Protocolos para el manejo de la Enfermedad Tromboembólica Venosa
Más datosLa correcta estratificación del riesgo de la embolia pulmonar (EP) es esencial para la toma de decisiones, en cuanto al tratamiento y para definir el lugar de ingreso del paciente. En la EP de riesgo alto se requiere un restablecimiento urgente de la circulación pulmonar e ingreso en una unidad de críticos. El tratamiento de reperfusión de elección es la trombólisis sistémica, aunque en determinadas situaciones, sobre todo cuando existe contraindicación para esta, valoraremos realizar una embolectomía quirúrgica o alguna de las terapias guiadas por catéter. En el resto de EP, el tratamiento de elección será la anticoagulación. En la actualidad, los anticoagulantes orales de acción directa han pasado a ser el tratamiento de elección para el tratamiento de la EP, por su mejor perfil de seguridad, aunque las heparinas de bajo peso molecular seguidas de los antivitaminas K siguen siendo el tratamiento más utilizado, por el hecho de estar financiados por el sistema público. En los casos de EP con parada cardiorrespiratoria o shock cardiogénico, siempre que esté disponible en nuestro centro, deberemos considerar la indicación de la extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). La reciente creación de los equipos de respuesta multidisciplinar (PERT team) han supuesto una mejoría en la atención de los pacientes con EP de riesgo intermedio-alto y alto. Durante el seguimiento de los pacientes con EP, es imprescindible realizar un correcto cribado de la hipertensión pulmonar tromboembólica crónica, para poder realizar un correcto abordaje diagnóstico y, en el caso que lo precisase, terapéutico.
The correct stratification of pulmonary embolism risk (PE) is essential for decision-making, regarding treatment and defining the patient's place of admission. In high-risk PE, urgent re-establishment of pulmonary circulation and admission to a critical unit is required. The reperfusion treatment of choice is systemic thrombolysis, although in certain situations, especially when there is a contraindication for it, we will evaluate a surgical embolectomy or one of the catheter-guided therapies. In the rest of PE, the treatment of choice will be anticoagulation. Currently, direct oral anticoagulants have become the treatment of choice for the treatment of PE, due to their better safety profile. However, low molecular weight heparins and subsequently antivitamins K, remain the most used treatment, because they are funded by the public system. In cases of PE with cardiorespiratory arrest and / or cardiogenic shock, whenever available at our center, we must consider the indication of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. The recent creation of PE response teams (PERT team), have meant an improvement in the care of patients with intermediate-high and high risk PE. During the follow-up of patients with PE, it is essential to perform a correct screening of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension, in order to perform a correct diagnostic and therapeutic approach.
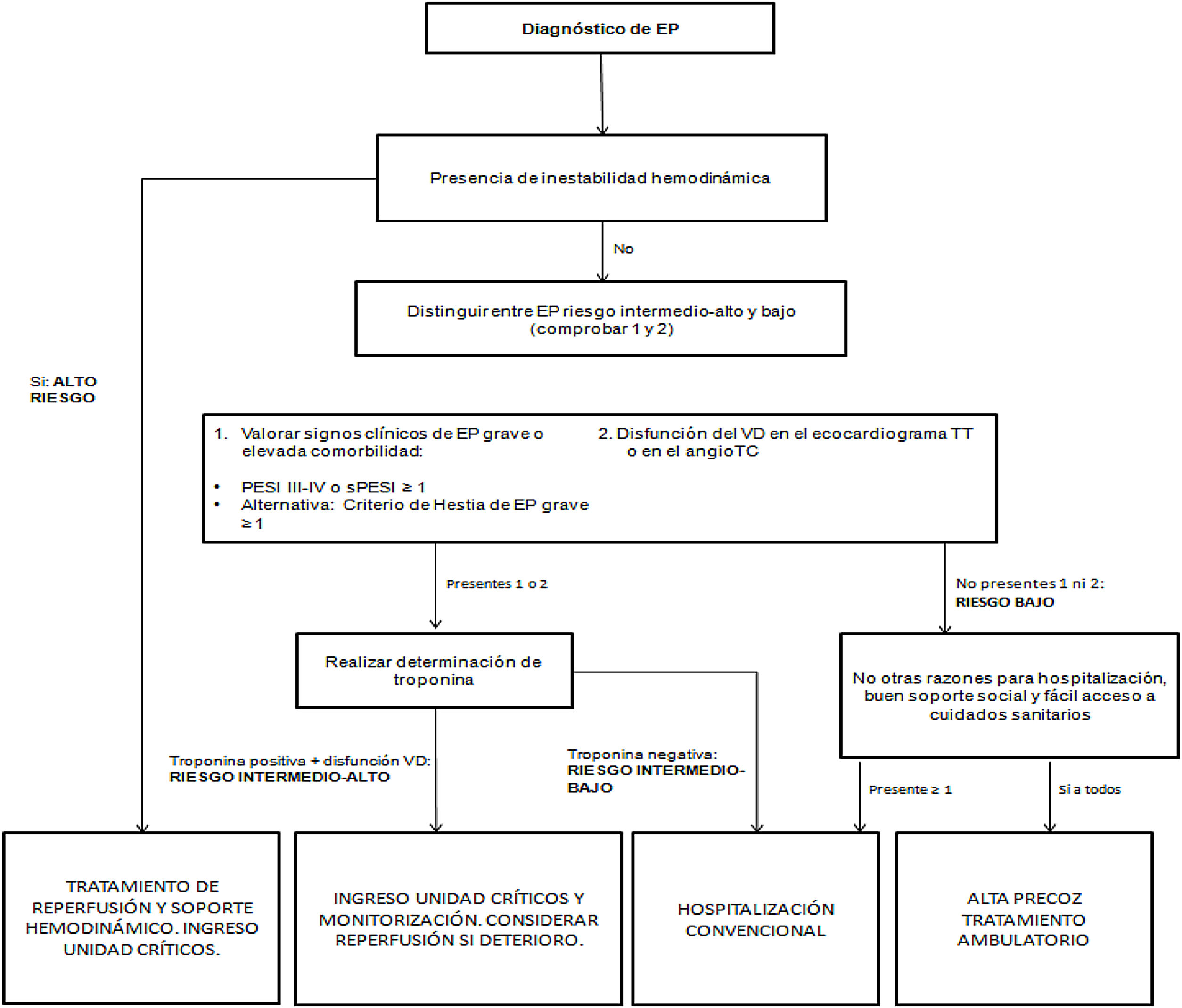
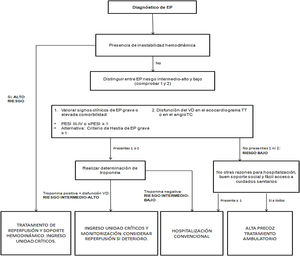
La presentación de la EP es muy heterogénea, por lo que es imprescindible identificar de manera precoz a los pacientes con alto riesgo de deterioro clínico y hemodinámico. Ver algoritmo de estratificació del riesgo en la figura 1. Asimismo, la tolerancia clínica y hemodinámica de la EP no dependerá únicamente de la extensión de la misma, sino que también dependerá de la reserva cardiopulmonar del paciente, siendo la disfunción del ventrículo derecho (VD) el factor pronóstico más importante1.
EP de alto riesgoSe considerarán pacientes de alto riesgo aquellos que se presentan con inestabilidad hemodinámica. Esta se define por hipotensión arterial con presión arterial sistólica (PAS) < 90mmHg o descenso de 40mmHg durante al menos 15 min y que no es causada por una arritmia de nueva aparición, hipovolemia o sepsis, o necesidad de fármacos vasoactivos para mantener PAS ≥ 90mmHg acompañado de signos de hipoperfusión. Así mismo, se considerarán de alto riesgo aquellos pacientes que debuten en forma de parada cardiorrespiratoria (aunque sea recuperada)1-3.
Este subgrupo de pacientes presenta una elevada probabilidad de deterioro clínico y muerte, con una mortalidad superior al 15%, por lo que se beneficiará de las llamadas terapias de reperfusión, siendo la de elección la trombólisis sistémica, a menos que exista una contraindicación absoluta para ello. En este último caso, deberemos valorar alternativas a esta, como son la trombólisis guiada por catéter, o si no disponemos de la técnica, la trombólisis sistémica a dosis reducidas (véase los apartados 1.3)1,2,4,5.
EP de riesgo intermedioEn este grupo están incluidos todos los pacientes estables hemodinámicamente pero que tienen criterios clínicos de gravedad o una importante comorbilidad, definido por la escala PESI o sPESI. A todos los pacientes con un PESI clase III-IV o sPESI ≥ 1 se deberá realizar una determinación de troponina. En los casos que la troponina sea positiva, se deberá valorar si existe disfunción del VD mediante tomografía computarizada (TC) o ecocardiograma y, en el caso que se confirme, clasificaremos al paciente como de riesgo intermedio-alto y será tributario de ingreso en una unidad de críticos por su elevado riesgo de deterioro clínico y hemodinámico en las primeras horas de diagnóstico de la EP. Por el contrario, si la troponina es negativa, se definirá como una EP de riesgo intermedio-bajo y podrá ingresar en una planta de hospitalización convencional1,6.
EP de riesgo bajoEn este grupo estarán incluidos todos los pacientes estables hemodinámicamente, sin criterios clínicos de gravedad ni comorbilidades importantes, definido por una escala PESI clase I-II o sPESI de 0. En este caso, se podrán beneficiar de un alta precoz a domicilio, ya que el riesgo de deterioro clínico y hemodinámico es muy bajo1,6.
Tratamiento de la EP con estabilidad hemodinámicaLa anticoagulación es el pilar del tratamiento de este grupo de pacientes1,6. El tratamiento anticoagulante de la EP, y de la enfermedad tromboembólica venosa en general, se divide en 3 fases: tratamiento de la fase aguda, tratamiento a largo plazo y tratamiento extendido1,6.
Tratamiento anticoagulante de la fase aguda de la embolia pulmonar aguda sintomática (primeros 7-21 días)En esta fase, el tratamiento tiene como objetivo evitar la progresión de la trombosis y, en consecuencia, evitar sus complicaciones derivadas.
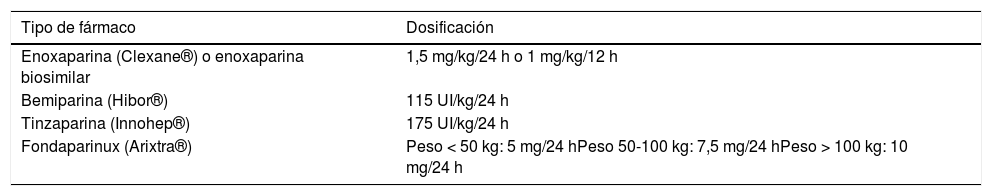
El tratamiento más extendido en esta fase es la heparina de bajo peso molecular (HBPM). En nuestro país disponemos de varios tipos, las más habituales de las cuales aparecen en la tabla 1. En pacientes seleccionados, una alternativa a la HBPM es la heparina no fraccionada1,6,7.
Dosificación de HBPM y fondaparinux para el tratamiento de la EP
| Tipo de fármaco | Dosificación |
|---|---|
| Enoxaparina (Clexane®) o enoxaparina biosimilar | 1,5 mg/kg/24 h o 1 mg/kg/12 h |
| Bemiparina (Hibor®) | 115 UI/kg/24 h |
| Tinzaparina (Innohep®) | 175 UI/kg/24 h |
| Fondaparinux (Arixtra®) | Peso < 50 kg: 5 mg/24 hPeso 50-100 kg: 7,5 mg/24 hPeso > 100 kg: 10 mg/24 h |
En los pacientes con antecedentes o sospecha clínica de trombocitopenia inducida por heparina (TIH), el tratamiento de elección será el fondaparinux SC (Arixtra®, Aspen Pharma.) (véase la dosificación en tabla 1). El fondaparinux es un heparinoide, con una tasa de recurrencias y hemorragias muy similar a la de la HBPM. Deberemos sospechar una TIH ante una trombocitopenia de nueva aparición, durante los primeros 7-10 días después de haber iniciado el tratamiento con HBPM. En estos casos, deberá confirmarse el diagnóstico mediante la solicitud de los anticuerpos antiplaquetares1,6,7.
Desde hace unos años, disponemos de los anticoagulantes orales de acción directa (ACOD), como alternativa a la HBPM, aunque en la actualidad no están financiados por el sistema público de salud. Estos han demostrado ser al menos tan eficaces y seguros, en cuanto al riesgo de hemorragia6-10, respecto a la HBPM. Existen 2ACOD aprobados para la fase aguda, los cuales son rivaroxabán (Xarelto®, Bayer) 15mg/12h durante 21 días y, posteriormente, 20mg/día, y apixabán (Eliquis®, Bristol-Myers Squibb y Pfizer) 10mg/12h durante 7 días y, posteriormente, 5mg/12h1,6-10.
Tratamiento anticoagulante a largo plazo (después de los primeros 7-21 días) y extendido (a partir 3 meses) de la embolia pulmonar agudaEl objetivo de la anticoagulación en la fase a largo plazo es la disolución del trombo formado, la cual se realiza mediante el sistema de lisis fisiológica, y el de la fase extendida la prevención de las recurrencias.
En esta fase del tratamiento de la EP, a partir de los 7-10 días del tratamiento con HBPM, 7 días con apixabán o 21 días con rivaroxabán, preferiblemente se indicarán anticoagulantes por vía oral por su comodidad. Como excepción, la mayoría de los casos de EP asociada a cáncer se tratarán con HBPM1,6-10.
Respecto a la anticoagulación oral, en la actualidad los fármacos más utilizados en nuestro país son los antivitaminas K (AVK), concretamente acenocumarol (Sintrom®, Merus Labs Luxco), porque la prescripción de ACOD está limitada por no estar financiados por el Sistema Nacional de Salud, pese a que las últimas guías de práctica clínica los recomiendan como tratamiento de elección de la EP1. Está recomendación está basada en ensayos clínicos y estudios clínicos en vida real, los cuales han demostrado que son al menos tan eficaces y claramente más seguros que AVK6-12. Estos datos se replican también en los pacientes de alto riesgo hemorrágico, como es el caso de los pacientes frágiles13. Para los pacientes con cáncer, véase el siguiente apartado. Los AVK requieren de los controles pertinentes en el centro médico de referencia, con el objetivo de alcanzar un INR entre 2 y 31,6,7.
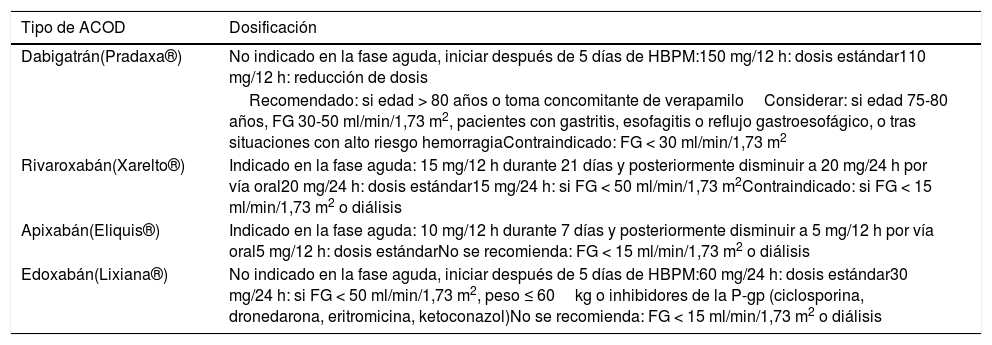
Respecto a los ACOD, para esta fase están aprobados los 4 ACOD disponibles en nuestro país (tabla 2)1,6,11. En el caso de dabigatrán, disponemos de un antídoto específico llamado idarucizumab (Praxbind®, Boehringer Ingelheim)14.
Dosificación de los ACOD aprobados para el tratamiento de la EP
| Tipo de ACOD | Dosificación |
|---|---|
| Dabigatrán(Pradaxa®) | No indicado en la fase aguda, iniciar después de 5 días de HBPM:150 mg/12 h: dosis estándar110 mg/12 h: reducción de dosis |
| Recomendado: si edad > 80 años o toma concomitante de verapamiloConsiderar: si edad 75-80 años, FG 30-50 ml/min/1,73 m2, pacientes con gastritis, esofagitis o reflujo gastroesofágico, o tras situaciones con alto riesgo hemorragiaContraindicado: FG < 30 ml/min/1,73 m2 | |
| Rivaroxabán(Xarelto®) | Indicado en la fase aguda: 15 mg/12 h durante 21 días y posteriormente disminuir a 20 mg/24 h por vía oral20 mg/24 h: dosis estándar15 mg/24 h: si FG < 50 ml/min/1,73 m2Contraindicado: si FG < 15 ml/min/1,73 m2 o diálisis |
| Apixabán(Eliquis®) | Indicado en la fase aguda: 10 mg/12 h durante 7 días y posteriormente disminuir a 5 mg/12 h por vía oral5 mg/12 h: dosis estándarNo se recomienda: FG < 15 ml/min/1,73 m2 o diálisis |
| Edoxabán(Lixiana®) | No indicado en la fase aguda, iniciar después de 5 días de HBPM:60 mg/24 h: dosis estándar30 mg/24 h: si FG < 50 ml/min/1,73 m2, peso ≤ 60kg o inhibidores de la P-gp (ciclosporina, dronedarona, eritromicina, ketoconazol)No se recomienda: FG < 15 ml/min/1,73 m2 o diálisis |
En la actualidad, el tratamiento estándar de la EP asociada a cáncer sigue siendo la HBPM (tabla 1). No obstante, en algunas situaciones clínicas podremos decantarnos por la anticoagulación oral, preferiblemente con ACOD, por su mejor perfil de seguridad respecto a AVK. Algunos estudios publicados han mostrado que debemos tener especial precaución con el uso de edoxabán y rivaroxabán en los pacientes con las neoplasias localizadas en el tracto digestivo superior, porque se han asociado a mayor tasa de hemorragias que la HBPM15,16. Recientemente, se ha publicado un artículo que evidencia la no inferioridad de apixabán respecto HBPM, sin un aumento de las hemorragias17. Asimismo, en los pacientes con tratamiento oncoespecífico activo, previo al inicio del tratamiento con ACOD deberemos comprobar si existen potenciales interacciones1,18.
Tratamiento de la EP de alto riesgo o con inestabilidad hemodinámicaEn estos casos, dada la gravedad del cuadro clínico, el cual se asocia a tasas de mortalidad de alrededor de un 15% sin tratamiento, la anticoagulación aislada será insuficiente y será necesario aplicar un tratamiento de reperfusión, con el fin de restablecer de manera rápida el flujo de la circulación pulmonar. En algunos casos seleccionados de EP de riesgo intermedio-alto, también se podrá valorar la terapia de reperfusión1,6. Además, deberán ingresar en una unidad de críticos para monitorización y vigilancia intensiva. Los tratamientos de recanalización de que disponemos son la trombólisis sistémica, las terapias guiadas por catéter (TGC) y la embolectomía quirúrgica1,6.
Trombólisis sistémicaLa trombólisis sistémica se administra por vía intravenosa, produciendo la disolución de los coágulos intravasculares, mediante el paso de plasminógeno a plasmina. El principal efecto adverso de este grupo de fármacos es el aumento del riesgo de hemorragia, con una tasa acumulada de hemorragia mayor del 13% y de hemorragias mortales o intracraneales del 1,8% según los datos de los ensayos clínicos publicados19,20. Se han descrito varios factores de riesgo asociados a un aumento del riesgo de hemorragia tras la administración de trombólisis, como edad > 70 años, Índice de masa corporal (IMC) > 30kg/m2 y presión arterial diastólica elevada21,22. Todo ello hace que sea necesaria una correcta individualización del riesgo/beneficio antes de indicar dicho tratamiento. En la tabla 3 se describen los diferentes tipos de trombolíticos aprobados para el tratamiento de la EP y los respectivos regímenes de administración. Existen estudios que demuestran una tasa de hemorragia grave superior en los pacientes tratados con tenecteplasa respecto a la forma recombinante del activador tisular del plasminógeno (rTPA)23. Actualmente, el fármaco más utilizado es la alteplasa o rTPA y el régimen aconsejado en las últimas guías europeas es el de 100mg de rTPA en 2 h1.
Regímenes trombolíticos aprobados para el tratamiento de la EP
| Fármaco | Régimen administración |
|---|---|
| Estreptoquinasa | Régimen estándar: dosis de carga de 250.000 UI en 30min, seguido de 100.000 UI/h en 12-24 hRégimen acelerado: 1.500.000 UI en 2 h |
| Uroquinasa | Régimen estándar: dosis de carga de 4.400 UI/kg en 10min, seguido de 4.400 UI/kg/h en 24 hRégimen acelerado: 3.000.000 UI en 2 h |
| Alteplasa o rTPA | Régimen estándar: 100mg en 2h (de elección)Régimen acelerado: 0,6 mg/kg en 15min (dosis máxima 50 mg) |
Tomado de Konstantinides et al.1
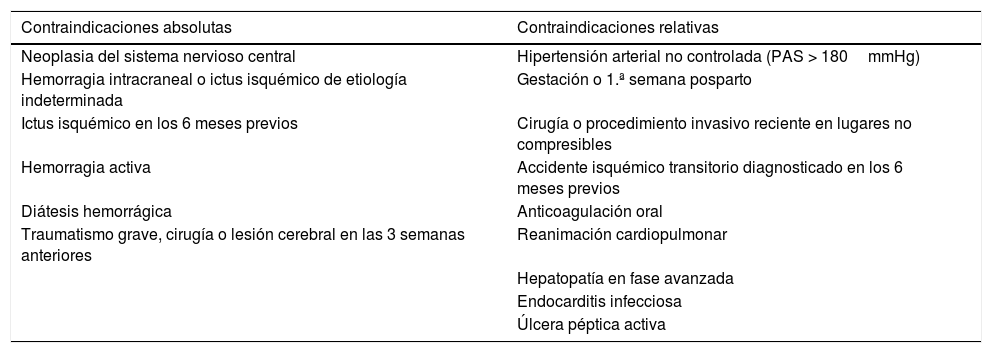
De manera general, se recomienda el uso de la trombólisis en la EP de alto riesgo, si no hay contraindicación para su administración1. En la tabla 4 se especifican las contraindicaciones absolutas y relativas para la trombólisis sistémica.
Contraindicaciones absolutas y relativas para la trombólisis sistémica
| Contraindicaciones absolutas | Contraindicaciones relativas |
|---|---|
| Neoplasia del sistema nervioso central | Hipertensión arterial no controlada (PAS > 180mmHg) |
| Hemorragia intracraneal o ictus isquémico de etiología indeterminada | Gestación o 1.ª semana posparto |
| Ictus isquémico en los 6 meses previos | Cirugía o procedimiento invasivo reciente en lugares no compresibles |
| Hemorragia activa | Accidente isquémico transitorio diagnosticado en los 6 meses previos |
| Diátesis hemorrágica | Anticoagulación oral |
| Traumatismo grave, cirugía o lesión cerebral en las 3 semanas anteriores | Reanimación cardiopulmonar |
| Hepatopatía en fase avanzada | |
| Endocarditis infecciosa | |
| Úlcera péptica activa |
Tomado de Konstantinides et al.1.
En pacientes seleccionados, con alto riesgo hemorrágico, la trombólisis sistémica reducida con 50mg de rTPA por vía intravenosa ha demostrado ser tan eficaz como la dosis estándar (100mg), pero con un menor riesgo de sangrado5.
Terapias guiadas por catéterLas TGC constituyen un nuevo abanico de posibilidades para el tratamiento de los pacientes con EP aguda sintomática. Estas están compuestas por una amplia variedad de técnicas, que tienen como objetivo el restablecimiento del flujo vascular mediante un catéter que fragmenta o aspira el trombo. Las TGC actúan sobre el trombo mediante un procedimiento mecánico, un trombolítico local administrado a nivel de las arterias pulmonares, fragmentación por ultrasonidos o mediante la combinación de algunas de las técnicas anteriores. Existen varias publicaciones que valoran favorablemente la efectividad y seguridad de las TGC en los pacientes con EP; sin embargo, se necesitan más estudios para disponer de mayor evidencia científica. En la actualidad, las guías de práctica clínica aconsejan valorar el tratamiento mediante las TGC en aquellos pacientes con EP aguda asociada a hipotensión arterial que además presenten contraindicación para la trombólisis sistémica, un alto riesgo hemorrágico, que previamente haya fallado la trombólisis sistémica o que estando en situación de shock cardiogénico se necesite una repermeabilización emergente de la circulación pulmonar (la trombólisis sistémica necesita unas horas para su inicio de efecto). En los casos en que se indique porque exista una hemorragia activa que contraindique la trombólisis sistémica, se aconseja optar por la trombectomía mecánica sin trombolítico local. Las guías remarcan que estas técnicas se deberían de realizar en centros con experiencia previa1,6,23,24.
Embolectomía quirúrgicaEn los últimos años, la embolectomía quirúrgica ha perdido protagonismo por la irrupción de las TCG y su implementación progresiva en los centros hospitalarios. En la literatura existe una mayor evidencia del beneficio clínico de la embolectomía quirúrgica respecto de la TGC25, aunque la necesidad de la disponibilidad de un cirujano cardíaco con experiencia ha hecho que en la actualidad en numerosos centros se haya sustituido por las TGC1,6.
Oxigenación por membrana extracorpórea/Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)Las guías actuales recomiendan valorar el uso temporal de la ECMO, principalmente con oxigenación de membrana extracorpórea veno-arterial, en aquellos pacientes con EP de alto riesgo y parada cardiorrespiratoria o shock cardiogénico1. Es necesario tener en cuenta que la ECMO, incluso cuando se utiliza en períodos cortos, está asociada a una importante tasa de complicaciones, sobre todo hemorrágicas, que en gran medida dependerá del tipo de paciente y de la experiencia del centro. En la actualidad, es controvertido el uso de la ECMO únicamente acompañada del tratamiento anticoagulante, por lo que siempre deberá considerarse tratamientos adicionales como la embolectomía quirúrgica o la trombectomía percutánea1,23,24.
Valoración de la respuesta del tratamiento de reperfusiónDespués de la administración de la trombólisis sistémica, embolectomía quirúrgica o de las TGC, es imprescindible la evaluación de la respuesta al tratamiento. Dicha evaluación se realiza mediante la valoración del estado hemodinámico del paciente, a través de las cifras de PAS y frecuencia cardíaca. En los casos en que el paciente persista con inestabilidad hemodinámica, definida por hipotensión persistente (sucede alrededor de un 8% de los casos), se deberá valorar una nueva terapia de reperfusión de rescate: retrombólisis sistémica, trombectomía percutánea o embolectomía quirúgica1,6,23,24. En este sentido, en este subgrupo de pacientes, un estudio evaluó la retrombólisis sistémica vs. embolectomía quirúrgica, siendo claramente favorable a esta última, aunque en el momento que se publicó este estudio no se disponía de las TGC actuales25. Por tanto, parece razonable aconsejar que en los casos de una primera trombólisis fallida, se indique la trombectomía percutánea o una embolectomía quirúrgica, excepto en los centros en que no se disponga de alguna de estas técnicas, en los que será necesario repetir la trombólisis sistémica, aunque teniendo esta una baja tasa de éxito1,6,25. Posteriormente a la administración de la trombólisis sistémica o de las TGC, se deberá iniciar la anticoagulación y el paciente deberá estar hospitalizado en una unidad de críticos para estricta monitorización1,6.
Filtros de vena cava inferiorEn un paciente con EP, deberemos considerar un filtro de vena cava (FVC) inferior en los casos en que exista una contraindicación para la anticoagulación, como es la existencia de una hemorragia activa, o que este deba suspenderse (p. ej., por la necesidad de cirugía). Asimismo, también se podría considerar en casos seleccionados en los que se produzca una re-EP bajo tratamiento anticoagulante correcto (véase el apartado siguiente.)1,6.
Tratamiento de la progresión o recurrencia de la EP durante el tratamiento anticoagulanteEn algunos casos, durante el tratamiento anticoagulante de la EP, se puede producir una progresión de los defectos de repleción o una recurrencia de la misma. En esta situación, en los casos que el paciente esté con un AVK se aconseja cambiar a HBPM y en los casos que ya esté con HBPM a las dosis óptimas, se aconseja aumentar la dosis de la misma un 20-30%. La implantación de un FVC constituye una alternativa a las estrategias anteriores1,6.
Grupos de respuesta multidisciplinar para la atención de pacientes con EP aguda sintomáticaLos equipos de respuesta multidisciplinar para la atención de pacientes con EP aguda sintomática (pulmonary embolism team response o PERT team en inglés) nacieron hace unos años en Estados Unidos, con el objetivo de ofrecer una atención multidisciplinar a los pacientes con EP de alto riesgo y algunos pacientes seleccionados de riesgo intermedio. Estos equipos se activan ante un diagnóstico de EP de las características comentadas y se valora el paciente en tiempo real, con el objetivo de individualizar la toma de decisiones, sobre todo respecto el tratamiento agudo de la EP1,26.
Duración de la anticoagulaciónLa duración del tratamiento anticoagulante dependerá, sobre todo, de la etiología de la EP. En este sentido, la EP puede ser no provocada, cuando no se identifica ningún factor de riesgo, o provocada, cuando sí que existe alguno. Dentro de la provocada, será muy importante analizar de manera individualizada la causa que se ha identificado, debido a que, dependiendo de la intensidad del factor predisponente, este marcará el riesgo de recurrencia al finalizar la anticoagulación. Paralelamente al riesgo de recurrencia, será imprescindible valorar periódicamente el riesgo hemorrágico y será este balance de riesgo/beneficio el que nos hará determinar la duración de la anticoagulación1,6,22-28.
De esta manera, en una EP provocada por un factor de riesgo intenso no persistente, mantendremos la anticoagulación 3-6 meses, si la evolución es la correcta. Mientras que en una EP no provocada, EP provocada por un factor de riesgo menor persistente o EP recurrente, valoraremos la anticoagulación extendida, siempre dependiendo del riesgo de sangrado1,6,28. En la EP asociada a cáncer, la anticoagulación habrá que mantenerla al menos 6 meses, y posteriormente valorar la duración dependiendo de las características del paciente, el tipo de cáncer y los factores relacionados con este, así como el riesgo de hemorragia1,6,29.
Detección de la hipertensión pulmonar tromboembólica crónicaEn las últimas guías, se aconseja no solo valorar la hipertensión pulmonar tromboembólica crónica (HPTEC), sino todo el espectro de secuelas después de una EP, que se conoce como enfermedad tromboembólica crónica (ETC)1. Un porcentaje variable de los pacientes (20-75% dependiendo del estudio) refieren persistencia de la disnea o limitación física al esfuerzo, aunque finalmente los pacientes con HPTEC confirmada son solo alrededor de un 3% del total1,30,31.
Diversos factores basales del paciente se han asociado a un mayor riesgo de desarrollar una ETC, como son la edad avanzada, la enfermedad cardiorrespiratoria previa, un IMC elevado, tabaquismo, presión arterial pulmonar sistólica elevada, disfunción del VD al diagnóstico y defectos de repleción pulmonares residuales32. Asimismo, existen diversos factores de riesgo de desarrollar una HPTEC que son inherentes al evento tromboembólico (véase la tabla 5)1,32.
Factores de riesgo predisponentes de HPTEC
| Factores relacionados con la EP aguda (en el momento del diagnóstico de la EP) | Enfermedades crónicas concomitantes y factores predisponentes de HPTEC (desde el momento del diagnóstico de la EP hasta los 3-6 meses de seguimiento) |
| Episodios previos de EP o TVP | Shunts ventrículo-auriculares |
| Elevada carga trombótica en el angio-TC | Infección crónica de catéteres o marcapasos |
| Signos ecocardiográficos de HP o disfunción VD | Esplenectomía |
| Angio-TC con hallazgos indicativos de HPTEC previa | Trombofilia (especialmente síndrome antifosfolípido y factor viii elevado) |
| No ser del grupo sanguíneo 0 | |
| Hipotiroidismo en tratamiento sustitutivo | |
| Cáncer | |
| Síndromes mieloproliferativos | |
| Enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal | |
| Osteomielitis crónica |
Tomado de Konstantinides et al.1
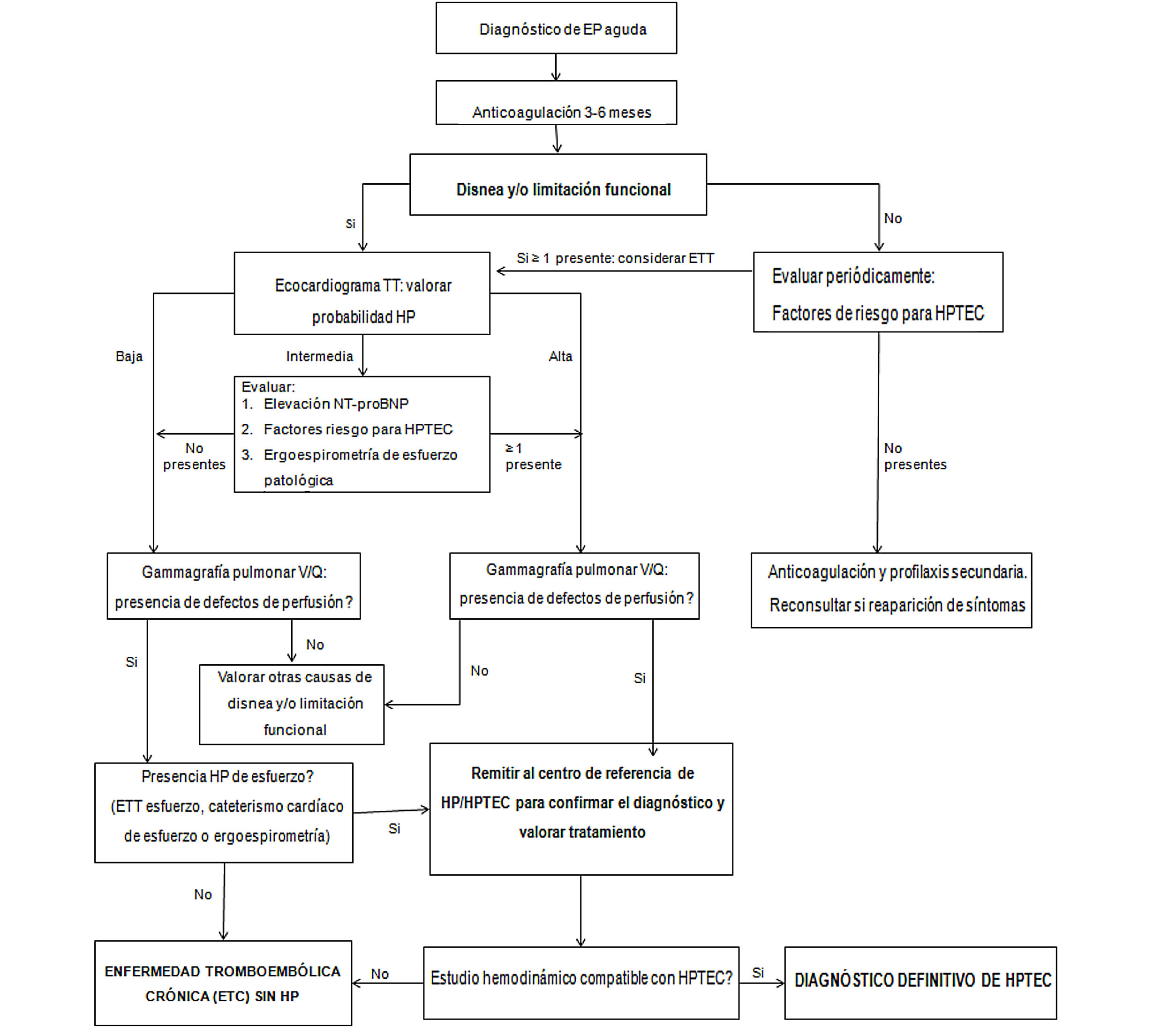
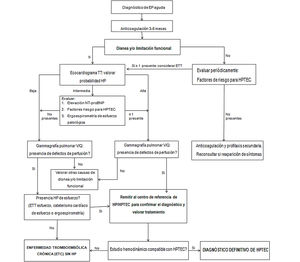
Ver Estrategia diagnóstica de la ETC en la figura 2. Después de mantener el tratamiento anticoagulante durante 3-6 meses, en la mayor parte de los casos se producirá la recanalización de los defectos de repleción en la circulación pulmonar. En los casos en que persista alguno/s de estos defecto/s, este hecho no siempre tendrá transcendencia clínica, sin existir, además, una relación directa entre el número y la extensión de los defectos residuales y los síntomas33. No obstante, en los pacientes con disnea o limitación física funcional, se debe solicitar un ecocardiograma transtorácico (ETT) para valorar la probabilidad de hipertensión pulmonar (HP). Si la probabilidad de HP es alta, se realizará una gammagrafía de ventilación/perfusión (V/Q), y si se objetivan defectos de repleción residuales, se deberá realizar un estudio hemodinámico para confirmar el diagnóstico de HPTEC. En los pacientes con probabilidad intermedia de HP, se solicitará un NT-proBNP y una ergoespirometría de esfuerzo que, conjuntamente a si el paciente presenta factores de riesgo para HPTEC (véase la tabla 4), nos harán valorar si es tributario de realizar una gammagrafía pulmonar de ventilación/perfusión1,31.
En otros casos, puede existir la sospecha clínica de HPTEC pero el ETT en reposo no evidencia HP. En esta situación, se realizará una gammagrafía pulmonar V/Q como prueba de cribado, por su elevado valor predictivo negativo. Si la gammagrafía V/Q evidencia defectos de perfusión, se debe valorar si existe HP de esfuerzo, mediante ETT de esfuerzo, estudio hemodinámico de esfuerzo o ergoespirometría. En los pacientes con HP de esfuerzo, se realizará el estudio hemodinámico para establecer el diagnóstico de HPTEC. Asimismo, en el caso de que no se evidencie HP de esfuerzo, se establecerá el diagnóstico de ETC sin HP. En ambos casos, se debe valorar la remisión del paciente al centro de referencia en HPTEC/HP1,34.
El diagnóstico confirmatorio de HPTEC requiere de una presión arteria pulmonar (PAP) media ≥ 25mmHg junto a una presión de enclavamiento pulmonar ≥ 15mmHg, documentado mediante cateterismo del corazón derecho, en un paciente con defectos de perfusión en la gammagrafía pulmonar. En los pacientes que presenten un estudio hemodinámico normal, será imprescindible descartar otras causas de la limitación funcional para establecer el diagnóstico de ETC. En los pacientes con diagnóstico definitivo de HPTEC, se mantendrá la anticoagulación y deberán ser remitidos al centro de referencia de HPTEC1,6,34.
Pese a todo ello, diversos estudios de cohortes han evidenciado que después de una EP la causa más habitual de disnea o limitación física al esfuerzo es el desacondicionamento físico, sobre todo en pacientes con IMC elevado y enfermedad cardiorrespiratoria previa1,29. Un aspecto a tener en cuenta es que el hecho de indicar terapias de reperfusión en el momento del diagnóstico no disminuye el riesgo de HPTEC35.
Conflicto de interesesEl Dr. J.J. López-Núñez ha recibido honorarios por conferencias por parte de BMS, Rovi y Boehringer, así como el pago de gastos de congresos por parte de Bayer y Sanofi.
Nota al suplementoEste artículo forma parte del suplemento «Protocolos de manejo de la enfermedad tromboembólica venosa. Actualización 2020», que cuenta con la colaboración de Laboratorios Rovi para la impresión y difusión del suplemento.