Describir el perfil clínico, la comorbilidad y los factores pronósticos de mortalidad intrahospitalaria en una cohorte COVID-19 de un hospital general.
Material y métodosEstudio de cohortes retrospectivo de pacientes con COVID-19 ingresados desde el 26 de febrero, y dados de alta o fallecidos hasta el 29 de abril de 2020; estudio descriptivo y análisis de factores asociados a la mortalidad intrahospitalaria.
ResultadosDe los pacientes ingresados (N=101), se analizaron 96: 79 (82%) dados de alta por curación y 17 (18%) fallecidos. En 92 casos (92,5%) se confirmó COVID-19 por reacción en cadena de la polimerasa a SARS-CoV-2. La edad media fue de 63 años, y el 66% eran varones. La comorbilidad previa más frecuente fue hipertensión arterial (40%), diabetes mellitus (16%) y cardiopatía (14%). Los pacientes que fallecieron tenían significativamente más edad (media 77 vs. 60 años), hipertensión arterial (71% vs. 33%), cardiopatía previa (47% vs. 6%), y niveles más elevados de lactato deshidrogenasa (LDH) (662 vs. 335UI/L) y proteína C reactiva (PCR) (193 vs. 121mg/L) al ingreso. En el análisis multivariante, se asociaron significativamente a mayor riesgo de muerte la presencia de cardiopatía (IC 95% OR 2,58-67,07), los niveles de LDH≥345UI/L (IC 95% OR 1,52-46,00), y la edad≥65 años (IC 95% OR 1,23-44,62).
ConclusionesEl antecedente de cardiopatía, los niveles de LDH≥345UI/L al ingreso y una edad≥65 años se asocian a una mayor mortalidad durante el ingreso por COVID-19. Hay que validar este modelo pronóstico en cohortes prospectivas.
To describe clinical features, comorbidity, and prognostic factors associated with in-hospital mortality in a cohort of COVID-19 admitted to a general hospital.
Material and methodsRetrospective cohort study of patients with COVID-19 admitted from 26th February, who had been discharged or died, up to 29th April, 2020. A descriptive study and an analysis of factors associated with intrahospital mortality were performed.
ResultsOut of the 101 patients, 96 were analysed. Of these, 79 (82%) recovered and were discharged, and 17 (18%) died in the hospital. Diagnosis of COVID-19 was confirmed by polymerase chain reaction to SARS-CoV-2 in 92 (92.5%). The mean age was 63 years, and 66% were male. The most frequent comorbidities were hypertension (40%), diabetes mellitus (16%) and cardiopathy (14%). Patients who died were older (mean 77 vs 60 years), had higher prevalence of hypertension (71% vs 33%), and cardiopathy (47% vs 6%), and higher levels of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and reactive C protein (mean 662 vs 335UI/L, and 193 vs 121mg/L respectively) on admission. In a multivariant analysis the variables significantly associated to mortality were the presence of cardiopathy (CI 95% OR 2,58-67,07), levels of LDH≥345IU/L (CI 95% OR 1,52-46,00), and age≥65 years (CI 95% OR 1,23-44,62).
ConclusionsThe presence of cardiopathy, levels of LDH≥345IU/L and age ≥65 years are associated with a higher risk of death during hospital stay for COVID-19. This model should be validated in prospective cohorts.
En diciembre de 2019 aparecieron en Wuhan (China) los primeros casos de neumonía originados por una nueva cepa de coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), denominándose la nueva enfermedad COVID-19. El 31 de enero de 2020 se registró el primero caso importado en España y el 26 de febrero el primer contagio local. El 11 de marzo fue declarada la pandemia por la Organización Mundial de la Salud.
A fecha de 10 de mayo de 2020, se han comunicado en el mundo 3.986.119 casos, de los que 278.814 han fallecido1; en este momento, España es el segundo país del mundo con más casos notificados: 224.390 casos confirmados por reacción en cadena de la polimerasa a SARS-CoV-2 (PCR-CoV-2), con 26.621 fallecidos y 136.166 infecciones resueltas2.
Desde el inicio de la pandemia se han ido incorporando recomendaciones terapéuticas basadas en estudios con muchas limitaciones de tamaño y diseño. Aún no existen tratamientos específicos con base científica sólida, y el manejo de los pacientes se sustenta en el tratamiento de soporte, especialmente la oxigenación, y en cambiantes protocolos farmacoterapéuticos, con la recomendación de incluir a los pacientes en ensayos clínicos siempre que sea posible.
En ausencia de un tratamiento efectivo, el conocimiento de las características de los pacientes que puedan predecir una peor evolución desde el mismo momento del ingreso puede ser útil para identificar a aquellos que deberían ingresar, o en los que hay que intensificar las medidas de soporte o iniciar precozmente los tratamientos recomendados. Por ello planteamos en este estudio describir los primeros casos de COVID-19 ingresados en un hospital general, y analizar las características al ingreso asociadas a la mortalidad intrahospitalaria.
Material y métodosSe realizó un estudio de cohortes retrospectivo, que incluyó a los pacientes ingresados de forma consecutiva en el Hospital Costa del Sol de Marbella (Málaga) por COVID-19, desde el primer caso (26/02/2020), que hubieran sido dados de alta por curación o que hubieran fallecido hasta el 29 de abril de 2020. El diagnóstico exigió la positividad de PCR-CoV-2 en muestras respiratorias de nasofaringe, esputo, o broncoaspirado, y/o la presencia de serología positiva y un cuadro clínico compatible.
Se obtuvo muestra nasofaríngea y de esputo siempre que el paciente pudiera expectorar. Cuando la PCR-CoV-2 era negativa en ambas y persistía la sospecha clínica se valoró la repetición de la toma de muestras y/o la realización de broncoscopia y toma de muestras respiratorias profundas. Se detectó la presencia de SARS-CoV-2 en muestras respiratorias mediante protocolos de reacción en cadena de la transcriptasa inversa-polimerasa (RT-PCR) de 2 proveedores (VIASURE SARS-CoV-2 de CerTest Biotec y LightMix Modular SARS-CoV —COVID19—, Roche). Las muestras con cycle threshold (Ct) entre 38 y 40 se repitieron por otra técnica de RT-PCR. Se detectaron anticuerpos IgG e IgM en suero mediante inmunocromatografía en fase sólida (COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid Test Cassette, Zhejiang Orient Gene Biotech Co.LTD).
El centro es un hospital de especialidades de 387 camas; su población de referencia es de 410.022 habitantes, con 12 puestos en la unidad de cuidados intensivos (UCI), ampliados a 31 con la ocupación de otras áreas hospitalarias.
No se protocolizó la recogida de consentimiento informado ya que la información utilizada es exclusivamente de la historia clínica, considerándose un riesgo innecesario tanto la firma como su posterior archivo, al tratarse de población infectada, además de considerarse los resultados de interés de salud pública. Todos los datos recogidos fueron registrados de forma anónima, siguiendo estrictamente las leyes y normas de protección de datos en vigor (Ley Orgánica 3/2018 de 5 de diciembre, de Protección de Datos Personales y Garantía de los Derechos Digitales).
Desde el primer ingreso por COVID-19, el 26 de febrero de 2020, se incluyeron todos los ingresos por COVID-19 en una base de datos prospectiva, con variables demográficas, antecedentes médicos y datos clínicos y analíticos al ingreso. Durante la estancia hospitalaria se registraron datos clínicos, radiológicos y analíticos evolutivos.
Entre las características basales registradas se incluyeron: edad, sexo, comorbilidad, tabaquismo, uso de inhibidores de la enzima convertidora de angiotensina (IECA) o antagonistas de los receptores de angiotensina II (ARAII) y polimedicación (definida como uso de más de 5 fármacos). Se registraron variables sobre la presentación clínica inicial (síntomas, SatO2 basal, variables analíticas y radiológicas). Realizamos un análisis descriptivo con variables cuantitativas como media y desviación estándar (DE), y cualitativas como número absoluto y porcentaje.
Se llevó a cabo un análisis bivariante para detectar diferencias entre supervivientes y fallecidos. Se utilizó t de Student para las variables continuas y χ2 o test exacto de Fisher para las variables categóricas. Se realizó un modelo de regresión logística multivariante tomando como variable resultado la muerte intrahospitalaria, e incluyendo aquellas variables con significación estadística en el análisis crudo (dicotomizando las variables cuantitativas utilizando como criterio la mediana para facilitar la interpretación del modelo). Se utilizó como criterio de entrada p<0,05 y salida p>0,1, con método adelante según razón de verosimilitud. Se evaluó la varianza a través de R cuadrado de Nagelkerke y la bondad de ajuste a través de la prueba de Hosmer y Lemeshow, describiendo las odds ratio con sus respectivos intervalos de confianza al 95%. En los análisis estadísticos, se estableció el nivel de significación en p<0,05. Se utilizó para el análisis estadístico el programa SPSS versión 15.
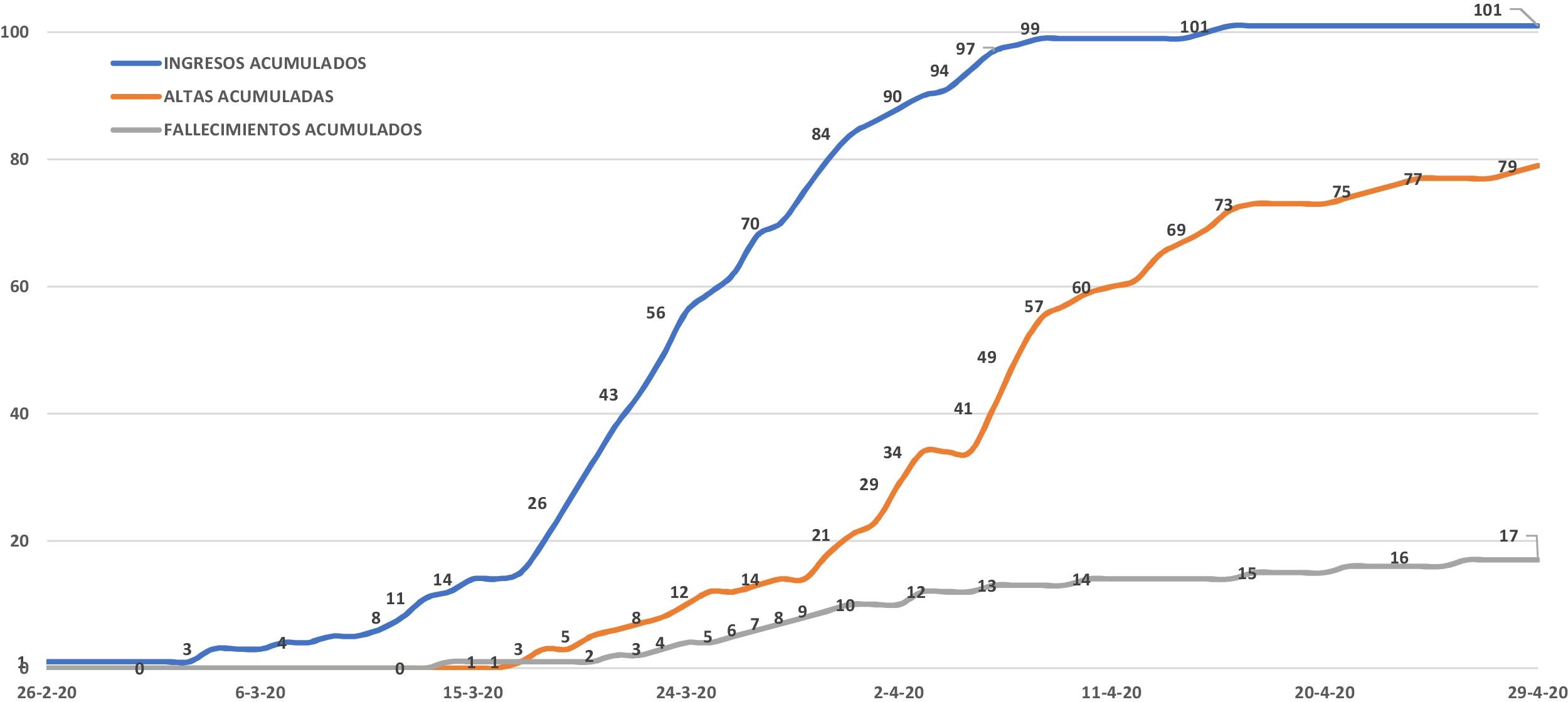
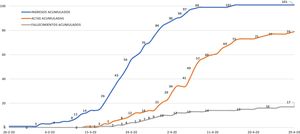
ResultadosDurante el período de estudio ingresaron 101 pacientes por COVID-19 en el Hospital Costa del Sol. A fecha de 29 de abril habían sido dados de alta o habían fallecido 96 de ellos, constituyendo el grupo de estudio. Los otros 5 pacientes fueron excluidos por continuar ingresados (fig. 1). Al cierre del estudio los casos de COVID-19 en el área de cobertura hospitalaria ascendían a 395, con 21 fallecimientos (tasa de incidencia de 96,34 y de mortalidad de 5,12 por 100.000 habitantes, respectivamente), con una letalidad del 5,31%.
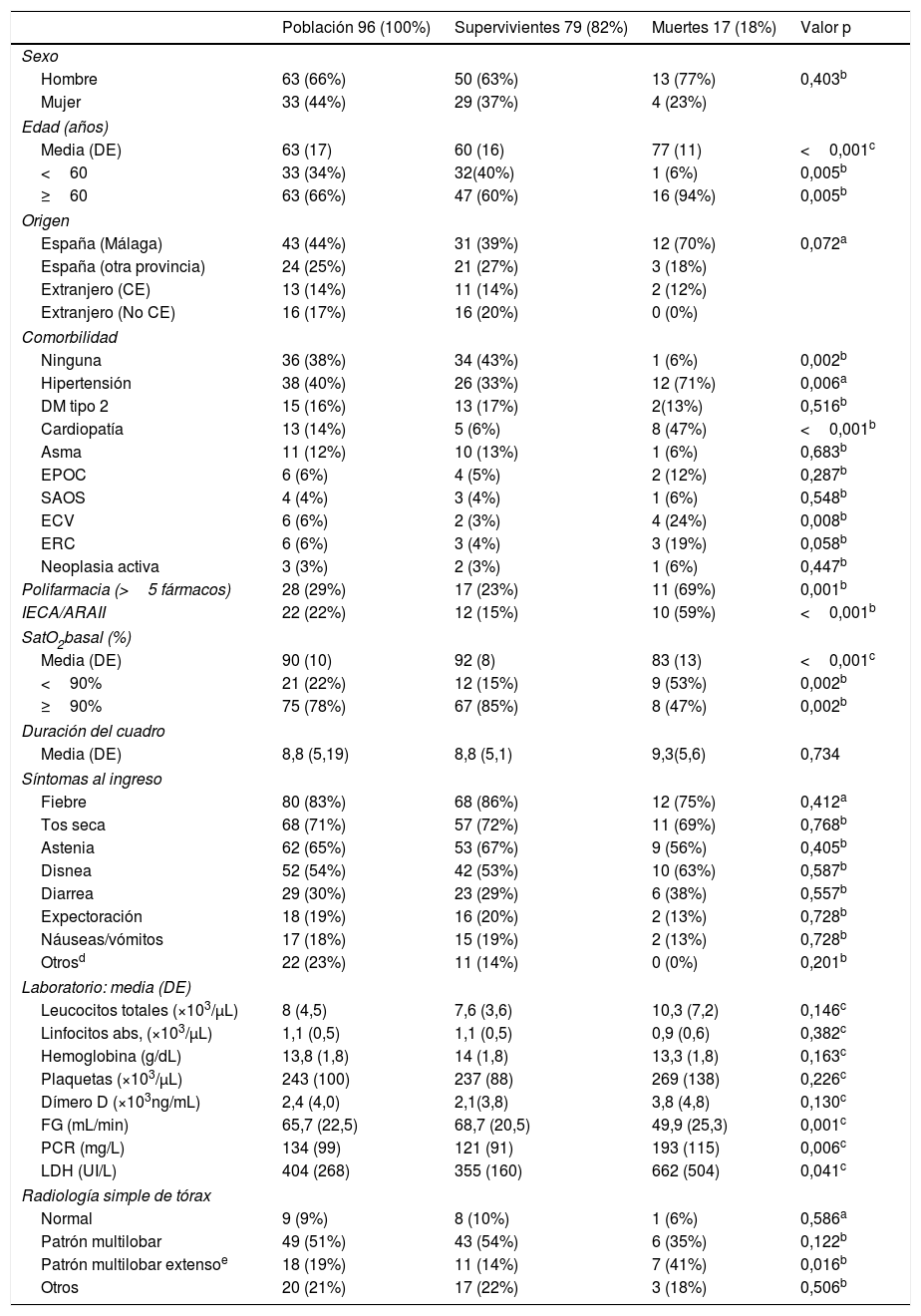
En la tabla 1 se muestran las características basales de los pacientes y los hallazgos clínicos, radiológicos y de laboratorio al ingreso. La edad media fue 63 años y el 66% eran varones. El 38% no presentaba ninguna comorbilidad y el 60% ningún hábito tóxico. Las comorbilidades más frecuentes fueron: hipertensión arterial, diabetes mellitus y cardiopatía. Casi la cuarta parte de los pacientes estaba en tratamiento con IECA o ARAII, y el 29% estaba polimedicado.
Características basales al ingreso analizadas por subgrupos según evolución clínica: supervivientes y muertes
| Población 96 (100%) | Supervivientes 79 (82%) | Muertes 17 (18%) | Valor p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sexo | ||||
| Hombre | 63 (66%) | 50 (63%) | 13 (77%) | 0,403b |
| Mujer | 33 (44%) | 29 (37%) | 4 (23%) | |
| Edad (años) | ||||
| Media (DE) | 63 (17) | 60 (16) | 77 (11) | <0,001c |
| <60 | 33 (34%) | 32(40%) | 1 (6%) | 0,005b |
| ≥60 | 63 (66%) | 47 (60%) | 16 (94%) | 0,005b |
| Origen | ||||
| España (Málaga) | 43 (44%) | 31 (39%) | 12 (70%) | 0,072a |
| España (otra provincia) | 24 (25%) | 21 (27%) | 3 (18%) | |
| Extranjero (CE) | 13 (14%) | 11 (14%) | 2 (12%) | |
| Extranjero (No CE) | 16 (17%) | 16 (20%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Comorbilidad | ||||
| Ninguna | 36 (38%) | 34 (43%) | 1 (6%) | 0,002b |
| Hipertensión | 38 (40%) | 26 (33%) | 12 (71%) | 0,006a |
| DM tipo 2 | 15 (16%) | 13 (17%) | 2(13%) | 0,516b |
| Cardiopatía | 13 (14%) | 5 (6%) | 8 (47%) | <0,001b |
| Asma | 11 (12%) | 10 (13%) | 1 (6%) | 0,683b |
| EPOC | 6 (6%) | 4 (5%) | 2 (12%) | 0,287b |
| SAOS | 4 (4%) | 3 (4%) | 1 (6%) | 0,548b |
| ECV | 6 (6%) | 2 (3%) | 4 (24%) | 0,008b |
| ERC | 6 (6%) | 3 (4%) | 3 (19%) | 0,058b |
| Neoplasia activa | 3 (3%) | 2 (3%) | 1 (6%) | 0,447b |
| Polifarmacia (>5 fármacos) | 28 (29%) | 17 (23%) | 11 (69%) | 0,001b |
| IECA/ARAII | 22 (22%) | 12 (15%) | 10 (59%) | <0,001b |
| SatO2basal (%) | ||||
| Media (DE) | 90 (10) | 92 (8) | 83 (13) | <0,001c |
| <90% | 21 (22%) | 12 (15%) | 9 (53%) | 0,002b |
| ≥90% | 75 (78%) | 67 (85%) | 8 (47%) | 0,002b |
| Duración del cuadro | ||||
| Media (DE) | 8,8 (5,19) | 8,8 (5,1) | 9,3(5,6) | 0,734 |
| Síntomas al ingreso | ||||
| Fiebre | 80 (83%) | 68 (86%) | 12 (75%) | 0,412a |
| Tos seca | 68 (71%) | 57 (72%) | 11 (69%) | 0,768b |
| Astenia | 62 (65%) | 53 (67%) | 9 (56%) | 0,405b |
| Disnea | 52 (54%) | 42 (53%) | 10 (63%) | 0,587b |
| Diarrea | 29 (30%) | 23 (29%) | 6 (38%) | 0,557b |
| Expectoración | 18 (19%) | 16 (20%) | 2 (13%) | 0,728b |
| Náuseas/vómitos | 17 (18%) | 15 (19%) | 2 (13%) | 0,728b |
| Otrosd | 22 (23%) | 11 (14%) | 0 (0%) | 0,201b |
| Laboratorio: media (DE) | ||||
| Leucocitos totales (×103/μL) | 8 (4,5) | 7,6 (3,6) | 10,3 (7,2) | 0,146c |
| Linfocitos abs, (×103/μL) | 1,1 (0,5) | 1,1 (0,5) | 0,9 (0,6) | 0,382c |
| Hemoglobina (g/dL) | 13,8 (1,8) | 14 (1,8) | 13,3 (1,8) | 0,163c |
| Plaquetas (×103/μL) | 243 (100) | 237 (88) | 269 (138) | 0,226c |
| Dímero D (×103ng/mL) | 2,4 (4,0) | 2,1(3,8) | 3,8 (4,8) | 0,130c |
| FG (mL/min) | 65,7 (22,5) | 68,7 (20,5) | 49,9 (25,3) | 0,001c |
| PCR (mg/L) | 134 (99) | 121 (91) | 193 (115) | 0,006c |
| LDH (UI/L) | 404 (268) | 355 (160) | 662 (504) | 0,041c |
| Radiología simple de tórax | ||||
| Normal | 9 (9%) | 8 (10%) | 1 (6%) | 0,586a |
| Patrón multilobar | 49 (51%) | 43 (54%) | 6 (35%) | 0,122b |
| Patrón multilobar extensoe | 18 (19%) | 11 (14%) | 7 (41%) | 0,016b |
| Otros | 20 (21%) | 17 (22%) | 3 (18%) | 0,506b |
ARAII: antagonistas de los receptores de angiotensina II; CE: Comunidad Europea; DE: desviación estándar; DM: diabetes mellitus; ECV: enfermedad cerebrovascular; EPOC: enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica; ERC: enfermedad renal crónica; FG: filtrado glomerular por CKD-EPI; IECA: inhibidores de la enzima convertidora de angiotensina; LDH: lactato deshidrogenasa; PCR: proteína C reactiva; SAOS: síndrome de la apnea obstructiva del sueño; SatO2: saturación de oxígeno.
Al ingreso, la duración media del cuadro clínico fue de 8,85 días (rango 1-27), inferior a las 2 o las 3 semanas en el 50% y 91,3%, respectivamente. Los síntomas más frecuentemente referidos fueron: fiebre (83%), tos seca (71%), astenia (65%) y disnea (54%). La SatO2 basal fue inferior al 90% en el 22%. La radiografía de tórax fue normal en el 9,4%; el 19% presentó patrón multilobar, y el 49% patrón multilobar extenso (definido como afectación unilateral de más de un 50% o bilateral de más de un 25%). Se realizó TAC de tórax a 7 pacientes y ecografía pulmonar a 12 pacientes. Al ingreso el recuento linfocitario medio fue bajo y los niveles medios de dímero D, PCR y LDH eran elevados. Se dispuso de niveles de ferritina en solo 62 casos, y de interleucina-6, en 42 casos, con una media (DE) de concentración de 1.037ng/mL (DE: 1.002) y 73,1pg/mL (DE: 191,5), respectivamente.
El diagnóstico de COVID-19 se estableció por PCR-CoV-2 en 92 pacientes (95,8%). Los 4 pacientes con PCR-CoV-2 negativa tuvieron serología positiva a SARS-CoV-2, IgG e IgM simultáneas en los 4 casos. La PCR-CoV-2 en muestra nasofaríngea fue positiva en 81 de 94 casos (86,2%) y en esputo, en 34 de 79 (43,03%). Se realizaron 4 broncoscopias, resultando positivas en todas la PCR-CoV-2 del broncoaspirado. De los 13 pacientes con PCR-CoV-2 nasofaríngea negativa, 8 tuvieron PCR-CoV-2 positiva en esputo, uno en broncoaspirado, y 4 serología positiva (IgG e IgM simultáneas). Los 2 pacientes a los que no se tomó muestra nasofaríngea presentaron PCR-CoV-2 positiva en esputo.
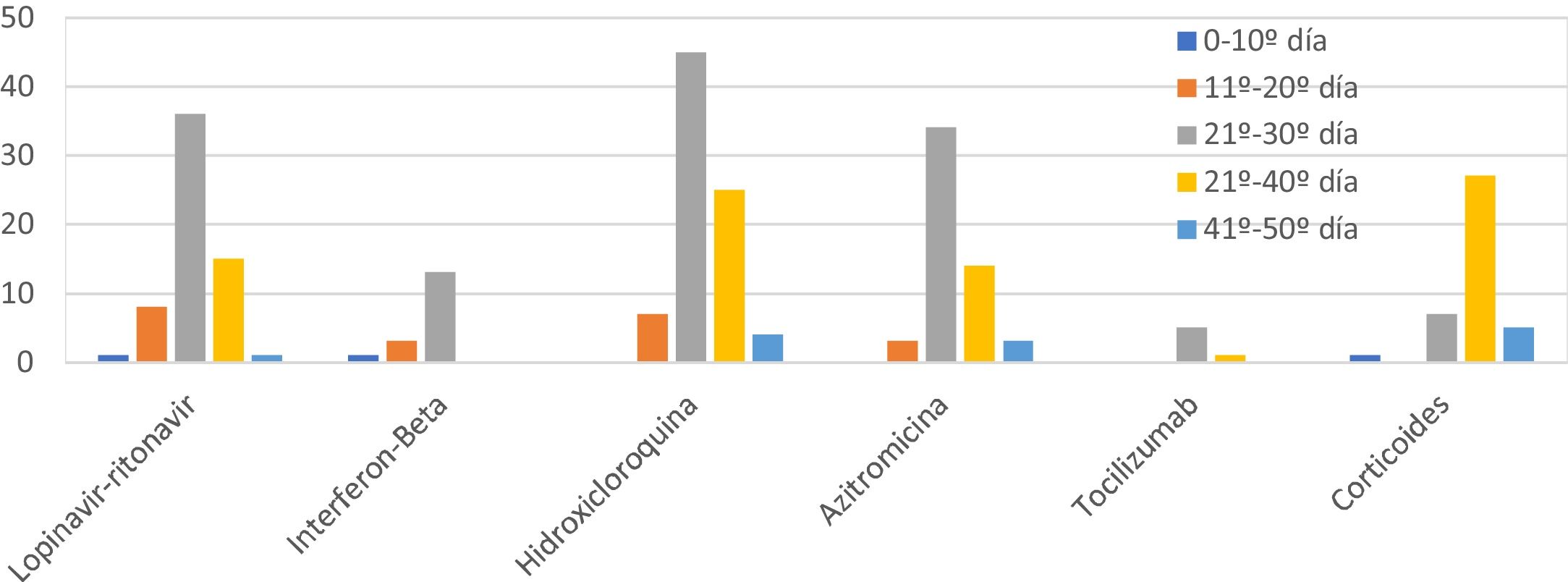
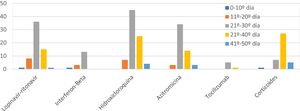
Las combinaciones de fármacos utilizados fueron cambiando durante el estudio por la aparición de nuevos protocolos (fig. 2). El fármaco más utilizado fue la hidroxicloroquina (85,4%), seguido de lopinavir/ritonavir (61,5%), azitromicina (58,3%), interferón beta-1B (IFNb) (17,7%) y tocilizumab (6,3%). El 39,6% de los pacientes recibió corticoides a dosis equivalentes≥80mg/día de metilprednisolona. La combinación más frecuente fue la de hidroxicloroquina con azitromicina y lopinavir-ritonavir (31, en 11 de ellos combinados a IFNb), seguida de hidroxicloroquina con azitromicina en 24 casos y lopinavir/ritonavir con hidroxicloroquina en 26. La mediana de duración fue: hidroxicloroquina 8 días, lopinavir/ritonavir 10 días, azitromicina 5 días, IFNb 9 días, y corticoides 9 días. No se produjeron arritmias significativas.
Precisaron oxigenoterapia de alto flujo 13 pacientes (13,5%), ventilación mecánica no invasiva un paciente y ventilación mecánica invasiva 18 (18,75%), con una duración media de ésta de 13 días.
De los 96 pacientes, 79 (82,3%) fueron dados de alta, considerados curados. Los otros 17 (17,7%) fallecieron transcurridos una media de 7,88 días de estancia (entre 1 y 33 días). La causa más frecuente de muerte fue el distrés respiratorio en 14 pacientes (82,3%), seguido de fallo multiorgánico en 2 (11,8%) y sepsis en uno (5,9%). No se identificaron eventos isquémicos cardíacos agudos ni arritmias. La estancia media global fue de 11 días y la de los supervivientes, de 12,03 días. Precisaron ingreso en UCI 18 pacientes (18,7%), falleciendo 4 (22,2%). De forma simultánea llegaron a estar en UCI hasta 15 pacientes con COVID-19. En la unidad de cuidados intermedios (creada ad-hoc como área para administración de oxígeno a alto flujo o ventilación mecánica no invasiva) ingresaron 13 pacientes (13,5%): 3 se trasladaron a UCI y, de los otros 10, fallecieron 4. Dos pacientes fallecieron en el área de Urgencias. La mortalidad combinada UCI-unidad de cuidados intermedios fue del 25,8%.
En el análisis bivariante no se detectó asociación estadísticamente significativa entre mortalidad y género. La edad, la polifarmacia y el tratamiento previo con IECA o ARAII fueron significativamente más frecuentes en los fallecidos. En solo el 6% de estos no se detectaron comorbilidades, frente al 43% en los supervivientes (p=0,004). Los fallecidos tenían significativamente mayor frecuencia de hipertensión, enfermedad cerebrovascular, y cardiopatía, peor SatO2 media basal, menores niveles de filtrado glomerular y concentraciones medias más elevadas de PCR y LDH. No se detectó relación significativa entre el recuento linfocitario medio ni la concentración media de dímero D y la mortalidad. El patrón radiográfico multilobar extenso fue significativamente más frecuente en los fallecidos (tabla 1).
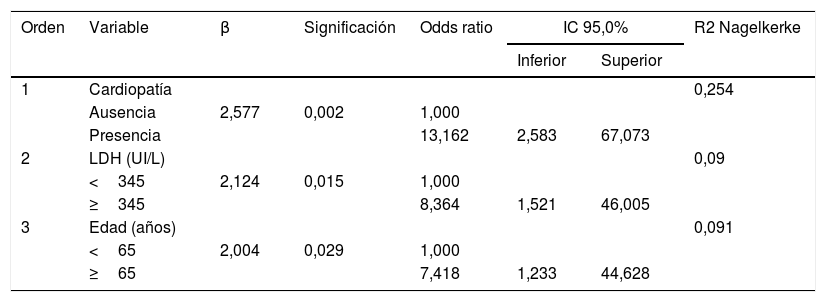
En el modelo multivariante se incluyeron las variables con significación estadística en el análisis crudo. Las variables continuas fueron dicotomizadas por el valor de la mediana. Se ajustaron como factores de riesgo independientes de mortalidad la presencia de cardiopatía con una OR de 13,162 (IC 95%: 2,583-67,073), unos niveles de LDH iguales o superiores a 345UI/L con una OR de 8,364 (IC 95%: 1,521-46,005), y la edad mayor o igual a 65 años con una OR de 7,418 (IC 95%: 1,233-44,628), El modelo mostró un correcto ajuste (p=0,994) y una varianza explicada (R2 de Nagelkerke) del 43,5% (tabla 2).
Modelo final de regresión logística predictivo de la mortalidad durante el ingreso, incluyendo la parte de la varianza de la variable dependiente explicada por cada variable (R2 de Nagelkerke)
| Orden | Variable | β | Significación | Odds ratio | IC 95,0% | R2 Nagelkerke | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inferior | Superior | ||||||
| 1 | Cardiopatía | 0,254 | |||||
| Ausencia | 2,577 | 0,002 | 1,000 | ||||
| Presencia | 13,162 | 2,583 | 67,073 | ||||
| 2 | LDH (UI/L) | 0,09 | |||||
| <345 | 2,124 | 0,015 | 1,000 | ||||
| ≥345 | 8,364 | 1,521 | 46,005 | ||||
| 3 | Edad (años) | 0,091 | |||||
| <65 | 2,004 | 0,029 | 1,000 | ||||
| ≥65 | 7,418 | 1,233 | 44,628 | ||||
El inicio de la pandemia de COVID-19 ha supuesto la mayor sobrecarga aguda no planificada en la historia del Sistema Nacional de Salud. Ha obligado a los hospitales a reorganizar espacios y tareas, y a anular o demorar la mayoría de las actividades programadas. La elevada proporción de pacientes graves ha sobrepasado la capacidad de la mayoría de los hospitales. En este contexto, y sin experiencia previa con la enfermedad, es esencial conocer qué factores pronósticos permiten identificar precozmente a los pacientes con riesgo de mala evolución.
Nuestro estudio demuestra que la edad, la presencia de cardiopatía y los niveles de LDH al ingreso se asocian a un riesgo elevado de muerte y explican una proporción elevada de los fallecidos.
En la extensa literatura generada ya sobre COVID-19, se han identificado factores pronósticos de mala evolución y mortalidad. Una revisión de estudios pronósticos demostró que la mayoría presentan limitaciones metodológicas3: excluyen una proporción significativa de pacientes que no alcanzan el evento resultado (muerte o alta), recogen variables en distintos momentos4, se basan en información del TAC de tórax (no siempre disponible al ingreso)5,6, o incluyen variables de difícil obtención7.
Desde las primeras series publicadas se evidenció que la edad avanzada y la comorbilidad conllevan mayor riesgo de mortalidad8–10. Un estudio en Wuhan encontró que la edad avanzada, puntuaciones elevadas de la escala SOFA y un dímero D elevado eran factores de riesgo de mortalidad11. Otra serie de Wuhan encontró relación entre mortalidad y la comorbilidad, infección secundaria y reactantes elevados12. Otros parámetros relacionados con el riesgo de muerte han sido niveles elevados de PCR9 o LDH4,10,13, recuentos linfocitarios4,10 o plaquetarios14 bajos y baja SatO2 al ingreso10.
En nuestra cohorte confirmamos que la edad es un factor de riesgo muy poderoso. Aunque, al ingreso hospitalario, los niveles de dímero D estaban más elevados y la SatO2 más baja en los pacientes que fallecieron, la diferencia no alcanzó la significación estadística. Sí se identificó el valor de LDH como una variable significativa. Los primeros estudios publicados constataron que las comorbilidades más frecuentemente asociadas a la enfermedad eran la hipertensión arterial, la diabetes y la cardiopatía11. La enfermedad cardiovascular se asocia especialmente a un incremento de la mortalidad15.
Como ha ocurrido en todas las series publicadas, en nuestros pacientes la causa más frecuente de muerte ha sido el síndrome de distrés respiratorio agudo. El daño miocárdico, con insuficiencia cardíaca y arritmias secundarias se han asociado a un aumento de mortalidad por COVID-1916, aunque en nuestra serie no hubo muertes por causa cardíaca.
Nuestro estudio tiene varias fortalezas. Nuestra serie es altamente representativa, ya que incluye 17 de los 21 fallecimientos totales (80,9%) ocurridos en el área de cobertura del hospital durante el período de estudio. Los datos fueron recogidos de forma prospectiva consecutiva, excluyendo solo 5 de los 101 pacientes por continuar ingresados. La mortalidad fue baja y no puede achacarse a que se ingresaran pacientes leves, ya que de los 290 pacientes con PCR-CoV-2 positiva atendidos en el hospital solo ingresaron el 34,4%, y el 29,2% precisó ingreso en UCI o en la unidad de cuidados intermedios, similar al 30% recientemente comunicado en una serie norteamericana17 e inferior a las primeras series publicadas en China4. La tasa de mortalidad en UCI también fue similar a otras reportadas previamente18,19 y muy inferior al 61,5% comunicado en una de las primeras series publicadas al inicio de la epidemia20.
La tasa de mortalidad de nuestro estudio es muy inferior a las primeras series publicadas en Wuhan11 y similar a series chinas y americanas más recientes15,16,21, aunque nuestros pacientes tenían una edad media más avanzada. Finalmente, pese al escaso número de fallecimientos que tuvimos, el modelo obtenido explica una amplia varianza (43,5%) de la mortalidad intrahospitalaria.
Una de las principales limitaciones para establecer relaciones causales entre nuestras variables y la mortalidad, común a otras series publicadas, es la heterogeneidad de tratamientos empleados, consecuencia de la evolución de las recomendaciones. Por otro lado, es probable que próximamente un mejor acceso al diagnóstico y la aparición de tratamientos específicos efectivos pueda cambiar el perfil de la enfermedad favoreciendo el diagnóstico precoz y una mejor estratificación pronóstica.
ConclusionesNuestro modelo demuestra que el antecedente de cardiopatía, niveles de LDH≥345UI/L al ingreso y una edad≥65 años se asocian a una mayor mortalidad durante el ingreso por COVID-19. Sin embargo, este modelo debería validarse en otras cohortes.
Conflicto de interesesLos autores declaran no tener ningún conflicto de intereses.
A los doctores María Luisa Hortas Nieto y Fernando Fernández Sánchez, que contribuyeron a la realización del estudio; a Francisco Rivas Ruiz, por el apoyo en el análisis estadístico; a Javier García Alegría y María Dolores Martín Escalante, por la revisión del manuscrito.