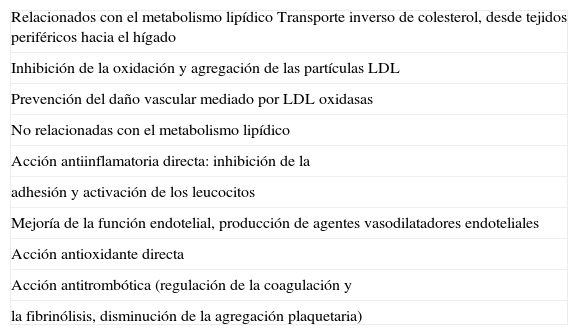
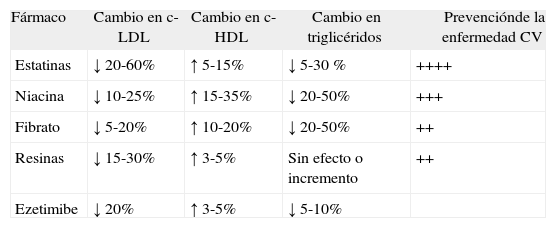
Las estatinas reducen la incidencia de enfermedad cardiovascular (CV) un 30-40%, pero persiste un riesgo de complicaciones CV que no previenen. Se precisan, pues, nuevos fármacos, que asociados a las estatinas modifiquen favorablemente los lípidos y reduzcan aún más la incidencia de complicaciones CV. En este comentario clínico revisamos la importancia de otros lípidos (colesterol ligado a lipoproteínas de alta densidad [c-HDL] y triglicéridos) en el riesgo CV y los fármacos potencialmente útiles para asociar a las estatinas. Los fibratos son especialmente efectivos para reducir los triglicéridos, mientras que la niacina tiene un efecto global, reduciendo el colesterol ligado a lipoproteínas de baja densidad (c-LDL) y los triglicéridos y es el fármaco más eficaz para elevar el c-HDL. La asociación de estatinas y niacina puede ser el futuro inmediato para abordar el tratamiento de la dislipidemia de forma integral y, potencialmente, reducir aún más el riesgo de enfermedad CV.
Statin therapy reduces the incidence of cardiovascular (CV) disease by 30-40%. However, some risk of unprevented CV complications still persists. Thus, new drugs that when associated to the statins favorably modify the lipid profile and further reduce CV risk are needed. In this clinical commentary, we review the role of other lipids (HDL cholesterol and triglycerides) in CV risk and those potentially useful agents that could be added to statins. Fibrates are especially effective to decrease triglycerides, whilst niacin has a global effect, decreasing LDL cholesterol and triglycerides and is the most effective drug to increase HDL cholesterol. The association of statins plus niacin may be the immediate future to tackle the comprehensive treatment of dyslipidemia and potentially further reduce the risk of CV disease.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<