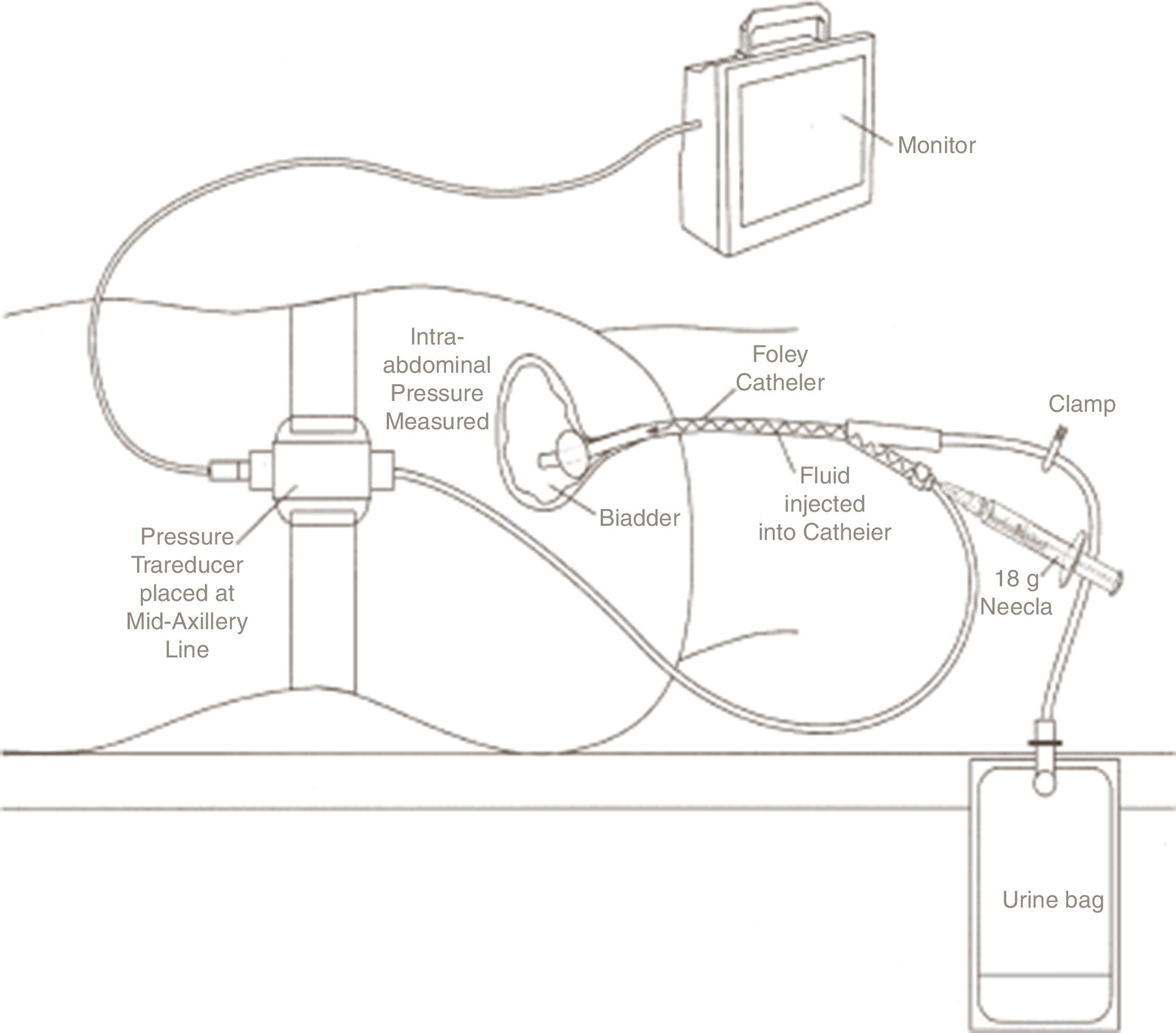
Pacientes y métodosEstudio descriptivo y prospectivo. Se incluyó a aquellos pacientes con una tasa de filtración glomerular > 30mL/min/1,73 m2, dispuestos a participar en el estudio y que otorgaron su consentimiento informado. El protocolo (PI 15 0227) fue aprobado por el Comité de Ética de Aragón.
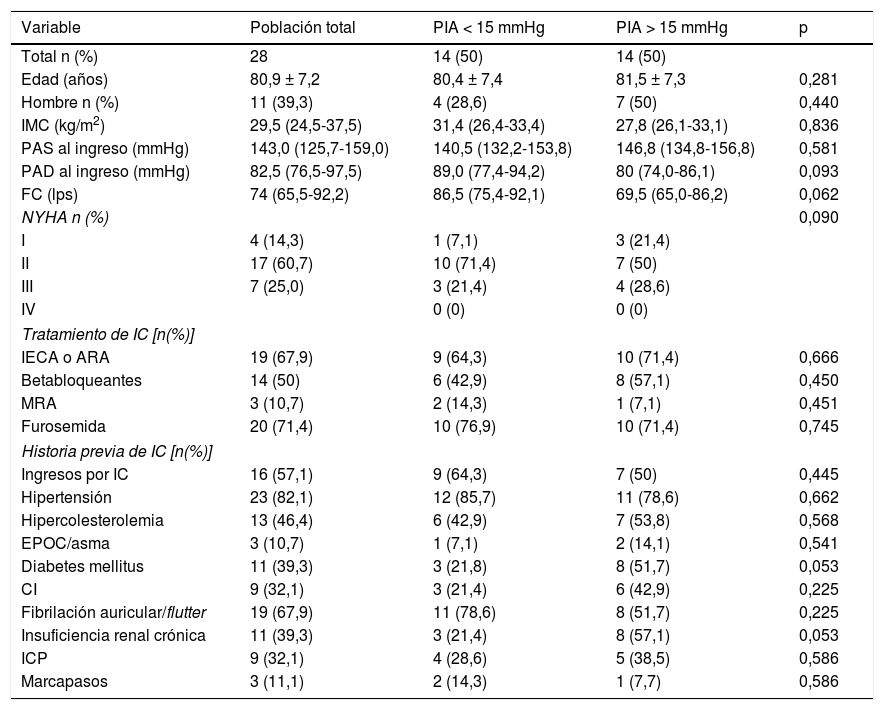
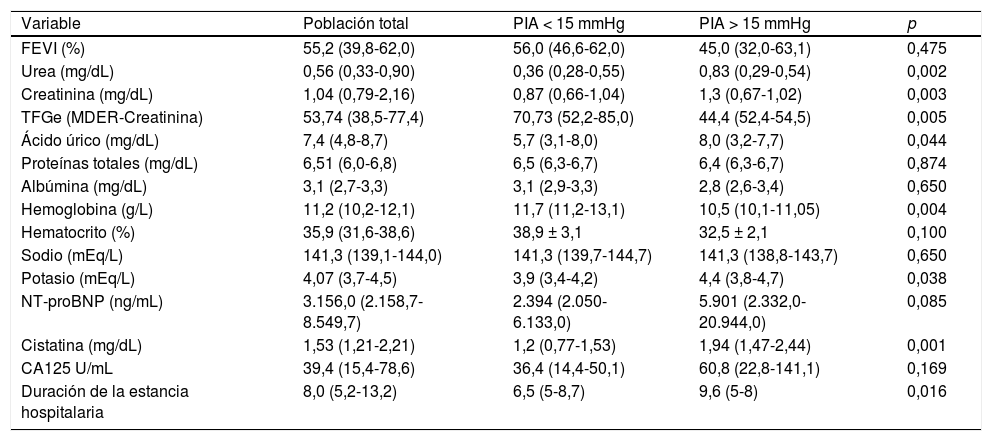
ResultadosPresentamos los resultados de un análisis preliminar llevado a cabo con los primeros 28 pacientes incluidos en el estudio. Los pacientes se segregaron en 2grupos según la mediana de la PIA, alta (PIA > 15mmHg) y baja (PIA < 15mmHg), medida durante las primeras 24 h tras el ingreso por ICAD. Cada grupo estuvo integrado por 14pacientes. No hubo diferencias entre los grupos en cuanto a características clínicas de referencia, comorbilidades ni tratamiento. Los pacientes con PIA superior a los 15mmHg presentaron una tasa de filtración glomerular basal significativamente baja (70,7 vs. 44,4mL/min/1,73 m2 con p = 0,004; urea en sangre 36 vs. 83mg/dL con p = 0,002; creatinina sérica 0,87 vs. 1,3mg/dL con p = 0,004 y cistatina C 1,2 vs. 1,94mg/dL con p = 0,002). Además, estos pacientes mostraron las concentraciones de ácido úrico más altas (5,7 vs. 8,0; p = 0,046), las de hemoglobina resultaron más bajas (11,7 vs. 10,5g/L; p = 0,04) y la estancia hospitalaria más larga (6,5 vs. 9,6 días; p = 0,017).
ConclusionesEl aumento de la PIA parece ser un hallazgo frecuente en pacientes ingresados por ICAD. Independientemente de la PIA, los pacientes comparten un perfil clínico similar, si bien el aumento de la PIA se asoció con un empeoramiento significativo de la función renal de referencia.
An increase in intraabdominal pressure (IAP) during acute heart failure, seems to be directly related to worsening renal function, which leads to worse clinical outcomes. We aimed to analyze the relationship between IAP and determinants of renal function during admission for acute decompensation of heart failure (ADHF) in a conventional Internal Medicine Ward.
Patients and methodsDescriptive and prospective study. Patients admitted for ADHF with an estimated glomerular filtration rate > 30mL/min/1.73 m2, willing to participate and who gave their informed consent were included. Ethics Committee of Aragon approved the protocol (PI 15 0227).
ResultsWe hereby report the results of an interim analysis of the first 28 patients included. Patients were divided in 2groups according to the median of IAP measured during the first 24h after admission for ADHF, namely high IAP (IAP>15mmHg) and low (IAP< 15mmHg). Fourteen patients were included in each group. No differences were found in baseline clinical characteristics, comorbidities or treatment between both groups. Patients with IAP above 15mmHg, showed a significant lower baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate (70.7 vs. 44.4mL/min/1.73 m2 with p=0.004], blood urea 36 vs. 83mg/dL with p=0.002]; serum creatinine 0.87 vs. 1.3mg/dL with p=0.004 and cystatin C 1.2 vs. 1.94mg/dL with p= 0.002. Additionally, these patients had higher uric acid (5.7 vs. 8.0, p=0.046), lower hemoglobin concentrations (11.7 vs. 10.5g/L, p=0.04) and longer length of hospital stay (6.5 vs. 9.6 days, p=0.017).
ConclusionsThe increase in IAP seems to be a frequent finding in patients admitted for ADHF. Patients share similar clinical profile irrespective of IAP, although the increase in IAP is associated with a significant baseline impairment of renal function.
Artículo
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<